Function Documentation
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| C_Polyhedron & | decreasing_mu_space, | ||
| C_Polyhedron & | bounded_mu_space | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 558 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), fill_constraint_systems_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::get_output_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::minimized_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::remove_higher_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::set_output_function(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS_2().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| C_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 514 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), fill_constraint_systems_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::get_output_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::minimized_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::remove_higher_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::set_output_function(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS_2().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs_before, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs_after, | ||
| NNC_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 656 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_2().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| NNC_Polyhedron & | mu_space | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 664 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs_in, |
| Constraint_System & | cs_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 35 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_equalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_2(), assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_2(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR_2().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation | ( | const C_Polyhedron & | ph, |
| Constraint_System & | cs | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 68 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_equalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::minimized_constraints().
|
inline |
Definition at line 166 of file termination_templates.hh.
References assign_all_inequalities_approximation().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS_2(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS_2(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS_2(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS_2().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::fill_constraint_system_PR | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs_before, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs_after, | ||
| Constraint_System & | cs_out, | ||
| Linear_Expression & | le_out | ||
| ) |
Fill the constraint system(s) for the application of the Podelski and Rybalchenko improved termination tests.
- Parameters
-
cs_before The input constraint system describing the state before the execution of the loop body, where variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 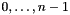 .
.
cs_after The input constraint system describing the state after the execution of the loop body, where variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 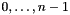 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 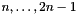 .
.
cs_out The output constraint system, where variables indices are allocated as follows: 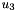 goes onto space dimensions
goes onto space dimensions 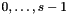 ;
;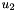 goes onto space dimensions
goes onto space dimensions 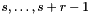 ;
;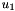 goes onto space dimensions
goes onto space dimensions 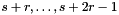 .
.
The improved Podelski-Rybalchenko method described in the paper is based on a loop encoding of the form
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} A_B & \vect{0} \\ A_C & A'_C \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} \vect{x} \\ \vect{x}' \end{pmatrix} \leq \begin{pmatrix} \vect{b}_B \\ \vect{b}_C \end{pmatrix}, \]](form_1174.png)
where 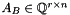 ,
, 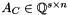 ,
, 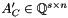 ,
, 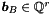 ,
, 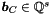 . The corresponding system is:
. The corresponding system is:
![\[ \begin{aligned} (\vect{v}_1-\vect{v}_2)^\transpose A_B - \vect{v}_3^\transpose A_C &= \vect{0}^\transpose, \\ \vect{v}_2^\transpose A_B + \vect{v}_3^\transpose (A_C+A_C') &= \vect{0}^\transpose, \\ \vect{v}_2 \vect{b}_B + \vect{v}_3 \vect{b}_C &< 0, \end{aligned} \]](form_1180.png)
where 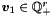 ,
, 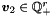 ,
, 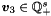 . The space of ranking functions is then spanned by
. The space of ranking functions is then spanned by 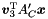 .
.
In contrast, our encoding is of the form
![\[ \begin{pmatrix} \vect{0} & E_B \\ E'_C & E_C \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} \vect{x}' \\ \vect{x} \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} \vect{d}_B \\ \vect{d}_C \end{pmatrix} \geq \vect{0}, \]](form_1185.png)
where  ,
,  ,
, 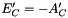 ,
, 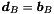 and
and 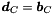 . The corresponding system is:
. The corresponding system is:
![\[ \begin{aligned} (\vect{u}_1-\vect{u}_2)^\transpose E_B - \vect{u}_3^\transpose E_C &= \vect{0}^\transpose, \\ \vect{u}_2^\transpose E_B + \vect{u}_3^\transpose (E_C+E_C') &= \vect{0}^\transpose, \\ \vect{u}_2 \vect{d}_B + \vect{u}_3 \vect{d}_C &> 0, \end{aligned} \]](form_1191.png)
where 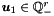 ,
, 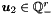 ,
, 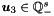 . The space of ranking functions is then spanned by
. The space of ranking functions is then spanned by 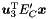 .
.
- Parameters
-
le_out The expression to be minimized in the context of cs_out:a value of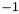 or less entails termination.
or less entails termination.
Definition at line 348 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), row_index, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::one_affine_ranking_function_PR(), and termination_test_PR().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::fill_constraint_system_PR_original | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| Constraint_System & | cs_out, | ||
| Linear_Expression & | le_out | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 431 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), row_index, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original(), and termination_test_PR_original().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::fill_constraint_systems_MS | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| Constraint_System & | cs_out1, | ||
| Constraint_System & | cs_out2 | ||
| ) |
Fill the constraint system(s) for the application of the Mesnard and Serebrenik improved termination tests.
- Parameters
-
cs The input constraint system, where variables indices are allocated as follows:  go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 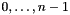 ,
, go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 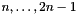 .
.
cs_out1 The first output constraint system. cs_out2 The second output constraint system, if any: it may be an alias for cs_out1.
The allocation of variable indices in the output constraint systems cs_out1 and cs_out2 is as follows, where 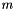 is the number of constraints in
is the number of constraints in cs:
 go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 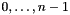 ;
;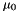 goes onto space dimension
goes onto space dimension 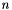 ;
; go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions  ;
;
if we use the same constraint system, that is &cs_out1 == &cs_out2, then
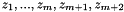 go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 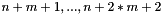 ;
;
otherwise
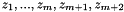 go onto space dimensions
go onto space dimensions 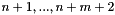 .
.
Definition at line 134 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::get_output_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::set_output_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign().
Referenced by all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), one_affine_ranking_function_MS(), and termination_test_MS().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_MS | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 497 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::feasible_point(), fill_constraint_systems_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_MS_2().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_PR | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs_before, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs_after, | ||
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 642 of file termination.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_2().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs, |
| Generator & | mu | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 650 of file termination.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::one_affine_ranking_function_PR().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_MS | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Definition at line 488 of file termination.cc.
References fill_constraint_systems_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_MS_2().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs_before, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs_after | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 611 of file termination.cc.
References fill_constraint_system_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::get_output_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::num_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::set_output_function(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR_2().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR_original | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Definition at line 596 of file termination.cc.
References fill_constraint_system_PR_original(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::termination_test_PR().
