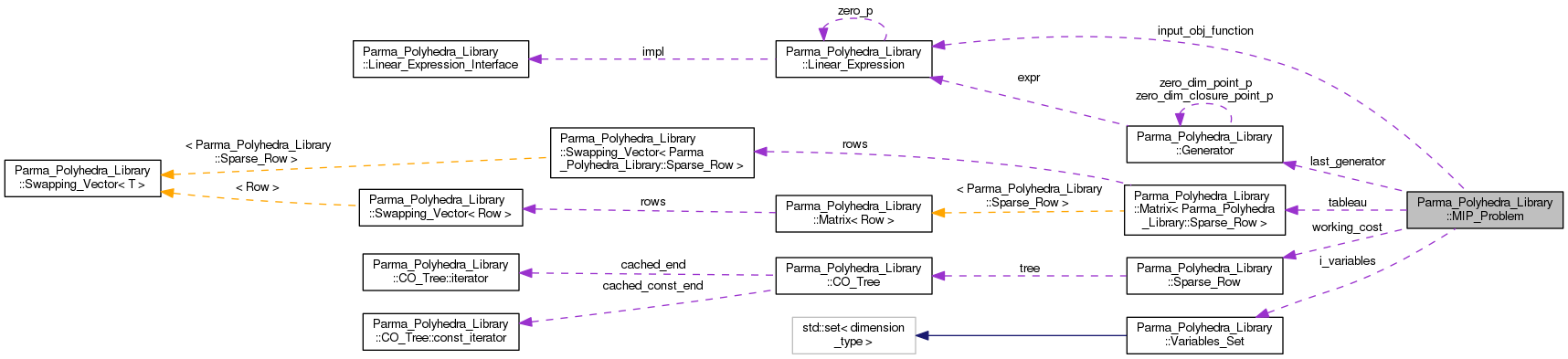
A Mixed Integer (linear) Programming problem. More...
#include <MIP_Problem_defs.hh>
Classes | |
| class | const_iterator |
| A read-only iterator on the constraints defining the feasible region. More... | |
| struct | Inherit_Constraints |
| A tag type to distinguish normal vs. inheriting copy constructor. More... | |
| struct | RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation |
| A helper class to temporarily relax a MIP problem using RAII. More... | |
Public Types | |
| enum | Control_Parameter_Name { PRICING } |
| Names of MIP problems' control parameters. More... | |
| enum | Control_Parameter_Value { PRICING_STEEPEST_EDGE_FLOAT, PRICING_STEEPEST_EDGE_EXACT, PRICING_TEXTBOOK } |
| Possible values for MIP problem's control parameters. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| MIP_Problem (dimension_type dim=0) | |
| Builds a trivial MIP problem. More... | |
| template<typename In > | |
| MIP_Problem (dimension_type dim, In first, In last, const Variables_Set &int_vars, const Linear_Expression &obj=Linear_Expression::zero(), Optimization_Mode mode=MAXIMIZATION) | |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range  , the objective function , the objective function obj and optimization mode mode; those dimensions whose indices occur in int_vars are constrained to take an integer value. More... | |
| template<typename In > | |
| MIP_Problem (dimension_type dim, In first, In last, const Linear_Expression &obj=Linear_Expression::zero(), Optimization_Mode mode=MAXIMIZATION) | |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range  , the objective function , the objective function obj and optimization mode mode. More... | |
| MIP_Problem (dimension_type dim, const Constraint_System &cs, const Linear_Expression &obj=Linear_Expression::zero(), Optimization_Mode mode=MAXIMIZATION) | |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the constraint system cs, the objective function obj and optimization mode mode. More... | |
| MIP_Problem (const MIP_Problem &y) | |
| Ordinary copy constructor. More... | |
| ~MIP_Problem () | |
| Destructor. More... | |
| MIP_Problem & | operator= (const MIP_Problem &y) |
| Assignment operator. More... | |
| dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
| Returns the space dimension of the MIP problem. More... | |
| const Variables_Set & | integer_space_dimensions () const |
| Returns a set containing all the variables' indexes constrained to be integral. More... | |
| const_iterator | constraints_begin () const |
| Returns a read-only iterator to the first constraint defining the feasible region. More... | |
| const_iterator | constraints_end () const |
| Returns a past-the-end read-only iterator to the sequence of constraints defining the feasible region. More... | |
| const Linear_Expression & | objective_function () const |
| Returns the objective function. More... | |
| Optimization_Mode | optimization_mode () const |
| Returns the optimization mode. More... | |
| void | clear () |
Resets *this to be equal to the trivial MIP problem. More... | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_embed (dimension_type m) |
Adds m new space dimensions and embeds the old MIP problem in the new vector space. More... | |
| void | add_to_integer_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &i_vars) |
Sets the variables whose indexes are in set i_vars to be integer space dimensions. More... | |
| void | add_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the MIP problem. More... | |
| void | add_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the MIP problem. More... | |
| void | set_objective_function (const Linear_Expression &obj) |
Sets the objective function to obj. More... | |
| void | set_optimization_mode (Optimization_Mode mode) |
Sets the optimization mode to mode. More... | |
| bool | is_satisfiable () const |
Checks satisfiability of *this. More... | |
| MIP_Problem_Status | solve () const |
| Optimizes the MIP problem. More... | |
| void | evaluate_objective_function (const Generator &evaluating_point, Coefficient &numer, Coefficient &denom) const |
Sets num and denom so that  is the result of evaluating the objective function on is the result of evaluating the objective function on evaluating_point. More... | |
| const Generator & | feasible_point () const |
Returns a feasible point for *this, if it exists. More... | |
| const Generator & | optimizing_point () const |
Returns an optimal point for *this, if it exists. More... | |
| void | optimal_value (Coefficient &numer, Coefficient &denom) const |
Sets numer and denom so that  is the solution of the optimization problem. More... is the solution of the optimization problem. More... | |
| bool | OK () const |
| Checks if all the invariants are satisfied. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump () const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump (std::ostream &s) const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | print () const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<. More... | |
| bool | ascii_load (std::istream &s) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise. More... | |
| memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this. More... | |
| memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this. More... | |
| void | m_swap (MIP_Problem &y) |
Swaps *this with y. More... | |
| Control_Parameter_Value | get_control_parameter (Control_Parameter_Name name) const |
Returns the value of the control parameter name. More... | |
| void | set_control_parameter (Control_Parameter_Value value) |
Sets control parameter value. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static dimension_type | max_space_dimension () |
| Returns the maximum space dimension an MIP_Problem can handle. More... | |
Private Types | |
| enum | Status { UNSATISFIABLE, SATISFIABLE, UNBOUNDED, OPTIMIZED, PARTIALLY_SATISFIABLE } |
| An enumerated type describing the internal status of the MIP problem. More... | |
| typedef std::vector< Constraint * > | Constraint_Sequence |
| A type alias for a sequence of constraints. More... | |
| typedef Sparse_Row | Row |
| typedef Row | working_cost_type |
Private Member Functions | |
| MIP_Problem (const MIP_Problem &y, Inherit_Constraints) | |
| Copy constructor inheriting constraints. More... | |
| void | add_constraint_helper (const Constraint &c) |
| Helper method: implements exception safe addition. More... | |
| void | process_pending_constraints () |
Processes the pending constraints of *this. More... | |
| void | second_phase () |
| Optimizes the MIP problem using the second phase of the primal simplex algorithm. More... | |
| MIP_Problem_Status | compute_tableau (std::vector< dimension_type > &worked_out_row) |
Assigns to this->tableau a simplex tableau representing the MIP problem, inserting into this->mapping the information that is required to recover the original MIP problem. More... | |
| bool | parse_constraints (dimension_type &additional_tableau_rows, dimension_type &additional_slack_variables, std::deque< bool > &is_tableau_constraint, std::deque< bool > &is_satisfied_inequality, std::deque< bool > &is_nonnegative_variable, std::deque< bool > &is_remergeable_variable) const |
| Parses the pending constraints to gather information on how to resize the tableau. More... | |
| dimension_type | get_exiting_base_index (dimension_type entering_var_index) const |
| Computes the row index of the variable exiting the base of the MIP problem. Implemented with anti-cycling rule. More... | |
| void | pivot (dimension_type entering_var_index, dimension_type exiting_base_index) |
| Performs the pivoting operation on the tableau. More... | |
| dimension_type | textbook_entering_index () const |
| Computes the column index of the variable entering the base, using the textbook algorithm with anti-cycling rule. More... | |
| dimension_type | steepest_edge_exact_entering_index () const |
| Computes the column index of the variable entering the base, using an exact steepest-edge algorithm with anti-cycling rule. More... | |
| dimension_type | steepest_edge_float_entering_index () const |
| Same as steepest_edge_exact_entering_index, but using floating points. More... | |
| bool | compute_simplex_using_exact_pricing () |
Returns true if and if only the algorithm successfully computed a feasible solution. More... | |
| bool | compute_simplex_using_steepest_edge_float () |
Returns true if and if only the algorithm successfully computed a feasible solution. More... | |
| void | erase_artificials (dimension_type begin_artificials, dimension_type end_artificials) |
| Drop unnecessary artificial variables from the tableau and get ready for the second phase of the simplex algorithm. More... | |
| bool | is_in_base (dimension_type var_index, dimension_type &row_index) const |
| void | compute_generator () const |
Computes a valid generator that satisfies all the constraints of the Linear Programming problem associated to *this. More... | |
| dimension_type | merge_split_variable (dimension_type var_index) |
| Merges back the positive and negative part of a (previously split) variable after detecting a corresponding nonnegativity constraint. More... | |
| bool | is_lp_satisfiable () const |
Returns true if and if only the LP problem is satisfiable. More... | |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| static void | linear_combine (Row &x, const Row &y, const dimension_type k) |
Linearly combines x with y so that *this[k] is 0. More... | |
| static void | linear_combine (Dense_Row &x, const Sparse_Row &y, const dimension_type k) |
Linearly combines x with y so that *this[k] is 0. More... | |
| static bool | is_unbounded_obj_function (const Linear_Expression &obj_function, const std::vector< std::pair< dimension_type, dimension_type > > &mapping, Optimization_Mode optimization_mode) |
| static bool | is_satisfied (const Constraint &c, const Generator &g) |
Returns true if and only if c is satisfied by g. More... | |
| static bool | is_saturated (const Constraint &c, const Generator &g) |
Returns true if and only if c is saturated by g. More... | |
| static MIP_Problem_Status | solve_mip (bool &have_incumbent_solution, mpq_class &incumbent_solution_value, Generator &incumbent_solution_point, MIP_Problem &mip, const Variables_Set &i_vars) |
| Returns a status that encodes the solution of the MIP problem. More... | |
| static bool | is_mip_satisfiable (MIP_Problem &mip, const Variables_Set &i_vars, Generator &p) |
Returns true if and if only the MIP problem mip is satisfiable when variables in i_vars can only take integral values. More... | |
| static bool | choose_branching_variable (const MIP_Problem &mip, const Variables_Set &i_vars, dimension_type &branching_index) |
Returns true if and if only mip.last_generator satisfies all the integrality conditions implicitly stated using by i_vars. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| dimension_type | external_space_dim |
| The dimension of the vector space. More... | |
| dimension_type | internal_space_dim |
The space dimension of the current (partial) solution of the MIP problem; it may be smaller than external_space_dim. More... | |
| Matrix< Row > | tableau |
| The matrix encoding the current feasible region in tableau form. More... | |
| working_cost_type | working_cost |
| The working cost function. More... | |
| std::vector< std::pair< dimension_type, dimension_type > > | mapping |
| A map between the variables of `input_cs' and `tableau'. More... | |
| std::vector< dimension_type > | base |
| The current basic solution. More... | |
| Status | status |
| The internal state of the MIP problem. More... | |
| Control_Parameter_Value | pricing |
| The pricing method in use. More... | |
| bool | initialized |
| A Boolean encoding whether or not internal data structures have already been properly sized and populated: useful to allow for deeper checks in method OK(). More... | |
| std::vector< Constraint * > | input_cs |
| The sequence of constraints describing the feasible region. More... | |
| dimension_type | inherited_constraints |
| The number of constraints that are inherited from our parent in the recursion tree built when solving via branch-and-bound. More... | |
| dimension_type | first_pending_constraint |
| The first index of `input_cs' containing a pending constraint. More... | |
| Linear_Expression | input_obj_function |
| The objective function to be optimized. More... | |
| Optimization_Mode | opt_mode |
| The optimization mode requested. More... | |
| Generator | last_generator |
| The last successfully computed feasible or optimizing point. More... | |
| Variables_Set | i_variables |
| A set containing all the indexes of variables that are constrained to have an integer value. More... | |
Friends | |
| struct | RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const MIP_Problem &mip) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const MIP_Problem &mip) |
| Output operator. More... | |
| void | swap (MIP_Problem &x, MIP_Problem &y) |
Swaps x with y. More... | |
| void | swap (MIP_Problem &x, MIP_Problem &y) |
Detailed Description
A Mixed Integer (linear) Programming problem.
An object of this class encodes a mixed integer (linear) programming problem. The MIP problem is specified by providing:
- the dimension of the vector space;
- the feasible region, by means of a finite set of linear equality and non-strict inequality constraints;
- the subset of the unknown variables that range over the integers (the other variables implicitly ranging over the reals);
- the objective function, described by a Linear_Expression;
- the optimization mode (either maximization or minimization).
The class provides support for the (incremental) solution of the MIP problem based on variations of the revised simplex method and on branch-and-bound techniques. The result of the resolution process is expressed in terms of an enumeration, encoding the feasibility and the unboundedness of the optimization problem. The class supports simple feasibility tests (i.e., no optimization), as well as the extraction of an optimal (resp., feasible) point, provided the MIP_Problem is optimizable (resp., feasible).
By exploiting the incremental nature of the solver, it is possible to reuse part of the computational work already done when solving variants of a given MIP_Problem: currently, incremental resolution supports the addition of space dimensions, the addition of constraints, the change of objective function and the change of optimization mode.
Definition at line 87 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Member Typedef Documentation
|
private |
A type alias for a sequence of constraints.
Definition at line 237 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
Definition at line 508 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
Definition at line 516 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
explicit |
Builds a trivial MIP problem.
A trivial MIP problem requires to maximize the objective function  on a vector space under no constraints at all: the origin of the vector space is an optimal solution.
on a vector space under no constraints at all: the origin of the vector space is an optimal solution.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space enclosing *this(optional argument with default value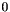 ).
).
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().
Definition at line 78 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References max_space_dimension(), and OK().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::MIP_Problem | ( | dimension_type | dim, |
| In | first, | ||
| In | last, | ||
| const Variables_Set & | int_vars, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | obj = Linear_Expression::zero(), |
||
| Optimization_Mode | mode = MAXIMIZATION |
||
| ) |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range 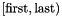 , the objective function
, the objective function obj and optimization mode mode; those dimensions whose indices occur in int_vars are constrained to take an integer value.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.first An input iterator to the start of the sequence of constraints. last A past-the-end input iterator to the sequence of constraints. int_vars The set of variables' indexes that are constrained to take integer values. obj The objective function (optional argument with default value 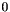 ).
).mode The optimization mode (optional argument with default value MAXIMIZATION).
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().std::invalid_argument Thrown if a constraint in the sequence is a strict inequality, if the space dimension of a constraint (resp., of the objective function or of the integer variables) or the space dimension of the integer variable set is strictly greater than dim.
Definition at line 32 of file MIP_Problem_templates.hh.
References add_constraint_helper(), external_space_dim, i_variables, input_cs, max_space_dimension(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::MIP_Problem | ( | dimension_type | dim, |
| In | first, | ||
| In | last, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | obj = Linear_Expression::zero(), |
||
| Optimization_Mode | mode = MAXIMIZATION |
||
| ) |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range 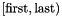 , the objective function
, the objective function obj and optimization mode mode.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.first An input iterator to the start of the sequence of constraints. last A past-the-end input iterator to the sequence of constraints. obj The objective function (optional argument with default value 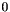 ).
).mode The optimization mode (optional argument with default value MAXIMIZATION).
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().std::invalid_argument Thrown if a constraint in the sequence is a strict inequality or if the space dimension of a constraint (resp., of the objective function or of the integer variables) is strictly greater than dim.
Definition at line 116 of file MIP_Problem_templates.hh.
References add_constraint_helper(), input_cs, max_space_dimension(), OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::MIP_Problem | ( | dimension_type | dim, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | obj = Linear_Expression::zero(), |
||
| Optimization_Mode | mode = MAXIMIZATION |
||
| ) |
Builds an MIP problem having space dimension dim from the constraint system cs, the objective function obj and optimization mode mode.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.cs The constraint system defining the feasible region. obj The objective function (optional argument with default value 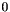 ).
).mode The optimization mode (optional argument with default value MAXIMIZATION).
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().std::invalid_argument Thrown if the constraint system contains any strict inequality or if the space dimension of the constraint system (resp., the objective function) is strictly greater than dim.
Definition at line 105 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References add_constraint_helper(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), max_space_dimension(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Ordinary copy constructor.
Definition at line 44 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References add_constraint_helper(), input_cs, and OK().
|
inline |
Destructor.
Definition at line 111 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References inherited_constraints, input_cs, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::nth_iter().
|
inlineprivate |
Copy constructor inheriting constraints.
Definition at line 70 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References OK().
Member Function Documentation
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraint | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the MIP problem.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the constraint cis a strict inequality or if its space dimension is strictly greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 164 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), is_mip_satisfiable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign(), and solve_mip().
|
inlineprivate |
Helper method: implements exception safe addition.
Definition at line 92 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::compute_capacity(), and input_cs.
Referenced by MIP_Problem().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraints | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the MIP problem.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the constraint system cscontains any strict inequality or if its space dimension is strictly greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 184 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::strongly_minimize_constraints().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_space_dimensions_and_embed | ( | dimension_type | m | ) |
Adds m new space dimensions and embeds the old MIP problem in the new vector space.
- Parameters
-
m The number of dimensions to add.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if adding mnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
The new space dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new MIP problem; they are initially unconstrained.
Definition at line 374 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::strongly_minimize_constraints().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_to_integer_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | i_vars | ) |
Sets the variables whose indexes are in set i_vars to be integer space dimensions.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if some index in i_varsdoes not correspond to a space dimension in*this.
Definition at line 392 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::ascii_dump | ( | ) | const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::ascii_dump | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this.
Definition at line 2545 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::ascii_load | ( | std::istream & | s | ) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise.
Definition at line 2631 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::ascii_load(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::zero_dim_positivity().
|
staticprivate |
Returns true if and if only mip.last_generator satisfies all the integrality conditions implicitly stated using by i_vars.
- Parameters
-
mip The MIP problem. This is assumed to have no integral space dimension (so that it is a pure LP problem). i_vars The variables that are constrained to take an integer value. branching_index If falseis returned, this will encode the non-integral variable index on which the `branch and bound' algorithm should be applied.
Definition at line 2137 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::gcd_assign(), input_cs, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::insert(), last_generator, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Resets *this to be equal to the trivial MIP problem.
The space dimension is reset to 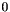 .
.
Definition at line 205 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
|
private |
Computes a valid generator that satisfies all the constraints of the Linear Programming problem associated to *this.
Definition at line 1760 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), last_generator, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::lcm_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign().
|
private |
Returns true if and if only the algorithm successfully computed a feasible solution.
- Note
- Uses an exact pricing method (either textbook or exact steepest edge), so that the result is deterministic across different architectures.
Definition at line 1629 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::maybe_abandon().
|
private |
Returns true if and if only the algorithm successfully computed a feasible solution.
- Note
- Uses a floating point implementation of the steepest edge pricing method, so that the result is correct, but not deterministic across different architectures.
Definition at line 1531 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::abs_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::maybe_abandon(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, WEIGHT_ADD, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
private |
Assigns to this->tableau a simplex tableau representing the MIP problem, inserting into this->mapping the information that is required to recover the original MIP problem.
- Returns
UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEMif the constraint system contains any trivially unfeasible constraint (tableau was not computed);UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEMif the problem is trivially unbounded (the computed tableau contains no constraints);OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM>if the problem is neither trivially unfeasible nor trivially unbounded (the tableau was computed successfully).
|
inline |
Returns a read-only iterator to the first constraint defining the feasible region.
Definition at line 150 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References input_cs.
Referenced by operator<<().
|
inline |
Returns a past-the-end read-only iterator to the sequence of constraints defining the feasible region.
Definition at line 155 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References input_cs.
Referenced by operator<<().
|
private |
Drop unnecessary artificial variables from the tableau and get ready for the second phase of the simplex algorithm.
- Note
- The two parameters denote a STL-like half-open range. It is assumed that
begin_artificialsis strictly greater than 0 and smaller thanend_artificials.
- Parameters
-
begin_artificials The start of the tableau column index range for artificial variables. end_artificials The end of the tableau column index range for artificial variables. Note that column index end_artificial is excluded from the range.
Definition at line 1679 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::m_swap().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::evaluate_objective_function | ( | const Generator & | evaluating_point, |
| Coefficient & | numer, | ||
| Coefficient & | denom | ||
| ) | const |
Sets num and denom so that  is the result of evaluating the objective function on
is the result of evaluating the objective function on evaluating_point.
- Parameters
-
evaluating_point The point on which the objective function will be evaluated. numer On exit will contain the numerator of the evaluated value. denom On exit will contain the denominator of the evaluated value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandevaluating_pointare dimension-incompatible or if the generatorevaluating_pointis not a point.
Definition at line 1942 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::normalize2(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), optimal_value(), and solve_mip().
|
inline |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this.
Definition at line 212 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References base, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::external_memory_in_bytes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::external_memory_in_bytes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::external_memory_in_bytes(), inherited_constraints, input_cs, input_obj_function, last_generator, mapping, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::nth_iter(), tableau, and working_cost.
Referenced by total_memory_in_bytes().
| const PPL::Generator & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::feasible_point | ( | ) | const |
Returns a feasible point for *this, if it exists.
- Exceptions
-
std::domain_error Thrown if the MIP problem is not satisfiable.
Definition at line 225 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original().
|
inline |
Returns the value of the control parameter name.
Definition at line 165 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References PPL_USED, PRICING, and pricing.
|
private |
Computes the row index of the variable exiting the base of the MIP problem. Implemented with anti-cycling rule.
- Returns
- The row index of the variable exiting the base.
- Parameters
-
entering_var_index The column index of the variable entering the base.
Definition at line 1472 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::abs_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::lcm_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), WEIGHT_ADD, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
inline |
Returns a set containing all the variables' indexes constrained to be integral.
Definition at line 160 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References i_variables.
Referenced by is_mip_satisfiable(), operator<<(), and solve().
|
private |
Definition at line 409 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
|
private |
Returns true if and if only the LP problem is satisfiable.
Definition at line 1969 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References external_space_dim, first_pending_constraint, initialized, internal_space_dim, mapping, process_pending_constraints(), and tableau.
Referenced by is_mip_satisfiable(), is_satisfiable(), solve(), and solve_mip().
|
staticprivate |
Returns true if and if only the MIP problem mip is satisfiable when variables in i_vars can only take integral values.
- Parameters
-
mip The MIP problem. This is assumed to have no integral space dimension (so that it is a pure LP problem). i_vars The variables that are constrained to take integral values. p If trueis returned, it will encode a feasible point.
Definition at line 2214 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::gcd_assign(), integer_space_dimensions(), is_lp_satisfiable(), last_generator, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, and space_dimension().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable | ( | ) | const |
Checks satisfiability of *this.
- Returns
trueif and only if the MIP problem is satisfiable.
Definition at line 247 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References i_variables, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::i_vars, is_lp_satisfiable(), last_generator, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::lp, and status.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::one_affine_ranking_function_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::one_affine_ranking_function_PR_original(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::termination_test_PR_original().
|
staticprivate |
Returns true if and only if c is satisfied by g.
Definition at line 467 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension().
|
staticprivate |
Returns true if and only if c is saturated by g.
Definition at line 478 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension().
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 1420 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION.
|
staticprivate |
Linearly combines x with y so that *this[k] is 0.
- Parameters
-
x The row that will be combined with yobject.y The row that will be combined with xobject.k The position of *thisthat have to be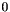 .
.
Computes a linear combination of x and y having the element of index k equal to 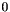 . Then it assigns the resulting Row to
. Then it assigns the resulting Row to x and normalizes it.
Definition at line 1360 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::find(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::linear_combine(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::normalize2(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::size(), WEIGHT_ADD_MUL, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
staticprivate |
Linearly combines x with y so that *this[k] is 0.
- Parameters
-
x The row that will be combined with yobject.y The row that will be combined with xobject.k The position of *thisthat have to be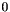 .
.
Computes a linear combination of x and y having the element of index k equal to 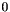 . Then it assigns the resulting Dense_Row to
. Then it assigns the resulting Dense_Row to x and normalizes it.
Definition at line 1392 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Dense_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::linear_combine(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Dense_Row::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::normalize2(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::size(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Dense_Row::size(), WEIGHT_ADD_MUL, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
inline |
Swaps *this with y.
Definition at line 177 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References base, external_space_dim, first_pending_constraint, i_variables, inherited_constraints, initialized, input_cs, input_obj_function, internal_space_dim, last_generator, mapping, opt_mode, pricing, status, swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), tableau, and working_cost.
Referenced by clear(), operator=(), and swap().
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the maximum space dimension an MIP_Problem can handle.
Definition at line 33 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::max_space_dimension().
Referenced by MIP_Problem().
|
private |
Merges back the positive and negative part of a (previously split) variable after detecting a corresponding nonnegativity constraint.
- Returns
- If the negative part of
var_indexwas in base, the index of the corresponding tableau row (which has become non-feasible); otherwisenot_a_dimension().
- Parameters
-
var_index The index of the variable that has to be merged.
Definition at line 420 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension().
|
inline |
Returns the objective function.
Definition at line 134 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References input_obj_function.
Referenced by operator<<().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::OK | ( | ) | const |
Checks if all the invariants are satisfied.
Definition at line 2314 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ascii_dump(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::gcd_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::lower_bound(), and PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT.
Referenced by MIP_Problem(), and set_optimization_mode().
|
inline |
Assignment operator.
Definition at line 198 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
|
inline |
Sets numer and denom so that  is the solution of the optimization problem.
is the solution of the optimization problem.
- Exceptions
-
std::domain_error Thrown if *thisdoes not not have an optimizing point, i.e., if the MIP problem is unbounded or not satisfiable.
Definition at line 144 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References evaluate_objective_function(), and optimizing_point().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::max_min(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inline |
Returns the optimization mode.
Definition at line 139 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References opt_mode.
Referenced by operator<<(), and solve_mip().
| const PPL::Generator & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimizing_point | ( | ) | const |
Returns an optimal point for *this, if it exists.
- Exceptions
-
std::domain_error Thrown if *thisdoes not not have an optimizing point, i.e., if the MIP problem is unbounded or not satisfiable.
Definition at line 236 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), and optimal_value().
|
private |
Parses the pending constraints to gather information on how to resize the tableau.
- Note
- All of the method parameters are output parameters; their value is only meaningful when the function exit returning value
true.
- Returns
falseif a trivially false constraint is detected,trueotherwise.
- Parameters
-
additional_tableau_rows On exit, this will store the number of rows that have to be added to the original tableau. additional_slack_variables This will store the number of slack variables that have to be added to the original tableau. is_tableau_constraint This container of Boolean flags is initially empty. On exit, it size will be equal to the number of pending constraints in input_cs. For each pending constraint indexi, the corresponding element of this container (having indexi - first_pending_constraint) will be set totrueif and only if the constraint has to be included in the tableau.is_satisfied_inequality This container of Boolean flags is initially empty. On exit, its size will be equal to the number of pending constraints in input_cs. For each pending constraint indexi, the corresponding element of this container (having indexi - first_pending_constraint) will be set totrueif and only if it is an inequality and it is already satisfied bylast_generator(hence it does not require the introduction of an artificial variable).is_nonnegative_variable This container of Boolean flags is initially empty. On exit, it size is equal to external_space_dim. For each variable (index), the corresponding element of this container istrueif the variable is known to be nonnegative (and hence should not be split into a positive and a negative part).is_remergeable_variable This container of Boolean flags is initially empty. On exit, it size is equal to internal_space_dim. For each variable (index), the corresponding element of this container istrueif the variable was previously split into positive and negative parts that can now be merged back, since it is known that the variable is nonnegative.
Definition at line 490 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::first_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn_b(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
private |
Performs the pivoting operation on the tableau.
- Parameters
-
entering_var_index The index of the variable entering the base. exiting_base_index The index of the row exiting the base.
Definition at line 1451 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::linear_combine().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::print | ( | ) | const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<.
|
private |
Processes the pending constraints of *this.
Definition at line 681 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_one(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::linear_combine(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension().
Referenced by is_lp_satisfiable().
|
private |
Optimizes the MIP problem using the second phase of the primal simplex algorithm.
Definition at line 1864 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_one(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::linear_combine(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
Referenced by solve(), and solve_mip().
|
inline |
Sets control parameter value.
Definition at line 172 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References pricing, and value.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_objective_function | ( | const Linear_Expression & | obj | ) |
Sets the objective function to obj.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the space dimension of objis strictly greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 208 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::strongly_minimize_constraints().
|
inline |
Sets the optimization mode to mode.
Definition at line 123 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References OK(), opt_mode, OPTIMIZED, SATISFIABLE, status, and UNBOUNDED.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::strongly_minimize_constraints().
| PPL::MIP_Problem_Status Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve | ( | ) | const |
Optimizes the MIP problem.
- Returns
- An MIP_Problem_Status flag indicating the outcome of the optimization attempt (unfeasible, unbounded or optimized problem).
Definition at line 293 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References i_variables, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::i_vars, integer_space_dimensions(), is_lp_satisfiable(), last_generator, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::lp, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, second_phase(), status, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::bounds(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::bounds(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::max_min(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::strongly_minimize_constraints().
|
staticprivate |
Returns a status that encodes the solution of the MIP problem.
- Parameters
-
have_incumbent_solution It is used to store if the solving process has found a provisional optimum point. incumbent_solution_value Encodes the evaluated value of the provisional optimum point found. incumbent_solution_point If the method returns `OPTIMIZED', this will contain the optimality point. mip The problem that has to be solved. i_vars The variables that are constrained to take an integer value.
Definition at line 2015 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), evaluate_objective_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::gcd_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_canonical(), is_lp_satisfiable(), last_generator, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, optimization_mode(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, second_phase(), space_dimension(), status, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM.
|
inline |
Returns the space dimension of the MIP problem.
Definition at line 38 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References external_space_dim.
Referenced by is_mip_satisfiable(), and solve_mip().
|
private |
Computes the column index of the variable entering the base, using an exact steepest-edge algorithm with anti-cycling rule.
- Returns
- The column index of the variable that enters the base. If no such variable exists, optimality was achieved and
0is returned.
To compute the entering_index, the steepest edge algorithm chooses the index `j' such that 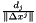 is the largest in absolute value, where
is the largest in absolute value, where
![\[ \|\Delta x^{j} \| = \left( 1+\sum_{i=1}^{m} \alpha_{ij}^2 \right)^{\frac{1}{2}}. \]](form_1025.png)
Recall that, due to the exact integer implementation of the algorithm, our tableau does not contain the ``real''  values, but these can be computed dividing the value of the coefficient by the value of the variable in base. Obviously the result may not be an integer, so we will proceed in another way: we compute the lcm of all the variables in base to get the good ``weight'' of each Coefficient of the tableau.
values, but these can be computed dividing the value of the coefficient by the value of the variable in base. Obviously the result may not be an integer, so we will proceed in another way: we compute the lcm of all the variables in base to get the good ``weight'' of each Coefficient of the tableau.
Definition at line 1134 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::lcm_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::lower_bound(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), WEIGHT_ADD_MUL, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
private |
Same as steepest_edge_exact_entering_index, but using floating points.
- Note
- Due to rounding errors, the index of the variable entering the base of the MIP problem is not predictable across different architectures. Hence, the overall simplex computation may differ in the path taken to reach the optimum. Anyway, the exact final result will be computed for the MIP_Problem.
Definition at line 1009 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::iterator::index(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), WEIGHT_ADD, WEIGHT_ADD_MUL, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
|
private |
Computes the column index of the variable entering the base, using the textbook algorithm with anti-cycling rule.
- Returns
- The column index of the variable that enters the base. If no such variable exists, optimality was achieved and
0is returned.
Definition at line 1333 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::CO_Tree::const_iterator::index(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn().
|
inline |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this.
Definition at line 236 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References external_memory_in_bytes().
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Output operator.
|
related |
Definition at line 2888 of file MIP_Problem.cc.
References constraints_begin(), constraints_end(), integer_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, objective_function(), and optimization_mode().
|
friend |
Definition at line 620 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
related |
|
related |
Definition at line 320 of file MIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
The current basic solution.
Definition at line 533 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), and m_swap().
|
private |
The dimension of the vector space.
Definition at line 499 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by is_lp_satisfiable(), m_swap(), MIP_Problem(), and space_dimension().
|
private |
The first index of `input_cs' containing a pending constraint.
Definition at line 585 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by is_lp_satisfiable(), and m_swap().
|
private |
A set containing all the indexes of variables that are constrained to have an integer value.
Definition at line 600 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by integer_space_dimensions(), is_satisfiable(), m_swap(), MIP_Problem(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation(), solve(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation::~RAII_Temporary_Real_Relaxation().
|
private |
The number of constraints that are inherited from our parent in the recursion tree built when solving via branch-and-bound.
The first inherited_constraints elements in input_cs point to the inherited constraints, whose resources are owned by our ancestors. The resources of the other elements in input_cs are owned by *this and should be appropriately released on destruction.
Definition at line 582 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), m_swap(), and ~MIP_Problem().
|
private |
A Boolean encoding whether or not internal data structures have already been properly sized and populated: useful to allow for deeper checks in method OK().
Definition at line 568 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by is_lp_satisfiable(), and m_swap().
|
private |
The sequence of constraints describing the feasible region.
Definition at line 571 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_constraint_helper(), choose_branching_variable(), constraints_begin(), constraints_end(), external_memory_in_bytes(), m_swap(), MIP_Problem(), and ~MIP_Problem().
|
private |
The objective function to be optimized.
Definition at line 588 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), m_swap(), and objective_function().
|
private |
The space dimension of the current (partial) solution of the MIP problem; it may be smaller than external_space_dim.
Definition at line 505 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by is_lp_satisfiable(), and m_swap().
|
private |
The last successfully computed feasible or optimizing point.
Definition at line 594 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by choose_branching_variable(), compute_generator(), external_memory_in_bytes(), is_mip_satisfiable(), is_satisfiable(), m_swap(), solve(), and solve_mip().
|
private |
A map between the variables of `input_cs' and `tableau'.
Contains all the pairs (i, j) such that mapping[i].first encodes the index of the column in the tableau where input_cs[i] is stored; if mapping[i].second is not a zero, it encodes the split part of the tableau of input_cs[i]. The "positive" one is represented by mapping[i].first and the "negative" one is represented by mapping[i].second.
Definition at line 530 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), is_lp_satisfiable(), and m_swap().
|
private |
The optimization mode requested.
Definition at line 591 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by m_swap(), optimization_mode(), and set_optimization_mode().
|
private |
The pricing method in use.
Definition at line 561 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by get_control_parameter(), m_swap(), and set_control_parameter().
|
private |
The internal state of the MIP problem.
Definition at line 554 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by is_satisfiable(), m_swap(), set_optimization_mode(), solve(), and solve_mip().
The matrix encoding the current feasible region in tableau form.
Definition at line 514 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), is_lp_satisfiable(), and m_swap().
|
private |
The working cost function.
Definition at line 519 of file MIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by external_memory_in_bytes(), and m_swap().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
