The core implementation of the Parma Polyhedra Library is written in C++. More...
Namespaces | |
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::IO_Operators | |
| All input/output operators are confined to this namespace. | |
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked | |
| Types and functions implementing checked numbers. | |
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation | |
| Implementation related data and functions. | |
| std | |
| The standard C++ namespace. | |
Macros | |
| #define | PPL_VERSION_MAJOR 1 |
| The major number of the PPL version. More... | |
| #define | PPL_VERSION_MINOR 2 |
| The minor number of the PPL version. More... | |
| #define | PPL_VERSION_REVISION 0 |
| The revision number of the PPL version. More... | |
| #define | PPL_VERSION_BETA 0 |
| The beta number of the PPL version. This is zero for official releases and nonzero for development snapshots. More... | |
| #define | PPL_VERSION "1.2" |
| A string containing the PPL version. More... | |
| #define | const_bool_nodef(name, value) enum const_bool_value_ ## name { PPL_U(name) = (value) } |
Declares a per-class constant of type bool, called name and with value value. More... | |
| #define | const_int_nodef(name, value) enum anonymous_enum_ ## name { PPL_U(name) = (value) } |
Declares a per-class constant of type int, called name and with value value. More... | |
| #define | const_value_nodef(type, name, value) |
Declares a per-class constant of type type, called name and with value value. The value of the constant is accessible by means of the syntax name(). More... | |
| #define | const_ref_nodef(type, name, value) |
Declares a per-class constant of type type, called name and with value value. A constant reference to the constant is accessible by means of the syntax name(). More... | |
| #define | PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK(e, msg) PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK_AUX(e, __LINE__) |
Produces a compilation error if the compile-time constant e does not evaluate to true More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef PPL_COEFFICIENT_TYPE | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient |
| An alias for easily naming the type of PPL coefficients. More... | |
| typedef Coefficient_traits_template< Coefficient > | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_traits |
| An alias for easily naming the coefficient traits. More... | |
| typedef size_t | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::dimension_type |
| An unsigned integral type for representing space dimensions. More... | |
| typedef size_t | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::memory_size_type |
| An unsigned integral type for representing memory size in bytes. More... | |
Functions | |
| template<typename T > | |
| Enable_If< Has_Assign_Or_Swap< T >::value, void >::type | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_or_swap (T &to, T &from) |
Variables | |
| const Throwable *volatile | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::abandon_expensive_computations = 0 |
| A pointer to an exception object. More... | |
Functions Inspecting and/or Combining Result Values | |
| Result | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator& (Result x, Result y) |
| Result | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator| (Result x, Result y) |
| Result | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator- (Result x, Result y) |
| Result_Class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::result_class (Result r) |
| Result_Relation | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::result_relation (Result r) |
| Result | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::result_relation_class (Result r) |
Functions Inspecting and/or Combining Rounding_Dir Values | |
| Rounding_Dir | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator& (Rounding_Dir x, Rounding_Dir y) |
| Rounding_Dir | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator| (Rounding_Dir x, Rounding_Dir y) |
| Rounding_Dir | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| Rounding_Dir | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_down (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_up (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_ignore (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_not_needed (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_not_requested (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_direct (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_inverse (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_strict_relation (Rounding_Dir dir) |
| fpu_rounding_direction_type | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_fpu_dir (Rounding_Dir dir) |
Functions for the Synthesis of Linear Rankings | |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS (const PSET &pset) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS (const PSET &pset, Generator &mu) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after, Generator &mu) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS (const PSET &pset, C_Polyhedron &mu_space) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after, C_Polyhedron &mu_space) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS (const PSET &pset, C_Polyhedron &decreasing_mu_space, C_Polyhedron &bounded_mu_space) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after, C_Polyhedron &decreasing_mu_space, C_Polyhedron &bounded_mu_space) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR (const PSET &pset) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR (const PSET &pset, Generator &mu) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after, Generator &mu) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR (const PSET &pset, NNC_Polyhedron &mu_space) |
| template<typename PSET > | |
| void | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_2 (const PSET &pset_before, const PSET &pset_after, NNC_Polyhedron &mu_space) |
Detailed Description
The core implementation of the Parma Polyhedra Library is written in C++.
See Namespace, Hierarchical and Compound indexes for additional information about each single data type.
Macro Definition Documentation
Declares a per-class constant of type bool, called name and with value value.
Differently from static constants, name needs not (and cannot) be defined (for static constants, the need for a further definition is mandated by Section 9.4.2/4 of the C++ standard).
Definition at line 42 of file meta_programming.hh.
Declares a per-class constant of type int, called name and with value value.
Differently from static constants, name needs not (and cannot) be defined (for static constants, the need for a further definition is mandated by Section 9.4.2/4 of the C++ standard).
Definition at line 56 of file meta_programming.hh.
| #define const_ref_nodef | ( | type, | |
| name, | |||
| value | |||
| ) |
Declares a per-class constant of type type, called name and with value value. A constant reference to the constant is accessible by means of the syntax name().
Differently from static constants, name needs not (and cannot) be defined (for static constants, the need for a further definition is mandated by Section 9.4.2/4 of the C++ standard).
Definition at line 88 of file meta_programming.hh.
| #define const_value_nodef | ( | type, | |
| name, | |||
| value | |||
| ) |
Declares a per-class constant of type type, called name and with value value. The value of the constant is accessible by means of the syntax name().
Differently from static constants, name needs not (and cannot) be defined (for static constants, the need for a further definition is mandated by Section 9.4.2/4 of the C++ standard).
Definition at line 71 of file meta_programming.hh.
| #define PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK | ( | e, | |
| msg | |||
| ) | PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK_AUX(e, __LINE__) |
Produces a compilation error if the compile-time constant e does not evaluate to true
Definition at line 133 of file meta_programming.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::affine_form_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::affine_form_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_form_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_form_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::integer_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::integer_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::interval_coefficient_upper_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::linear_form_upper_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::linear_form_upper_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Concrete_Expression< Target >::linearize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::overapproximate_linear_form(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_fp_interval_abstract_store(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::refine_fp_interval_abstract_store(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_fp_interval_abstract_store(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::set_unbounded(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::tight_closure_assign().
| #define PPL_VERSION "1.2" |
A string containing the PPL version.
Let M and m denote the numbers associated to PPL_VERSION_MAJOR and PPL_VERSION_MINOR, respectively. The format of PPL_VERSION is M "." m if both PPL_VERSION_REVISION (r) and PPL_VERSION_BETA (b)are zero, M "." m "pre" b if PPL_VERSION_REVISION is zero and PPL_VERSION_BETA is not zero, M "." m "." r if PPL_VERSION_REVISION is not zero and PPL_VERSION_BETA is zero, M "." m "." r "pre" b if neither PPL_VERSION_REVISION nor PPL_VERSION_BETA are zero.
Definition at line 59 of file version.hh.
| #define PPL_VERSION_BETA 0 |
The beta number of the PPL version. This is zero for official releases and nonzero for development snapshots.
Definition at line 45 of file version.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::version_beta().
| #define PPL_VERSION_MAJOR 1 |
The major number of the PPL version.
Definition at line 30 of file version.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::version_major().
| #define PPL_VERSION_MINOR 2 |
The minor number of the PPL version.
Definition at line 34 of file version.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::version_minor().
| #define PPL_VERSION_REVISION 0 |
The revision number of the PPL version.
Definition at line 38 of file version.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::version_revision().
Typedef Documentation
| typedef PPL_COEFFICIENT_TYPE Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient |
An alias for easily naming the type of PPL coefficients.
Objects of type Coefficient are used to implement the integral valued coefficients occurring in linear expressions, constraints, generators, intervals, bounding boxes and so on. Depending on the chosen configuration options (see file README.configure), a Coefficient may actually be:
- The GMP_Integer type, which in turn is an alias for the
mpz_classtype implemented by the C++ interface of the GMP library (this is the default configuration). - An instance of the Checked_Number class template: with the policy Bounded_Integer_Coefficient_Policy, this implements overflow detection on top of a native integral type (available template instances include checked integers having 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits); with the Checked_Number_Transparent_Policy, this is a wrapper for native integral types with no overflow detection (available template instances are as above).
Definition at line 172 of file Coefficient_types.hh.
| typedef Coefficient_traits_template<Coefficient> Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_traits |
An alias for easily naming the coefficient traits.
Definition at line 178 of file Coefficient_types.hh.
| typedef size_t Parma_Polyhedra_Library::dimension_type |
An unsigned integral type for representing space dimensions.
Definition at line 22 of file globals_types.hh.
| typedef size_t Parma_Polyhedra_Library::memory_size_type |
An unsigned integral type for representing memory size in bytes.
Definition at line 26 of file globals_types.hh.
Enumeration Type Documentation
\ Overflow behavior of bounded integer types.
See the section on approximating bounded integers.
Definition at line 121 of file globals_types.hh.
\ Representation of bounded integer types.
See the section on approximating bounded integers.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| UNSIGNED |
Unsigned binary. |
| SIGNED_2_COMPLEMENT |
Signed binary where negative values are represented by the two's complement of the absolute value. |
Definition at line 104 of file globals_types.hh.
\ Widths of bounded integer types.
See the section on approximating bounded integers.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| BITS_8 |
8 bits. |
| BITS_16 |
16 bits. |
| BITS_32 |
32 bits. |
| BITS_64 |
64 bits. |
| BITS_128 |
128 bits. |
Definition at line 81 of file globals_types.hh.
Complexity pseudo-classes.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| POLYNOMIAL_COMPLEXITY |
Worst-case polynomial complexity. |
| SIMPLEX_COMPLEXITY |
Worst-case exponential complexity but typically polynomial behavior. |
| ANY_COMPLEXITY |
Any complexity. |
Definition at line 57 of file globals_types.hh.
| enum Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bool::const_bool_value |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| value | |
Definition at line 144 of file meta_programming.hh.
| enum Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Is_Same_Or_Derived::const_bool_value |
Definition at line 247 of file meta_programming.hh.
Names of MIP problems' control parameters.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| PRICING |
The pricing rule. |
Definition at line 475 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Possible names for PIP_Problem control parameters.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| CUTTING_STRATEGY |
Cutting strategy. |
| PIVOT_ROW_STRATEGY |
Pivot row strategy. |
| CONTROL_PARAMETER_NAME_SIZE |
Number of different enumeration values. |
Definition at line 708 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Possible values for MIP problem's control parameters.
Definition at line 481 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Possible values for PIP_Problem control parameters.
Definition at line 720 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Kinds of degenerate abstract elements.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| UNIVERSE |
The universe element, i.e., the whole vector space. |
| EMPTY |
The empty element, i.e., the empty set. |
Definition at line 30 of file globals_types.hh.
|
private |
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| PARAMETER | |
| LINE | |
| GEN_VIRTUAL | |
| PROPER_CONGRUENCE | |
| CON_VIRTUAL | |
| EQUALITY | |
Definition at line 1985 of file Grid_defs.hh.
\ Floating point formats known to the library.
The parameters of each format are defined by a specific struct in file Float_defs.hh. See the section on Analysis of floating point computations for more information.
Definition at line 187 of file globals_types.hh.
The result of an operation on intervals.
Definition at line 37 of file intervals_defs.hh.
The possible kinds of Grid_Generator objects.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LINE_OR_EQUALITY | |
| RAY_OR_POINT_OR_INEQUALITY | |
Definition at line 275 of file Grid_Generator_defs.hh.
|
private |
The possible kinds of Constraint objects.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LINE_OR_EQUALITY | |
| RAY_OR_POINT_OR_INEQUALITY | |
Definition at line 528 of file Constraint_defs.hh.
|
private |
The possible kinds of Generator objects.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LINE_OR_EQUALITY | |
| RAY_OR_POINT_OR_INEQUALITY | |
Definition at line 537 of file Generator_defs.hh.
Possible outcomes of the MIP_Problem solver.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM |
The problem is unfeasible. |
| UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEM |
The problem is unbounded. |
| OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM |
The problem has an optimal solution. |
Definition at line 20 of file MIP_Problem_types.hh.
Possible optimization modes.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| MINIMIZATION |
Minimization is requested. |
| MAXIMIZATION |
Maximization is requested. |
Definition at line 68 of file globals_types.hh.
Possible outcomes of the PIP_Problem solver.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| UNFEASIBLE_PIP_PROBLEM |
The problem is unfeasible. |
| OPTIMIZED_PIP_PROBLEM |
The problem has an optimal solution. |
Definition at line 20 of file PIP_Problem_types.hh.
Relation symbols.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| EQUAL |
Equal to. |
| LESS_THAN |
Less than. |
| LESS_OR_EQUAL |
Less than or equal to. |
| GREATER_THAN |
Greater than. |
| GREATER_OR_EQUAL |
Greater than or equal to. |
| NOT_EQUAL |
Not equal to. |
Definition at line 40 of file globals_types.hh.
\ Possible representations of coefficient sequences (i.e. linear expressions and more complex objects containing linear expressions, e.g. Constraints, Generators, etc.).
Definition at line 161 of file globals_types.hh.
Possible outcomes of a checked arithmetic computation.
Definition at line 76 of file Result_defs.hh.
Rounding directions for arithmetic computations.
Definition at line 34 of file Rounding_Dir_defs.hh.
|
private |
An enumerated type describing the internal status of the MIP problem.
Definition at line 536 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
An enumerated type describing the internal status of the PIP problem.
Definition at line 773 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
Kinds of polyhedra domains.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| NECESSARILY_CLOSED | |
| NOT_NECESSARILY_CLOSED | |
Definition at line 22 of file Topology_types.hh.
The constraint type.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| EQUALITY |
The constraint is an equality. |
| NONSTRICT_INEQUALITY |
The constraint is a non-strict inequality. |
| STRICT_INEQUALITY |
The constraint is a strict inequality. |
Definition at line 288 of file Constraint_defs.hh.
The generator type.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LINE |
The generator is a grid line. |
| PARAMETER |
The generator is a parameter. |
| POINT |
The generator is a grid point. |
Definition at line 414 of file Grid_Generator_defs.hh.
The generator type.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| LINE |
The generator is a line. |
| RAY |
The generator is a ray. |
| POINT |
The generator is a point. |
| CLOSURE_POINT |
The generator is a closure point. |
Definition at line 429 of file Generator_defs.hh.
Function Documentation
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS | ( | const PSET & | pset, |
| C_Polyhedron & | decreasing_mu_space, | ||
| C_Polyhedron & | bounded_mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Computes the spaces of affine quasi ranking functions using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset A pointset approximating the behavior of a loop whose termination is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 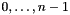 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 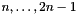 ,
,
decreasing_mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 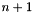 representing the space of all the decreasing affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the decreasing affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset.bounded_mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 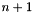 representing the space of all the lower bounded affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the lower bounded affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset.
These quasi-ranking functions are of the form 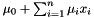 where
where 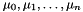 identify any point of the
identify any point of the decreasing_mu_space and bounded_mu_space polyhedrons. The variables 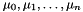 correspond to the space dimensions
correspond to the space dimensions 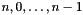 , respectively. When
, respectively. When decreasing_mu_space (resp., bounded_mu_space) is empty, it means that the test is inconclusive. However, if pset precisely characterizes the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, then decreasing_mu_space (resp., bounded_mu_space) will be empty if and only if there is no decreasing (resp., lower bounded) affine function, so that the loop does not terminate.
Definition at line 374 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after, | ||
| C_Polyhedron & | decreasing_mu_space, | ||
| C_Polyhedron & | bounded_mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Computes the spaces of affine quasi ranking functions using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset_before A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables before the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 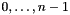 .
.
pset_after A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables after the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 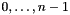 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 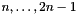 ,
,
Note that unprimed variables represent the values of the loop-relevant program variables before the update performed in the loop body, and primed variables represent the values of those program variables after the update. Note also that unprimed variables are assigned to different space dimensions in pset_before and pset_after.
- Parameters
-
decreasing_mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 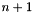 representing the space of all the decreasing affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the decreasing affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset.bounded_mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 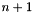 representing the space of all the lower bounded affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the lower bounded affine functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset.
These ranking functions are of the form 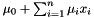 where
where 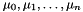 identify any point of the
identify any point of the decreasing_mu_space and bounded_mu_space polyhedrons. The variables 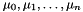 correspond to the space dimensions
correspond to the space dimensions 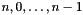 , respectively. When
, respectively. When decreasing_mu_space (resp., bounded_mu_space) is empty, it means that the test is inconclusive. However, if pset_before and pset_after precisely characterize the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, then decreasing_mu_space (resp., bounded_mu_space) will be empty if and only if there is no decreasing (resp., lower bounded) affine function, so that the loop does not terminate.
Definition at line 403 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS | ( | const PSET & | pset, |
| C_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Termination test with ranking function space using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset A pointset approximating the behavior of a loop whose termination is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 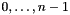 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 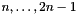 ,
,
mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 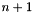 representing the space of all the affine ranking functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the affine ranking functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset. These ranking functions are of the form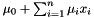 where
where 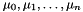 identify any point of the
identify any point of the mu_spacepolyhedron. The variables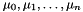 correspond to the space dimensions of
correspond to the space dimensions of mu_space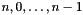 , respectively. When
, respectively. When mu_spaceis empty, it means that the test is inconclusive. However, ifpsetprecisely characterizes the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thenmu_spaceis empty if and only if the loop does not terminate.
Definition at line 322 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after, | ||
| C_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Termination test with ranking function space using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset_before A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables before the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 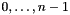 .
.
pset_after A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables after the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 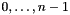 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 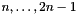 ,
,
Note that unprimed variables represent the values of the loop-relevant program variables before the update performed in the loop body, and primed variables represent the values of those program variables after the update. Note also that unprimed variables are assigned to different space dimensions in pset_before and pset_after.
- Parameters
-
mu_space This is assigned a closed polyhedron of space dimension 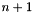 representing the space of all the affine ranking functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by
representing the space of all the affine ranking functions for the loops that are precisely characterized by pset. These ranking functions are of the form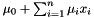 where
where 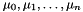 identify any point of the
identify any point of the mu_spacepolyhedron. The variables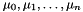 correspond to the space dimensions of
correspond to the space dimensions of mu_space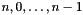 , respectively. When
, respectively. When mu_spaceis empty, it means that the test is inconclusive. However, ifpset_beforeandpset_afterprecisely characterize the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thenmu_spaceis empty if and only if the loop does not terminate.
Definition at line 345 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR | ( | const PSET & | pset, |
| NNC_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Like all_affine_ranking_functions_MS() but using the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 549 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after, | ||
| NNC_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
\ Like all_affine_ranking_functions_MS_2() but using an alternative formalization of the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 519 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation().
|
inline |
If there is an assign_or_swap() method, use it.
Definition at line 40 of file assign_or_swap.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::add_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OR_Matrix< T >::grow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::intersect_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::join_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::remove_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::remove_space_dimensions(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::sub_assign().
|
inline |
\ Returns the inverse rounding mode of dir, ROUND_IGNORE being the inverse of itself.
Definition at line 125 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_IGNORE, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_STRICT_RELATION, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::affine_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_preimage(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::DB_Matrix< T >::l_m_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::l_m_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OR_Matrix< T >::l_m_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::l_m_distance_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sqrt_mpq().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS | ( | const PSET & | pset, |
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
\ Termination test with witness ranking function using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset A pointset approximating the behavior of a loop whose termination is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 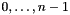 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 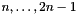 ,
,
mu When trueis returned, this is assigned a point of space dimension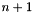 encoding one (not further specified) affine ranking function for the loop being analyzed. The ranking function is of the form
encoding one (not further specified) affine ranking function for the loop being analyzed. The ranking function is of the form 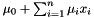 where
where 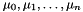 are the coefficients of
are the coefficients of mucorresponding to the space dimensions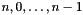 , respectively.
, respectively.
- Returns
trueif any loop approximated bypsetdefinitely terminates;falseif the test is inconclusive. However, ifpsetprecisely characterizes the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thentrueis returned if and only if the loop terminates.
Definition at line 281 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_MS().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after, | ||
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
\ Termination test with witness ranking function using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset_before A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables before the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 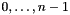 .
.
pset_after A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables after the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 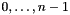 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 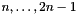 ,
,
Note that unprimed variables represent the values of the loop-relevant program variables before the update performed in the loop body, and primed variables represent the values of those program variables after the update. Note also that unprimed variables are assigned to different space dimensions in pset_before and pset_after.
- Parameters
-
mu When trueis returned, this is assigned a point of space dimension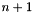 encoding one (not further specified) affine ranking function for the loop being analyzed. The ranking function is of the form
encoding one (not further specified) affine ranking function for the loop being analyzed. The ranking function is of the form 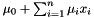 where
where 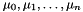 are the coefficients of
are the coefficients of mucorresponding to the space dimensions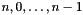 , respectively.
, respectively.
- Returns
trueif any loop approximated bypsetdefinitely terminates;falseif the test is inconclusive. However, ifpset_beforeandpset_afterprecisely characterize the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thentrueis returned if and only if the loop terminates.
Definition at line 299 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_MS().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR | ( | const PSET & | pset, |
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
\ Like one_affine_ranking_function_MS() but using the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 501 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after, | ||
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
\ Like one_affine_ranking_function_MS_2() but using an alternative formalization of the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 476 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_PR().
|
inline |
Definition at line 33 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
Definition at line 33 of file Result_inlines.hh.
Definition at line 47 of file Result_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Definition at line 40 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
Definition at line 40 of file Result_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
\ Extracts the value class part of r (representable number, unrepresentable minus/plus infinity or nan).
Definition at line 54 of file Result_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::VC_MASK.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Extended_Number_Policy::handle_result(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::WRD_Extended_Number_Policy::handle_result(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Debug_WRD_Extended_Number_Policy::handle_result(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::idiv_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::input_mpq(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::result_overflow().
|
inline |
\ Extracts the relation part of r.
Definition at line 61 of file Result_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::VR_MASK.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::DB_Matrix< T >::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OR_Matrix< T >::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_result(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::set_minus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::set_plus_infinity(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::set_unbounded().
|
inline |
Definition at line 68 of file Result_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::VC_MASK, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::VR_MASK.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::adjust_boundary(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::I_Constraint_Common< I_Constraint< T, Val_Or_Ref_Criteria, extended > >::convert_integer(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::I_Constraint_Common< I_Constraint< T, Val_Or_Ref_Criteria, extended > >::convert_real(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::I_Constraint_Rel::I_Constraint_Rel(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::Interval(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::operator>>(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Boxes::propagate_constraint_check_result().
|
inline |
Definition at line 47 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DIR_MASK.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::idiv_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::result_relation(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_direct(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_down(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_ignore(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_not_needed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_not_requested(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::set_neg_overflow_float(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::set_pos_overflow_float().
|
inline |
Definition at line 83 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DIRECT.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_int_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_float(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::fpu_direct_rounding().
|
inline |
Definition at line 53 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_mpq(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_special_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_lt_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_lt_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_lt_int_no_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_lt_mpz(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::set_pos_overflow_int().
| fpu_rounding_direction_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_fpu_dir | ( | Rounding_Dir | dir | ) |
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::add_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::add_mul_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_float_float_inexact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_float_int_inexact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::ceil_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::floor_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Init::Init(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::mul_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::set_rounding_for_PPL(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sqrt_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sub_float(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sub_mul_float().
|
inline |
Definition at line 65 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_IGNORE.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_mpq(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_mpz().
|
inline |
Definition at line 89 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_INVERSE.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::fpu_inverse_rounding().
|
inline |
Definition at line 71 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_mpq(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::prepare_inexact(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::result_relation().
|
inline |
Definition at line 77 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_IGNORE, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_int_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_int_mpq(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::construct_mpz_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_signed_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_unsigned_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_signed_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_unsigned_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::fpu_direct_rounding(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sqrt_mpz(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::sqrt_unsigned_int().
|
inline |
Definition at line 95 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_STRICT_RELATION.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_mpq(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::prepare_inexact(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::result_relation().
|
inline |
Definition at line 59 of file Rounding_Dir_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::round_dir(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_mpz_mpq(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::assign_special_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_2exp_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::div_mpz(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_gt_float(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_gt_int(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_gt_int_no_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::round_gt_mpz(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked::set_neg_overflow_int().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS | ( | const PSET & | pset | ) |
\ Termination test using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset A pointset approximating the behavior of a loop whose termination is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 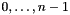 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 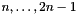 ,
,
- Returns
trueif any loop approximated bypsetdefinitely terminates;falseif the test is inconclusive. However, ifpsetprecisely characterizes the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thentrueis returned if and only if the loop terminates.
Definition at line 242 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_MS().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after | ||
| ) |
\ Termination test using an improvement of the method by Mesnard and Serebrenik [BMPZ10].
- Template Parameters
-
PSET Any pointset supported by the PPL that provides the minimized_constraints()method.
- Parameters
-
pset_before A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables before the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 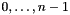 .
.
pset_after A pointset approximating the values of loop-relevant variables after the update performed in the loop body that is being analyzed. The variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 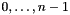 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 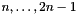 ,
,
Note that unprimed variables represent the values of the loop-relevant program variables before the update performed in the loop body, and primed variables represent the values of those program variables after the update. Note also that unprimed variables are assigned to different space dimensions in pset_before and pset_after.
- Returns
trueif any loop approximated bypsetdefinitely terminates;falseif the test is inconclusive. However, ifpset_beforeandpset_afterprecisely characterize the effect of the loop body onto the loop-relevant program variables, thentrueis returned if and only if the loop terminates.
Definition at line 260 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_MS().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR | ( | const PSET & | pset | ) |
\ Like termination_test_MS() but using the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 458 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR_original().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR_2 | ( | const PSET & | pset_before, |
| const PSET & | pset_after | ||
| ) |
\ Like termination_test_MS_2() but using an alternative formalization of the method by Podelski and Rybalchenko [BMPZ10].
Definition at line 436 of file termination_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR().
Variable Documentation
| const Throwable *volatile Parma_Polyhedra_Library::abandon_expensive_computations = 0 |
A pointer to an exception object.
This pointer, which is initialized to zero, is repeatedly checked along any super-linear (i.e., computationally expensive) computation path in the library. When it is found nonzero the exception it points to is thrown. In other words, making this pointer point to an exception (and leaving it in this state) ensures that the library will return control to the client application, possibly by throwing the given exception, within a time that is a linear function of the size of the representation of the biggest object (powerset of polyhedra, polyhedron, system of constraints or generators) on which the library is operating upon.
- Note
- The only sensible way to assign to this pointer is from within a signal handler or from a parallel thread. For this reason, the library, apart from ensuring that the pointer is initially set to zero, never assigns to it. In particular, it does not zero it again when the exception is thrown: it is the client's responsibility to do so.
Definition at line 34 of file globals.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::concatenate_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::maybe_abandon(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Powerset< D >::omega_reduce().
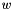 -bit bounded integer, the computation happens modulo
-bit bounded integer, the computation happens modulo 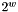 .
. 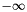 .
. 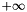 .
. 