A dimension of the vector space. More...
#include <ppl.hh>
Classes | |
| struct | Compare |
| Binary predicate defining the total ordering on variables. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef void | output_function_type(std::ostream &s, const Variable v) |
| Type of output functions. | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Variable (dimension_type i) | |
Builds the variable corresponding to the Cartesian axis of index i. More... | |
| dimension_type | id () const |
| Returns the index of the Cartesian axis associated to the variable. | |
| dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this. More... | |
| memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this. | |
| memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this. | |
| bool | OK () const |
| Checks if all the invariants are satisfied. | |
| void | m_swap (Variable &v) |
| Swaps *this and v. | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static dimension_type | max_space_dimension () |
| Returns the maximum space dimension a Variable can handle. | |
| static void | default_output_function (std::ostream &s, const Variable v) |
| The default output function. | |
| static void | set_output_function (output_function_type *p) |
| Sets the output function to be used for printing Variable objects. | |
| static output_function_type * | get_output_function () |
| Returns the pointer to the current output function. | |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const Variable v) |
| Output operator. More... | |
| bool | less (Variable v, Variable w) |
| Defines a total ordering on variables. More... | |
| void | swap (Variable &x, Variable &y) |
| bool | less (const Variable v, const Variable w) |
Detailed Description
A dimension of the vector space.
An object of the class Variable represents a dimension of the space, that is one of the Cartesian axes. Variables are used as basic blocks in order to build more complex linear expressions. Each variable is identified by a non-negative integer, representing the index of the corresponding Cartesian axis (the first axis has index 0). The space dimension of a variable is the dimension of the vector space made by all the Cartesian axes having an index less than or equal to that of the considered variable; thus, if a variable has index 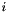 , its space dimension is
, its space dimension is 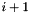 .
.
Note that the ``meaning'' of an object of the class Variable is completely specified by the integer index provided to its constructor: be careful not to be mislead by C++ language variable names. For instance, in the following example the linear expressions e1 and e2 are equivalent, since the two variables x and z denote the same Cartesian axis.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds the variable corresponding to the Cartesian axis of index i.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if i+1exceedsVariable::max_space_dimension().
Member Function Documentation
|
inline |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.
The returned value is id()+1.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Output operator.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
- ppl.hh
