Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Float< T > Class Template Reference
#include <Float_defs.hh>
Inheritance diagram for Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Float< T >:
Collaboration diagram for Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Float< T >:
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| bool | is_less_precise_than (Floating_Point_Format f1, Floating_Point_Format f2) |
| template<typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| const FP_Interval_Type & | compute_absolute_error (Floating_Point_Format analyzed_format) |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bool< false > Public Types inherited from Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bool< false > | |
| enum | const_bool_value |
Detailed Description
template<typename T>
class Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Float< T >
Definition at line 285 of file Float_defs.hh.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
template<typename FP_Interval_Type >
|
related |
Computes the absolute error of floating point computations.
- Template type parameters
- The class template parameter
FP_Interval_Typerepresents the type of the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Parameters
-
analyzed_format The floating point format used by the analyzed program.
- Returns
- The interval
![$[-\omega, \omega]$](form_936.png) where
where 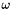 is the smallest non-zero positive number in the less precise floating point format between the analyzer format and the analyzed format.
is the smallest non-zero positive number in the less precise floating point format between the analyzer format and the analyzed format.
Definition at line 35 of file Float_templates.hh.
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:261
I_Constraint< T > i_constraint(I_Constraint_Rel rel, const T &v)
Definition: intervals_defs.hh:443
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:220
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:93
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:171
IEEE 754 half precision, 16 bits (5 exponent, 10 mantissa).
Definition: globals_types.hh:189
IEEE 754 quad precision, 128 bits (15 exponent, 112 mantissa).
Definition: globals_types.hh:198
IBM single precision, 32 bits (7 exponent, 24 mantissa).
Definition: globals_types.hh:204
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:62
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:169
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:91
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:137
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:172
unsigned int msb_position(unsigned long long v)
If v is nonzero, returns the position of the most significant bit in a.
Definition: Float_inlines.hh:518
Intel double extended precision, 80 bits (15 exponent, 64 mantissa)
Definition: globals_types.hh:201
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:222
static const unsigned int BASE
Definition: Float_defs.hh:58
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:263
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:95
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:141
IEEE 754 double precision, 64 bits (11 exponent, 52 mantissa).
Definition: globals_types.hh:195
IEEE 754 single precision, 32 bits (8 exponent, 23 mantissa).
Definition: globals_types.hh:192
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:139
static const unsigned int MANTISSA_BITS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:60
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:265
static const int EXPONENT_BIAS
Definition: Float_defs.hh:224
template<typename T>
|
related |
Returns true if and only if there is some floating point number that is representable by f2 but not by f1.
Definition at line 513 of file Float_inlines.hh.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
