A bounded difference shape. More...
#include <BD_Shape_defs.hh>
Classes | |
| class | Status |
| A conjunctive assertion about a BD_Shape<T> object. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef T | coefficient_type_base |
| The numeric base type upon which bounded differences are built. More... | |
| typedef N | coefficient_type |
| The (extended) numeric type of the inhomogeneous term of the inequalities defining a BDS. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| void | ascii_dump () const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump (std::ostream &s) const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | print () const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<. More... | |
| bool | ascii_load (std::istream &s) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise. More... | |
| memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this. More... | |
| memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this. More... | |
| int32_t | hash_code () const |
Returns a 32-bit hash code for *this. More... | |
Constructors, Assignment, Swap and Destructor | |
| BD_Shape (dimension_type num_dimensions=0, Degenerate_Element kind=UNIVERSE) | |
| Builds a universe or empty BDS of the specified space dimension. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const BD_Shape &y, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Ordinary copy constructor. More... | |
| template<typename U > | |
| BD_Shape (const BD_Shape< U > &y, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
Builds a conservative, upward approximation of y. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const Constraint_System &cs) | |
Builds a BDS from the system of constraints cs. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const Congruence_System &cgs) | |
| Builds a BDS from a system of congruences. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const Generator_System &gs) | |
Builds a BDS from the system of generators gs. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const Polyhedron &ph, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
Builds a BDS from the polyhedron ph. More... | |
| template<typename Interval > | |
| BD_Shape (const Box< Interval > &box, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Builds a BDS out of a box. More... | |
| BD_Shape (const Grid &grid, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Builds a BDS out of a grid. More... | |
| template<typename U > | |
| BD_Shape (const Octagonal_Shape< U > &os, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Builds a BDS from an octagonal shape. More... | |
| BD_Shape & | operator= (const BD_Shape &y) |
The assignment operator (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible). More... | |
| void | m_swap (BD_Shape &y) |
Swaps *this with y (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible). More... | |
| ~BD_Shape () | |
| Destructor. More... | |
Member Functions that Do Not Modify the BD_Shape | |
| dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this. More... | |
| dimension_type | affine_dimension () const |
Returns 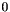 , if , if *this is empty; otherwise, returns the affine dimension of *this. More... | |
| Constraint_System | constraints () const |
Returns a system of constraints defining *this. More... | |
| Constraint_System | minimized_constraints () const |
Returns a minimized system of constraints defining *this. More... | |
| Congruence_System | congruences () const |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this. More... | |
| Congruence_System | minimized_congruences () const |
Returns a minimal system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this with the same affine dimension as *this. More... | |
| bool | bounds_from_above (const Linear_Expression &expr) const |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from above in *this. More... | |
| bool | bounds_from_below (const Linear_Expression &expr) const |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from below in *this. More... | |
| bool | maximize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &sup_n, Coefficient &sup_d, bool &maximum) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value is computed. More... | |
| bool | maximize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &sup_n, Coefficient &sup_d, bool &maximum, Generator &g) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed. More... | |
| bool | minimize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &inf_n, Coefficient &inf_d, bool &minimum) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value is computed. More... | |
| bool | minimize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &inf_n, Coefficient &inf_d, bool &minimum, Generator &g) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed. More... | |
| bool | frequency (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &freq_n, Coefficient &freq_d, Coefficient &val_n, Coefficient &val_d) const |
Returns true if and only if there exist a unique value val such that *this saturates the equality expr = val. More... | |
| bool | contains (const BD_Shape &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains y. More... | |
| bool | strictly_contains (const BD_Shape &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this strictly contains y. More... | |
| bool | is_disjoint_from (const BD_Shape &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this and y are disjoint. More... | |
| Poly_Con_Relation | relation_with (const Constraint &c) const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the constraint c. More... | |
| Poly_Con_Relation | relation_with (const Congruence &cg) const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the congruence cg. More... | |
| Poly_Gen_Relation | relation_with (const Generator &g) const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the generator g. More... | |
| bool | is_empty () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is an empty BDS. More... | |
| bool | is_universe () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a universe BDS. More... | |
| bool | is_discrete () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is discrete. More... | |
| bool | is_topologically_closed () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a topologically closed subset of the vector space. More... | |
| bool | is_bounded () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a bounded BDS. More... | |
| bool | contains_integer_point () const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains at least one integer point. More... | |
| bool | constrains (Variable var) const |
Returns true if and only if var is constrained in *this. More... | |
| bool | OK () const |
Returns true if and only if *this satisfies all its invariants. More... | |
Space-Dimension Preserving Member Functions that May Modify the BD_Shape | |
| void | add_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the system of bounded differences defining *this. More... | |
| void | add_congruence (const Congruence &cg) |
Adds a copy of congruence cg to the system of congruences of *this. More... | |
| void | add_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of bounded differences defining *this. More... | |
| void | add_recycled_constraints (Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this. More... | |
| void | add_congruences (const Congruence_System &cgs) |
Adds to *this constraints equivalent to the congruences in cgs. More... | |
| void | add_recycled_congruences (Congruence_System &cgs) |
Adds to *this constraints equivalent to the congruences in cgs. More... | |
| void | refine_with_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_congruence (const Congruence &cg) |
Uses a copy of congruence cg to refine the system of bounded differences of *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Uses a copy of the constraints in cs to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_congruences (const Congruence_System &cgs) |
Uses a copy of the congruences in cgs to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | refine_with_linear_form_inequality (const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &right) |
Refines the system of BD_Shape constraints defining *this using the constraint expressed by left 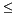 right. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | generalized_refine_with_linear_form_inequality (const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &right, Relation_Symbol relsym) |
Refines the system of BD_Shape constraints defining *this using the constraint expressed by left  right, where 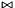 is the relation symbol specified by is the relation symbol specified by relsym. More... | |
| template<typename U > | |
| void | export_interval_constraints (U &dest) const |
Applies to dest the interval constraints embedded in *this. More... | |
| void | unconstrain (Variable var) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to space dimension var, assigning the result to *this. More... | |
| void | unconstrain (const Variables_Set &vars) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to the set of space dimensions vars, assigning the result to *this. More... | |
| void | intersection_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the intersection of *this and y. More... | |
| void | upper_bound_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the smallest BDS containing the union of *this and y. More... | |
| bool | upper_bound_assign_if_exact (const BD_Shape &y) |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact, it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| bool | integer_upper_bound_assign_if_exact (const BD_Shape &y) |
If the integer upper bound of *this and y is exact, it is assigned to *this and true is returned; otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| void | difference_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the smallest BD shape containing the set difference of *this and y. More... | |
| bool | simplify_using_context_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this a meet-preserving simplification of *this with respect to y. If false is returned, then the intersection is empty. More... | |
| void | affine_image (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the affine image of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression specified by expr and denominator. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | affine_form_image (Variable var, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &lf) |
Assigns to *this the affine form image of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression(s) specified by lf. More... | |
| void | affine_preimage (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the affine preimage of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression specified by expr and denominator. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_image (Variable var, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the affine relation 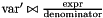 , where , where 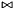 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_image (const Linear_Expression &lhs, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &rhs) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the affine relation 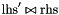 , where , where 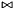 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_preimage (Variable var, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the affine relation 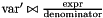 , where , where 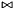 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_preimage (const Linear_Expression &lhs, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &rhs) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the affine relation 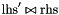 , where , where 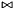 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | bounded_affine_image (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &lb_expr, const Linear_Expression &ub_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 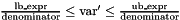 . More... . More... | |
| void | bounded_affine_preimage (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &lb_expr, const Linear_Expression &ub_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 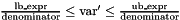 . More... . More... | |
| void | time_elapse_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the time-elapse between *this and y. More... | |
| void | wrap_assign (const Variables_Set &vars, Bounded_Integer_Type_Width w, Bounded_Integer_Type_Representation r, Bounded_Integer_Type_Overflow o, const Constraint_System *cs_p=0, unsigned complexity_threshold=16, bool wrap_individually=true) |
| Wraps the specified dimensions of the vector space. More... | |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points (Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates. More... | |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points (const Variables_Set &vars, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to vars. More... | |
| void | topological_closure_assign () |
Assigns to *this its topological closure. More... | |
| void | CC76_extrapolation_assign (const BD_Shape &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the CC76-extrapolation between *this and y. More... | |
| template<typename Iterator > | |
| void | CC76_extrapolation_assign (const BD_Shape &y, Iterator first, Iterator last, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the CC76-extrapolation between *this and y. More... | |
| void | BHMZ05_widening_assign (const BD_Shape &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the BHMZ05-widening of *this and y. More... | |
| void | limited_BHMZ05_extrapolation_assign (const BD_Shape &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Improves the result of the BHMZ05-widening computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this. More... | |
| void | CC76_narrowing_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the result of restoring in y the constraints of *this that were lost by CC76-extrapolation applications. More... | |
| void | limited_CC76_extrapolation_assign (const BD_Shape &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Improves the result of the CC76-extrapolation computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this. More... | |
| void | H79_widening_assign (const BD_Shape &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the H79-widening between *this and y. More... | |
| void | widening_assign (const BD_Shape &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
| Same as H79_widening_assign(y, tp). More... | |
| void | limited_H79_extrapolation_assign (const BD_Shape &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Improves the result of the H79-widening computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this. More... | |
Member Functions that May Modify the Dimension of the Vector Space | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_embed (dimension_type m) |
Adds m new dimensions and embeds the old BDS into the new space. More... | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_project (dimension_type m) |
Adds m new dimensions to the BDS and does not embed it in the new vector space. More... | |
| void | concatenate_assign (const BD_Shape &y) |
Assigns to *this the concatenation of *this and y, taken in this order. More... | |
| void | remove_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &vars) |
| Removes all the specified dimensions. More... | |
| void | remove_higher_space_dimensions (dimension_type new_dimension) |
Removes the higher dimensions so that the resulting space will have dimension new_dimension. More... | |
| template<typename Partial_Function > | |
| void | map_space_dimensions (const Partial_Function &pfunc) |
| Remaps the dimensions of the vector space according to a partial function. More... | |
| void | expand_space_dimension (Variable var, dimension_type m) |
Creates m copies of the space dimension corresponding to var. More... | |
| void | fold_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &vars, Variable dest) |
Folds the space dimensions in vars into dest. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | refine_fp_interval_abstract_store (Box< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &store) const |
Refines store with the constraints defining *this. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static dimension_type | max_space_dimension () |
| Returns the maximum space dimension that a BDS can handle. More... | |
| static bool | can_recycle_constraint_systems () |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle constraints. More... | |
| static bool | can_recycle_congruence_systems () |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle congruences. More... | |
Private Types | |
| typedef Checked_Number< T, Debug_WRD_Extended_Number_Policy > | N |
| The (extended) numeric type of the inhomogeneous term of the inequalities defining a BDS. More... | |
Private Member Functions | |
| bool | marked_zero_dim_univ () const |
Returns true if the BDS is the zero-dimensional universe. More... | |
| bool | marked_empty () const |
Returns true if the BDS is known to be empty. More... | |
| bool | marked_shortest_path_closed () const |
Returns true if the system of bounded differences is known to be shortest-path closed. More... | |
| bool | marked_shortest_path_reduced () const |
Returns true if the system of bounded differences is known to be shortest-path reduced. More... | |
| void | set_empty () |
Turns *this into an empty BDS. More... | |
| void | set_zero_dim_univ () |
Turns *this into an zero-dimensional universe BDS. More... | |
| void | set_shortest_path_closed () |
Marks *this as shortest-path closed. More... | |
| void | set_shortest_path_reduced () |
Marks *this as shortest-path closed. More... | |
| void | reset_shortest_path_closed () |
Marks *this as possibly not shortest-path closed. More... | |
| void | reset_shortest_path_reduced () |
Marks *this as possibly not shortest-path reduced. More... | |
| void | shortest_path_closure_assign () const |
Assigns to this->dbm its shortest-path closure. More... | |
| void | shortest_path_reduction_assign () const |
Assigns to this->dbm its shortest-path closure and records into this->redundancy_dbm which of the entries in this->dbm are redundant. More... | |
| bool | is_shortest_path_reduced () const |
Returns true if and only if this->dbm is shortest-path closed and this->redundancy_dbm correctly flags the redundant entries in this->dbm. More... | |
| void | incremental_shortest_path_closure_assign (Variable var) const |
Incrementally computes shortest-path closure, assuming that only constraints affecting variable var need to be considered. More... | |
| bool | bounds (const Linear_Expression &expr, bool from_above) const |
Checks if and how expr is bounded in *this. More... | |
| bool | max_min (const Linear_Expression &expr, bool maximize, Coefficient &ext_n, Coefficient &ext_d, bool &included, Generator &g) const |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this. More... | |
| bool | max_min (const Linear_Expression &expr, bool maximize, Coefficient &ext_n, Coefficient &ext_d, bool &included) const |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this. More... | |
| bool | BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact (const BD_Shape &y) |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| template<bool integer_upper_bound> | |
| bool | BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact (const BD_Shape &y) |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| void | refine_no_check (const Constraint &c) |
Uses the constraint c to refine *this. More... | |
| void | refine_no_check (const Congruence &cg) |
Uses the congruence cg to refine *this. More... | |
| void | add_dbm_constraint (dimension_type i, dimension_type j, const N &k) |
Adds the constraint dbm[i][j] <= k. More... | |
| void | add_dbm_constraint (dimension_type i, dimension_type j, Coefficient_traits::const_reference numer, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denom) |
Adds the constraint dbm[i][j] <= numer/denom. More... | |
| void | refine (Variable var, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Adds to the BDS the constraint 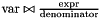 . More... . More... | |
| void | forget_all_dbm_constraints (dimension_type v) |
Removes all the constraints on row/column v. More... | |
| void | forget_binary_dbm_constraints (dimension_type v) |
Removes all binary constraints on row/column v. More... | |
| void | deduce_v_minus_u_bounds (dimension_type v, dimension_type last_v, const Linear_Expression &sc_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference sc_denom, const N &ub_v) |
| An helper function for the computation of affine relations. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | inhomogeneous_affine_form_image (const dimension_type &var_id, const Interval< T, Interval_Info > &b) |
Auxiliary function for affine form image that handle the general case: 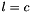 . More... . More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | one_variable_affine_form_image (const dimension_type &var_id, const Interval< T, Interval_Info > &b, const Interval< T, Interval_Info > &w_coeff, const dimension_type &w_id, const dimension_type &space_dim) |
Auxiliary function for affine formimage" that handle the general case: 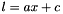 . More... . More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | two_variables_affine_form_image (const dimension_type &var_id, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &lf, const dimension_type &space_dim) |
Auxiliary function for affine form image that handle the general case: 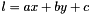 . More... . More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | left_inhomogeneous_refine (const dimension_type &right_t, const dimension_type &right_w_id, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &right) |
Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case: 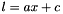 . More... . More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | left_one_var_refine (const dimension_type &left_w_id, const dimension_type &right_t, const dimension_type &right_w_id, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &right) |
Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case: 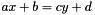 . More... . More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | general_refine (const dimension_type &left_w_id, const dimension_type &right_w_id, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &right) |
| Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case. More... | |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | linear_form_upper_bound (const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &lf, N &result) const |
| void | deduce_u_minus_v_bounds (dimension_type v, dimension_type last_v, const Linear_Expression &sc_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference sc_denom, const N &minus_lb_v) |
| An helper function for the computation of affine relations. More... | |
| void | get_limiting_shape (const Constraint_System &cs, BD_Shape &limiting_shape) const |
Adds to limiting_shape the bounded differences in cs that are satisfied by *this. More... | |
| void | compute_predecessors (std::vector< dimension_type > &predecessor) const |
| Compute the (zero-equivalence classes) predecessor relation. More... | |
| void | compute_leaders (std::vector< dimension_type > &leaders) const |
| Compute the leaders of zero-equivalence classes. More... | |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points_helper (N &elem) |
Private Attributes | |
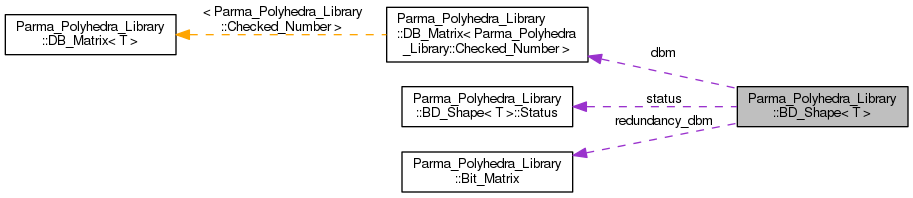
| DB_Matrix< N > | dbm |
| The matrix representing the system of bounded differences. More... | |
| Status | status |
| The status flags to keep track of the internal state. More... | |
| Bit_Matrix | redundancy_dbm |
| A matrix indicating which constraints are redundant. More... | |
Friends | |
| template<typename U > | |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape |
| template<typename Interval > | |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box |
| bool | operator== (const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename U > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< U > &x, const BD_Shape< U > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename U > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< U > &x, const BD_Shape< U > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename U > | |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< U > &x, const BD_Shape< U > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| std::ostream & | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::IO_Operators::operator<< (std::ostream &s, const BD_Shape< T > &c) |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| bool | extract_bounded_difference (const Constraint &c, dimension_type &c_num_vars, dimension_type &c_first_var, dimension_type &c_second_var, Coefficient &c_coeff) |
| void | compute_leader_indices (const std::vector< dimension_type > &predecessor, std::vector< dimension_type > &indices) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const BD_Shape< T > &bds) |
| Output operator. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | swap (BD_Shape< T > &x, BD_Shape< T > &y) |
Swaps x with y. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator== (const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y) |
Returns true if and only if x and y are the same BDS. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator!= (const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y) |
Returns true if and only if x and y are not the same BDS. More... | |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the 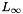 distance between distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir) |
Computes the 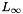 distance between distance between x and y. More... | |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
Computes the 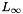 distance between distance between x and y. More... | |
| void | compute_leader_indices (const std::vector< dimension_type > &predecessor, std::vector< dimension_type > &indices) |
| Extracts leader indices from the predecessor relation. More... | |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator== (const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y) |
| template<typename T > | |
| bool | operator!= (const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | rectilinear_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | euclidean_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir, Temp &tmp0, Temp &tmp1, Temp &tmp2) |
| template<typename Temp , typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename To , typename T > | |
| bool | l_infinity_distance_assign (Checked_Number< To, Extended_Number_Policy > &r, const BD_Shape< T > &x, const BD_Shape< T > &y, const Rounding_Dir dir) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | swap (BD_Shape< T > &x, BD_Shape< T > &y) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const BD_Shape< T > &bds) |
Exception Throwers | |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const BD_Shape &y) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, dimension_type required_dim) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const Constraint &c) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const Congruence &cg) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const Generator &g) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *le_name, const Linear_Expression &le) const |
| template<typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *lf_name, const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > &lf) const |
| static void | throw_expression_too_complex (const char *method, const Linear_Expression &le) |
| static void | throw_invalid_argument (const char *method, const char *reason) |
Detailed Description
template<typename T>
class Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >
A bounded difference shape.
The class template BD_Shape<T> allows for the efficient representation of a restricted kind of topologically closed convex polyhedra called bounded difference shapes (BDSs, for short). The name comes from the fact that the closed affine half-spaces that characterize the polyhedron can be expressed by constraints of the form 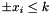 or
or 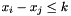 , where the inhomogeneous term
, where the inhomogeneous term 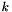 is a rational number.
is a rational number.
Based on the class template type parameter T, a family of extended numbers is built and used to approximate the inhomogeneous term of bounded differences. These extended numbers provide a representation for the value  , as well as rounding-aware implementations for several arithmetic functions. The value of the type parameter
, as well as rounding-aware implementations for several arithmetic functions. The value of the type parameter T may be one of the following:
- a bounded precision integer type (e.g.,
int32_torint64_t); - a bounded precision floating point type (e.g.,
floatordouble); - an unbounded integer or rational type, as provided by GMP (i.e.,
mpz_classormpq_class).
The user interface for BDSs is meant to be as similar as possible to the one developed for the polyhedron class C_Polyhedron.
The domain of BD shapes optimally supports:
- tautological and inconsistent constraints and congruences;
- bounded difference constraints;
- non-proper congruences (i.e., equalities) that are expressible as bounded-difference constraints.
Depending on the method, using a constraint or congruence that is not optimally supported by the domain will either raise an exception or result in a (possibly non-optimal) upward approximation.
A constraint is a bounded difference if it has the form
![\[ a_i x_i - a_j x_j \relsym b \]](form_733.png)
where 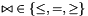 and
and 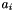 ,
, 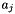 ,
, 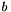 are integer coefficients such that
are integer coefficients such that  , or
, or 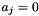 , or
, or 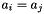 . The user is warned that the above bounded difference Constraint object will be mapped into a correct and optimal approximation that, depending on the expressive power of the chosen template argument
. The user is warned that the above bounded difference Constraint object will be mapped into a correct and optimal approximation that, depending on the expressive power of the chosen template argument T, may loose some precision. Also note that strict constraints are not bounded differences.
For instance, a Constraint object encoding 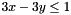 will be approximated by:
will be approximated by:
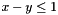 , if
, if Tis a (bounded or unbounded) integer type;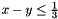 , if
, if Tis the unbounded rational typempq_class;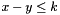 , where
, where 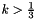 , if
, if Tis a floating point type (having no exact representation for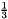 ).
).
On the other hand, depending from the context, a Constraint object encoding 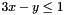 will be either upward approximated (e.g., by safely ignoring it) or it will cause an exception.
will be either upward approximated (e.g., by safely ignoring it) or it will cause an exception.
In the following examples it is assumed that the type argument T is one of the possible instances listed above and that variables x, y and z are defined (where they are used) as follows:
- Example 1
- The following code builds a BDS corresponding to a cube in
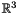 , given as a system of constraints: Since only those constraints having the syntactic form of a bounded difference are optimally supported, the following code will throw an exception (caused by constraints 7, 8 and 9):Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 1);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 1);cs.insert(z >= 0);cs.insert(z <= 1);BD_Shape<T> bd(cs);Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 1);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 1);cs.insert(z >= 0);cs.insert(z <= 1);cs.insert(x + y <= 0); // 7cs.insert(x - z + x >= 0); // 8cs.insert(3*z - y <= 1); // 9BD_Shape<T> bd(cs);
, given as a system of constraints: Since only those constraints having the syntactic form of a bounded difference are optimally supported, the following code will throw an exception (caused by constraints 7, 8 and 9):Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 1);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 1);cs.insert(z >= 0);cs.insert(z <= 1);BD_Shape<T> bd(cs);Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 1);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 1);cs.insert(z >= 0);cs.insert(z <= 1);cs.insert(x + y <= 0); // 7cs.insert(x - z + x >= 0); // 8cs.insert(3*z - y <= 1); // 9BD_Shape<T> bd(cs);
Definition at line 412 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Member Typedef Documentation
| typedef N Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::coefficient_type |
The (extended) numeric type of the inhomogeneous term of the inequalities defining a BDS.
Definition at line 432 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
| typedef T Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::coefficient_type_base |
The numeric base type upon which bounded differences are built.
Definition at line 426 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
|
private |
The (extended) numeric type of the inhomogeneous term of the inequalities defining a BDS.
Definition at line 419 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a universe or empty BDS of the specified space dimension.
- Parameters
-
num_dimensions The number of dimensions of the vector space enclosing the BDS; kind Specifies whether the universe or the empty BDS has to be built.
Definition at line 115 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed().
|
inline |
Ordinary copy constructor.
The complexity argument is ignored.
Definition at line 132 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_reduced(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm.
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a conservative, upward approximation of y.
The complexity argument is ignored.
Definition at line 142 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_zero_dim_univ(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_zero_dim_univ().
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a BDS from the system of constraints cs.
The BDS inherits the space dimension of cs.
- Parameters
-
cs A system of BD constraints.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if cscontains a constraint which is not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 285 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
|
explicit |
Builds a BDS from a system of congruences.
The BDS inherits the space dimension of cgs
- Parameters
-
cgs A system of congruences.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if cgscontains congruences which are not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 50 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_congruences().
|
explicit |
Builds a BDS from the system of generators gs.
Builds the smallest BDS containing the polyhedron defined by gs. The BDS inherits the space dimension of gs.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the system of generators is not empty but has no points.
Definition at line 58 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::throw_invalid_argument(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type().
|
explicit |
Builds a BDS from the polyhedron ph.
Builds a BDS containing ph using algorithms whose complexity does not exceed the one specified by complexity. If complexity is ANY_COMPLEXITY, then the BDS built is the smallest one containing ph.
Definition at line 205 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ANY_COMPLEXITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::constraints_are_minimized(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::constraints_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::evaluate_objective_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generators_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::is_satisfiable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::is_universe(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimizing_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::POLYNOMIAL_COMPLEXITY, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_objective_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_optimization_mode(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::SIMPLEX_COMPLEXITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a BDS out of a box.
The BDS inherits the space dimension of the box. The built BDS is the most precise BDS that includes the box.
- Parameters
-
box The box representing the BDS to be built. complexity This argument is ignored as the algorithm used has polynomial complexity.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if the space dimension of boxexceeds the maximum allowed space dimension.
Definition at line 297 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::space_dimension().
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a BDS out of a grid.
The BDS inherits the space dimension of the grid. The built BDS is the most precise BDS that includes the grid.
- Parameters
-
grid The grid used to build the BDS. complexity This argument is ignored as the algorithm used has polynomial complexity.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if the space dimension of gridexceeds the maximum allowed space dimension.
Definition at line 313 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::minimized_congruences(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_congruences(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::space_dimension().
|
inlineexplicit |
Builds a BDS from an octagonal shape.
The BDS inherits the space dimension of the octagonal shape. The built BDS is the most precise BDS that includes the octagonal shape.
- Parameters
-
os The octagonal shape used to build the BDS. complexity This argument is ignored as the algorithm used has polynomial complexity.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if the space dimension of osexceeds the maximum allowed space dimension.
Definition at line 327 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Member Function Documentation
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_congruence | ( | const Congruence & | cg | ) |
Adds a copy of congruence cg to the system of congruences of *this.
- Parameters
-
cg The congruence to be added.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecgare dimension-incompatible, orcgis not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 490 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_proper_congruence(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_tautological(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Adds to *this constraints equivalent to the congruences in cgs.
- Parameters
-
cgs Contains the congruences that will be added to the system of constraints of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible, orcgscontains a congruence which is not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 180 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::begin(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::end().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_constraint | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the system of bounded differences defining *this.
- Parameters
-
c The constraint to be added.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare dimension-incompatible, orcis not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 414 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign().
|
inline |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of bounded differences defining *this.
- Parameters
-
cs The constraints that will be added.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare dimension-incompatible, orcscontains a constraint which is not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
Definition at line 165 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
|
inlineprivate |
Adds the constraint dbm[i][j] <= k.
Definition at line 698 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inlineprivate |
Adds the constraint dbm[i][j] <= numer/denom.
Definition at line 714 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), and PPL_DIRTY_TEMP.
|
inline |
Adds to *this constraints equivalent to the congruences in cgs.
- Parameters
-
cgs Contains the congruences that will be added to the system of constraints of *this. Its elements may be recycled.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible, orcgscontains a congruence which is not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
- Warning
- The only assumption that can be made on
cgsupon successful or exceptional return is that it can be safely destroyed.
Definition at line 189 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this.
- Parameters
-
cs The constraint system to be added to *this. The constraints incsmay be recycled.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare dimension-incompatible, orcscontains a constraint which is not optimally supported by the BD shape domain.
- Warning
- The only assumption that can be made on
csupon successful or exceptional return is that it can be safely destroyed.
Definition at line 174 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_space_dimensions_and_embed | ( | dimension_type | m | ) |
Adds m new dimensions and embeds the old BDS into the new space.
- Parameters
-
m The number of dimensions to add.
The new dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new BDS, which is defined by a system of bounded differences in which the variables running through the new dimensions are unconstrained. For instance, when starting from the BDS 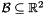 and adding a third dimension, the result will be the BDS
and adding a third dimension, the result will be the BDS
![\[ \bigl\{\, (x, y, z)^\transpose \in \Rset^3 \bigm| (x, y)^\transpose \in \cB \,\bigr\}. \]](form_753.png)
Definition at line 2779 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_space_dimensions_and_project | ( | dimension_type | m | ) |
Adds m new dimensions to the BDS and does not embed it in the new vector space.
- Parameters
-
m The number of dimensions to add.
The new dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new BDS, which is defined by a system of bounded differences in which the variables running through the new dimensions are all constrained to be equal to 0. For instance, when starting from the BDS 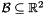 and adding a third dimension, the result will be the BDS
and adding a third dimension, the result will be the BDS
![\[ \bigl\{\, (x, y, 0)^\transpose \in \Rset^3 \bigm| (x, y)^\transpose \in \cB \,\bigr\}. \]](form_754.png)
Definition at line 2808 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
| dimension_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_dimension | ( | ) | const |
Returns 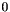 , if
, if *this is empty; otherwise, returns the affine dimension of *this.
Definition at line 330 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_form_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > & | lf | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine form image of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression(s) specified by lf.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is assigned. lf The linear form on intervals with floating point coefficients that defines the affine expression. ALL of its coefficients MUST be bounded.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if lfand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a dimension of*this.
Definition at line 4369 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), and PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine image of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression specified by expr and denominator.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is assigned. expr The numerator of the affine expression. denominator The denominator of the affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a dimension of*this.
Definition at line 4025 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, PPL_UNINITIALIZED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine preimage of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression specified by expr and denominator.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is substituted. expr The numerator of the affine expression. denominator The denominator of the affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a dimension of*this.
Definition at line 5132 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::ascii_dump | ( | ) | const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::ascii_dump | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this.
Definition at line 6848 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::ascii_load | ( | std::istream & | s | ) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise.
Definition at line 6860 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
|
private |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned.
Current implementation is based on a variant of Algorithm 4.1 in A. Bemporad, K. Fukuda, and F. D. Torrisi Convexity Recognition of the Union of Polyhedra Technical Report AUT00-13, ETH Zurich, 2000 tailored to the special case of BD shapes.
- Note
- It is assumed that
*thisandyare dimension-compatible; if the assumption does not hold, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 2194 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimal_value(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::upper_bound_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y, |
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the BHMZ05-widening of *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3245 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::affine_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign().
|
private |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned.
Implementation for the rational (resp., integer) case is based on Theorem 5.2 (resp. Theorem 5.3) of [BHZ09b]. The Boolean template parameter integer_upper_bound allows for choosing between the rational and integer upper bound algorithms.
- Note
- It is assumed that
*thisandyare dimension-compatible; if the assumption does not hold, the behavior is undefined. - The integer case is only enabled if T is an integer data type.
Definition at line 2363 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_closed(), PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::upper_bound_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::bounded_affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | lb_expr, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | ub_expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 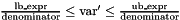 .
.
- Parameters
-
var The variable updated by the affine relation; lb_expr The numerator of the lower bounding affine expression; ub_expr The numerator of the upper bounding affine expression; denominator The (common) denominator for the lower and upper bounding affine expressions (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or iflb_expr(resp.,ub_expr) and*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 5238 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, PPL_UNINITIALIZED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::bounded_affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | lb_expr, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | ub_expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 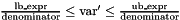 .
.
- Parameters
-
var The variable updated by the affine relation; lb_expr The numerator of the lower bounding affine expression; ub_expr The numerator of the upper bounding affine expression; denominator The (common) denominator for the lower and upper bounding affine expressions (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or iflb_expr(resp.,ub_expr) and*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 5487 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
private |
Checks if and how expr is bounded in *this.
Returns true if and only if from_above is true and expr is bounded from above in *this, or from_above is false and expr is bounded from below in *this.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to test; from_above trueif and only if the boundedness of interest is "from above".
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1202 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from above in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 384 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from below in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 390 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inlinestatic |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle congruences.
Definition at line 279 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inlinestatic |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle constraints.
Definition at line 272 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the CC76-extrapolation between *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 832 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y, |
| Iterator | first, | ||
| Iterator | last, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the CC76-extrapolation between *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.first An iterator referencing the first stop-point. last An iterator referencing one past the last stop-point. tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3062 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_narrowing_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the result of restoring in y the constraints of *this that were lost by CC76-extrapolation applications.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must contain *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
- Note
- As was the case for widening operators, the argument
yis meant to denote the value computed in the previous iteration step, whereas*thisdenotes the value computed in the current iteration step (in the decreasing iteration sequence). Hence, the callx.CC76_narrowing_assign(y)will assign toxthe result of the computation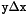 .
.
Definition at line 3357 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
private |
Compute the leaders of zero-equivalence classes.
It is assumed that the BDS is not empty and shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 997 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
Compute the (zero-equivalence classes) predecessor relation.
It is assumed that the BDS is not empty and shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 965 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::concatenate_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the concatenation of *this and y, taken in this order.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if the concatenation would cause the vector space to exceed dimension max_space_dimension().
Definition at line 579 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this.
Definition at line 159 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constrains | ( | Variable | var | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if var is constrained in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if varis not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 936 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| Constraint_System Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constraints | ( | ) | const |
Returns a system of constraints defining *this.
Definition at line 6409 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::zero_dim_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::zero_dim_false().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::H79_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::NNC_Polyhedron(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::time_elapse_assign().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 625 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::strictly_contains().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains_integer_point | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains at least one integer point.
Definition at line 782 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::reset_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
|
private |
An helper function for the computation of affine relations.
For each dbm index u (less than or equal to last_v and different from v), deduce constraints of the form u - v <= c, starting from minus_lb_v which is a lower bound for v.
The shortest-path closure is able to deduce the constraint u - v <= ub_u - lb_v. We can be more precise if variable u played an active role in the computation of the lower bound for v, i.e., if the corresponding coefficient q == sc_expr[u]/sc_denom is greater than zero. In particular:
- if
q >= 1, thenu - v <= lb_u - lb_v; - if
0 < q < 1, thenu - v <= (q*lb_u + (1-q)*ub_u) - lb_v.
Definition at line 3475 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
|
private |
An helper function for the computation of affine relations.
For each dbm index u (less than or equal to last_v and different from v), deduce constraints of the form v - u <= c, starting from ub_v which is an upper bound for v.
The shortest-path closure is able to deduce the constraint v - u <= ub_v - lb_u. We can be more precise if variable u played an active role in the computation of the upper bound for v, i.e., if the corresponding coefficient q == sc_expr[u]/sc_denom is greater than zero. In particular:
- if
q >= 1, thenv - u <= ub_v - ub_u; - if
0 < q < 1, thenv - u <= ub_v - (q*ub_u + (1-q)*lb_u).
Definition at line 3408 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the smallest BD shape containing the set difference of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2470 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::relation_with(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::drop_some_non_integer_points | ( | Complexity_Class | complexity = ANY_COMPLEXITY | ) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates.
- Parameters
-
complexity The maximal complexity of any algorithms used.
- Note
- Currently there is no optimality guarantee, not even if
complexityisANY_COMPLEXITY.
Definition at line 6664 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::drop_some_non_integer_points | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars, |
| Complexity_Class | complexity = ANY_COMPLEXITY |
||
| ) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to vars.
- Parameters
-
vars Points with non-integer coordinates for these variables/space-dimensions can be discarded. complexity The maximal complexity of any algorithms used.
- Note
- Currently there is no optimality guarantee, not even if
complexityisANY_COMPLEXITY.
Definition at line 6686 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
|
inlineprivate |
Definition at line 939 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer(), PPL_USED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::V_EQ.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::expand_space_dimension | ( | Variable | var, |
| dimension_type | m | ||
| ) |
Creates m copies of the space dimension corresponding to var.
- Parameters
-
var The variable corresponding to the space dimension to be replicated; m The number of replicas to be created.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if vardoes not correspond to a dimension of the vector space.std::length_error Thrown if adding mnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
If *this has space dimension 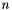 , with
, with  , and
, and var has space dimension  , then the
, then the  -th space dimension is expanded to
-th space dimension is expanded to m new space dimensions 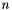 ,
, 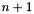 ,
,  ,
, 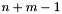 .
.
Definition at line 6574 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::export_interval_constraints | ( | U & | dest | ) | const |
Applies to dest the interval constraints embedded in *this.
- Parameters
-
dest The object to which the constraints will be added.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withdest.
The template type parameter U must provide the following methods.
returns the space dimension of the object.
sets the object to an empty object.
restricts the object by applying the lower bound lb to the space dimension dim and returns false if and only if the object becomes empty.
restricts the object by applying the upper bound ub to the space dimension dim and returns false if and only if the object becomes empty.
Definition at line 4704 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Checked_Number< T, Policy >::raw_value(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN.
| memory_size_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::external_memory_in_bytes | ( | ) | const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this.
Definition at line 6875 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::fold_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars, |
| Variable | dest | ||
| ) |
Folds the space dimensions in vars into dest.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the space dimensions to be folded; dest The variable corresponding to the space dimension that is the destination of the folding operation.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withdestor with one of the Variable objects contained invars. Also thrown ifdestis contained invars.
If *this has space dimension 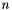 , with
, with 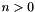 ,
, dest has space dimension 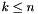 ,
, vars is a set of variables whose maximum space dimension is also less than or equal to 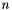 , and
, and dest is not a member of vars, then the space dimensions corresponding to variables in vars are folded into the  -th space dimension.
-th space dimension.
Definition at line 6619 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
|
private |
Removes all the constraints on row/column v.
Definition at line 3544 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
|
private |
Removes all binary constraints on row/column v.
Definition at line 3555 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::frequency | ( | const Linear_Expression & | expr, |
| Coefficient & | freq_n, | ||
| Coefficient & | freq_d, | ||
| Coefficient & | val_n, | ||
| Coefficient & | val_d | ||
| ) | const |
Returns true if and only if there exist a unique value val such that *this saturates the equality expr = val.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression for which the frequency is needed; freq_n If trueis returned, the value is set to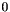 ; Present for interface compatibility with class Grid, where the frequency can have a non-zero value;
; Present for interface compatibility with class Grid, where the frequency can have a non-zero value;freq_d If trueis returned, the value is set to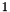 ;
;val_n The numerator of val;val_d The denominator of val;
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If false is returned, then freq_n, freq_d, val_n and val_d are left untouched.
Definition at line 829 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::normalize2(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign().
|
private |
Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case.
Definition at line 4937 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the affine relation 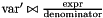 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
var The left hand side variable of the generalized affine transfer function. relsym The relation symbol. expr The numerator of the right hand side affine expression. denominator The denominator of the right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a dimension of*thisor ifrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 5559 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, PPL_UNINITIALIZED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_image | ( | const Linear_Expression & | lhs, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | rhs | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the affine relation 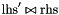 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
lhs The left hand side affine expression. relsym The relation symbol. rhs The right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withlhsorrhsor ifrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 5975 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::have_a_common_variable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the affine relation 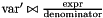 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
var The left hand side variable of the generalized affine transfer function. relsym The relation symbol. expr The numerator of the right hand side affine expression. denominator The denominator of the right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a dimension of*thisor ifrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 6163 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::generalized_affine_preimage | ( | const Linear_Expression & | lhs, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | rhs | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the affine relation 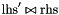 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
lhs The left hand side affine expression. relsym The relation symbol. rhs The right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withlhsorrhsor ifrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 6243 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::have_a_common_variable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Refines the system of BD_Shape constraints defining *this using the constraint expressed by left 
right, where  is the relation symbol specified by
is the relation symbol specified by relsym.
- Parameters
-
left The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is at the left of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. right The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is at the right of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. relsym The relation symbol.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if left(orright) is dimension-incompatible with*this.std::runtime_error Thrown if relsymis not a valid relation symbol.
This function is used in abstract interpretation to model a filter that is generated by a comparison of two expressions that are correctly approximated by left and right respectively.
Definition at line 896 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL.
|
private |
Adds to limiting_shape the bounded differences in cs that are satisfied by *this.
Definition at line 3133 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::reset_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the H79-widening between *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 849 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constraints(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::H79_widening_assign().
|
inline |
Returns a 32-bit hash code for *this.
If x and y are such that x == y, then x.hash_code() == y.hash_code().
Definition at line 889 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::hash_code_from_dimension().
|
private |
Incrementally computes shortest-path closure, assuming that only constraints affecting variable var need to be considered.
- Note
- It is assumed that
*this, which was shortest-path closed, has only been modified by adding constraints affecting variablevar. If this assumption is not satisfied, i.e., if a non-redundant constraint not affecting variablevarhas been added, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 1940 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::min_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
Auxiliary function for affine form image that handle the general case: 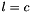 .
.
Definition at line 4443 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::lower(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::upper().
|
inline |
If the integer upper bound of *this and y is exact, it is assigned to *this and true is returned; otherwise false is returned.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
- Note
- The integer upper bound of two rational BDS is the smallest rational BDS containing all the integral points of the two arguments. This method requires that the coefficient type parameter
Tis an integral type.
Definition at line 766 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_integer(), PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::intersection_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the intersection of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3014 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_bounded | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a bounded BDS.
Definition at line 757 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is discrete.
Definition at line 434 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_disjoint_from | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this and y are disjoint.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if xandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 688 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is an empty BDS.
Definition at line 377 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains_integer_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::Pointset_Powerset(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
Returns true if and only if this->dbm is shortest-path closed and this->redundancy_dbm correctly flags the redundant entries in this->dbm.
Definition at line 1017 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is a topologically closed subset of the vector space.
Definition at line 428 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_universe | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a universe BDS.
Definition at line 732 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity().
|
private |
Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case: 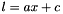 .
.
Definition at line 4746 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
|
private |
Auxiliary function for refine with linear form that handle the general case: 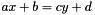 .
.
Definition at line 4785 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_BHMZ05_extrapolation_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Improves the result of the BHMZ05-widening computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened BDS. tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare dimension-incompatible or ifcscontains a strict inequality.
Definition at line 3311 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_CC76_extrapolation_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Improves the result of the CC76-extrapolation computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened BDS. tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare dimension-incompatible or ifcscontains a strict inequality.
Definition at line 3198 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
|
inline |
Improves the result of the H79-widening computation by also enforcing those constraints in cs that are satisfied by all the points of *this.
- Parameters
-
y A BDS that must be contained in *this.cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened BDS. tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 868 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constraints(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::limited_H79_extrapolation_assign().
|
private |
Definition at line 5055 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP.
|
inline |
Swaps *this with y (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible).
Definition at line 362 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::swap().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::map_space_dimensions | ( | const Partial_Function & | pfunc | ) |
Remaps the dimensions of the vector space according to a partial function.
- Parameters
-
pfunc The partial function specifying the destiny of each dimension.
The template type parameter Partial_Function must provide the following methods.
returns true if and only if the represented partial function has an empty co-domain (i.e., it is always undefined). The has_empty_codomain() method will always be called before the methods below. However, if has_empty_codomain() returns true, none of the functions below will be called.
returns the maximum value that belongs to the co-domain of the partial function.
Let  be the represented function and
be the represented function and 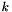 be the value of
be the value of i. If 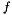 is defined in
is defined in 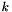 , then
, then 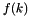 is assigned to
is assigned to j and true is returned. If 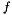 is undefined in
is undefined in 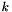 , then
, then false is returned.
The result is undefined if pfunc does not encode a partial function with the properties described in the specification of the mapping operator.
Definition at line 2945 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_or_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::has_empty_codomain(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::maps(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::max_in_codomain(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the BDS is known to be empty.
The return value false does not necessarily implies that *this is non-empty.
Definition at line 61 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_narrowing_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::concatenate_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::euclidean_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_disjoint_from(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_shortest_path_reduced(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::l_infinity_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_BHMZ05_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator==(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::rectilinear_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of bounded differences is known to be shortest-path closed.
The return value false does not necessarily implies that this->dbm is not shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 67 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::get_limiting_shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of bounded differences is known to be shortest-path reduced.
The return value false does not necessarily implies that this->dbm is not shortest-path reduced.
Definition at line 73 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator=().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the BDS is the zero-dimensional universe.
Definition at line 55 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
|
private |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized or minimized subject to this;maximize trueif maximization is what is wanted;ext_n The numerator of the extremum value; ext_d The denominator of the extremum value; included trueif and only if the extremum ofexprcan actually be reached in*this;g When maximization or minimization succeeds, will be assigned a point or closure point where exprreaches the corresponding extremum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded in the appropriate direction, false is returned and ext_n, ext_d, included and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 1351 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::evaluate_objective_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimizing_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
private |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized or minimized subject to this;maximize trueif maximization is what is wanted;ext_n The numerator of the extremum value; ext_d The denominator of the extremum value; included trueif and only if the extremum ofexprcan actually be reached in*this;
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded in the appropriate direction, false is returned and ext_n, ext_d, included and point are left untouched.
Definition at line 1247 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MINIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimal_value(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the maximum space dimension that a BDS can handle.
Definition at line 46 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value is computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized subject to *this;sup_n The numerator of the supremum value; sup_d The denominator of the supremum value; maximum trueif and only if the supremum is also the maximum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from above, false is returned and sup_n, sup_d and maximum are left untouched.
Definition at line 396 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized subject to *this;sup_n The numerator of the supremum value; sup_d The denominator of the supremum value; maximum trueif and only if the supremum is also the maximum value;g When maximization succeeds, will be assigned the point or closure point where exprreaches its supremum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from above, false is returned and sup_n, sup_d, maximum and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 404 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value is computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be minimized subject to *this;inf_n The numerator of the infimum value; inf_d The denominator of the infimum value; minimum trueif and only if the infimum is also the minimum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from below, false is returned and inf_n, inf_d and minimum are left untouched.
Definition at line 412 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be minimized subject to *this;inf_n The numerator of the infimum value; inf_d The denominator of the infimum value; minimum trueif and only if the infimum is also the minimum value;g When minimization succeeds, will be assigned a point or closure point where exprreaches its infimum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from below, false is returned and inf_n, inf_d, minimum and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 420 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| Congruence_System Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::minimized_congruences | ( | ) | const |
Returns a minimal system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this with the same affine dimension as *this.
Definition at line 362 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::zero_dim_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::zero_dim_false().
| Constraint_System Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::minimized_constraints | ( | ) | const |
Returns a minimized system of constraints defining *this.
Definition at line 6489 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::zero_dim_empty(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::zero_dim_false().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this satisfies all its invariants.
Definition at line 6882 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_minus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::reset_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::reset_shortest_path_reduced(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
|
private |
Auxiliary function for affine formimage" that handle the general case: 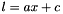 .
.
Definition at line 4467 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::lower(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interval< Boundary, Info >::upper().
|
inline |
The assignment operator (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible).
Definition at line 346 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_reduced(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::status.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::print | ( | ) | const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<.
|
private |
Adds to the BDS the constraint 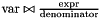 .
.
Note that the coefficient of var in expr is null.
Definition at line 3618 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, PPL_UNINITIALIZED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Refines store with the constraints defining *this.
- Parameters
-
store The interval floating point abstract store to refine.
Definition at line 925 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
|
private |
Uses the constraint c to refine *this.
- Parameters
-
c The constraint to be added. Non BD constraints are ignored.
- Warning
- If
cand*thisare dimension-incompatible, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 518 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::div_round_up(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
inlineprivate |
Uses the congruence cg to refine *this.
- Parameters
-
cg The congruence to be added. Nontrivial proper congruences are ignored. Non BD equalities are ignored.
- Warning
- If
cgand*thisare dimension-incompatible, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 253 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_proper_congruence(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Uses a copy of congruence cg to refine the system of bounded differences of *this.
- Parameters
-
cg The congruence. If it is not a bounded difference equality, it will be ignored.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecgare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 224 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_congruences | ( | const Congruence_System & | cgs | ) |
Uses a copy of the congruences in cgs to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this.
- Parameters
-
cgs The congruence system to be used. Congruences that are not bounded difference equalities are ignored.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 238 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::end(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
|
inline |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this.
- Parameters
-
c The constraint. If it is not a bounded difference, it will be ignored.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 195 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Uses a copy of the constraints in cs to refine the system of bounded differences defining *this.
- Parameters
-
cs The constraint system to be used. Constraints that are not bounded differences are ignored.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 209 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::refine_with_linear_form_inequality | ( | const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > & | left, |
| const Linear_Form< Interval< T, Interval_Info > > & | right | ||
| ) |
Refines the system of BD_Shape constraints defining *this using the constraint expressed by left 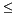
right.
- Parameters
-
left The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is at the left of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. right The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is at the right of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if left(orright) is dimension-incompatible with*this.
This function is used in abstract interpretation to model a filter that is generated by a comparison of two expressions that are correctly approximated by left and right respectively.
Definition at line 4605 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
| Poly_Con_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::relation_with | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the constraint c.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1494 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape_Helpers::extract_bounded_difference(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_disjoint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_nonstrict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::saturates(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::strictly_intersects().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign().
| Poly_Con_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::relation_with | ( | const Congruence & | cg | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the congruence cg.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecgare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1399 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_disjoint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::modulus(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::saturates(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::strictly_intersects().
| Poly_Gen_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::relation_with | ( | const Generator & | g | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between *this and the generator g.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand generatorgare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1764 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::nothing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::subsumes().
|
inline |
Removes the higher dimensions so that the resulting space will have dimension new_dimension.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if new_dimensionis greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 780 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::remove_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars | ) |
Removes all the specified dimensions.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the dimensions to be removed.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible with one of the Variable objects contained invars.
Definition at line 2857 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_or_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
|
inlineprivate |
Marks *this as possibly not shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 103 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains_integer_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::get_limiting_shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Marks *this as possibly not shortest-path reduced.
Definition at line 109 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK().
|
inlineprivate |
Turns *this into an empty BDS.
Definition at line 85 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Marks *this as shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 91 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Marks *this as shortest-path closed.
Definition at line 97 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Turns *this into an zero-dimensional universe BDS.
Definition at line 79 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::Status::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
Assigns to this->dbm its shortest-path closure.
Definition at line 1880 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::min_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_narrowing_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::euclidean_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_disjoint_from(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_shortest_path_reduced(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::l_infinity_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator==(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::rectilinear_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign().
|
private |
Assigns to this->dbm its shortest-path closure and records into this->redundancy_dbm which of the entries in this->dbm are redundant.
Definition at line 2052 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::clear(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::clear(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_shortest_path_reduced(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this a meet-preserving simplification of *this with respect to y. If false is returned, then the intersection is empty.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2544 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::compute_leaders(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::incremental_shortest_path_closure_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_shortest_path_closed(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::redundancy_dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::reset_shortest_path_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_UP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::set_zero_dim_univ(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
|
inline |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.
Definition at line 371 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_narrowing_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::concatenate_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::euclidean_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::integer_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_disjoint_from(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::l_infinity_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_BHMZ05_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator==(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::rectilinear_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::throw_dimension_incompatible(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::time_elapse_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign_if_exact().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this strictly contains y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 745 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains().
|
private |
Definition at line 6975 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
private |
Definition at line 6986 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
|
private |
Definition at line 6997 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
private |
Definition at line 7008 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
|
private |
Definition at line 7019 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension().
|
private |
Definition at line 7042 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
private |
Definition at line 7056 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 7030 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 7070 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape().
|
inline |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the time-elapse between *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 728 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::time_elapse_assign().
|
inline |
Assigns to *this its topological closure.
Definition at line 440 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
inline |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this.
Definition at line 883 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::external_memory_in_bytes().
|
private |
Auxiliary function for affine form image that handle the general case: 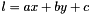 .
.
Definition at line 4563 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::negate(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::unconstrain | ( | Variable | var | ) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to space dimension var, assigning the result to *this.
- Parameters
-
var The space dimension that will be unconstrained.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if varis not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 3566 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::unconstrain | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars | ) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to the set of space dimensions vars, assigning the result to *this.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of space dimension that will be unconstrained.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible with one of the Variable objects contained invars.
Definition at line 3588 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign | ( | const BD_Shape< T > & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the smallest BDS containing the union of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2152 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::difference_assign().
|
inline |
If the upper bound of *this and y is exact, it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 752 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Same as H79_widening_assign(y, tp).
Definition at line 862 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::wrap_assign | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars, |
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Width | w, | ||
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Representation | r, | ||
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Overflow | o, | ||
| const Constraint_System * | cs_p = 0, |
||
| unsigned | complexity_threshold = 16, |
||
| bool | wrap_individually = true |
||
| ) |
Wraps the specified dimensions of the vector space.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the space dimensions to be wrapped. w The width of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. r The representation of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. o The overflow behavior of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. cs_p Possibly null pointer to a constraint system whose variables are contained in vars. If*cs_pdepends on variables not invars, the behavior is undefined. When non-null, the pointed-to constraint system is assumed to represent the conditional or looping construct guard with respect to which wrapping is performed. Since wrapping requires the computation of upper bounds and due to non-distributivity of constraint refinement over upper bounds, passing a constraint system in this way can be more precise than refining the result of the wrapping operation with the constraints in*cs_p.complexity_threshold A precision parameter of the wrapping operator: higher values result in possibly improved precision. wrap_individually trueif the dimensions should be wrapped individually (something that results in much greater efficiency to the detriment of precision).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *cs_pis dimension-incompatible withvars, or if*thisis dimension-incompatiblevarsor with*cs_p.
Definition at line 817 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::wrap_assign().
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Definition at line 85 of file BD_Shape.cc.
|
related |
Extracts leader indices from the predecessor relation.
|
related |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y.
If the euclidean distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<To, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y.
If the euclidean distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<Temp, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the euclidean distance between x and y.
If the euclidean distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using the temporary variables tmp0, tmp1 and tmp2.
|
related |
Definition at line 560 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
related |
Definition at line 606 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References PPL_DIRTY_TEMP.
|
related |
Definition at line 620 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
related |
Definition at line 33 of file BD_Shape.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::first_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::get(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
related |
Computes the 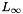 distance between
distance between x and y.
If the 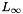 distance between
distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<To, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the  distance between
distance between x and y.
If the  distance between
distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<Temp, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the  distance between
distance between x and y.
If the  distance between
distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using the temporary variables tmp0, tmp1 and tmp2.
|
related |
Definition at line 630 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
related |
Definition at line 675 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References PPL_DIRTY_TEMP.
|
related |
Definition at line 689 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Returns true if and only if x and y are not the same BDS.
Note that x and y may be dimension-incompatible shapes: in this case, the value true is returned.
Definition at line 483 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
|
related |
Output operator.
Writes a textual representation of bds on s: false is written if bds is an empty polyhedron; true is written if bds is the universe polyhedron; a system of constraints defining bds is written otherwise, all constraints separated by ", ".
|
related |
Definition at line 6730 of file BD_Shape_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_additive_inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_plus_infinity(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn().
Returns true if and only if x and y are the same BDS.
Note that x and y may be dimension-incompatible shapes: in this case, the value false is returned.
Definition at line 446 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
Definition at line 1936 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Definition at line 1937 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
|
friend |
|
friend |
|
friend |
|
friend |
|
related |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y.
If the rectilinear distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<To, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y.
If the rectilinear distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using variables of type Checked_Number<Temp, Extended_Number_Policy>.
|
related |
Computes the rectilinear (or Manhattan) distance between x and y.
If the rectilinear distance between x and y is defined, stores an approximation of it into r and returns true; returns false otherwise.
The direction of the approximation is specified by dir.
All computations are performed using the temporary variables tmp0, tmp1 and tmp2.
|
related |
Definition at line 490 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::dbm, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PLUS_INFINITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::space_dimension().
|
related |
Definition at line 536 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References PPL_DIRTY_TEMP.
|
related |
Definition at line 550 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
Definition at line 951 of file BD_Shape_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::m_swap().
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
The matrix representing the system of bounded differences.
Definition at line 1940 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_extrapolation_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::CC76_narrowing_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::concatenate_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::contains_integer_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::euclidean_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::get_limiting_shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_disjoint_from(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::is_shortest_path_reduced(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::l_infinity_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator=(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator==(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::rectilinear_distance_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_closure_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::upper_bound_assign().
|
private |
A matrix indicating which constraints are redundant.
Definition at line 1950 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BFT00_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHMZ05_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BHZ09_upper_bound_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator=(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::shortest_path_reduction_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
The status flags to keep track of the internal state.
Definition at line 1947 of file BD_Shape_defs.hh.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::m_swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::operator=().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
