The base class for convex polyhedra. More...
#include <Polyhedron_defs.hh>
Classes | |
| class | Status |
| A conjunctive assertion about a polyhedron. More... | |
Public Types | |
| typedef Coefficient | coefficient_type |
| The numeric type of coefficients. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| template<typename Input > | |
| Input & | check_obj_space_dimension_overflow (Input &input, const Topology topol, const char *method, const char *reason) |
Member Functions that Do Not Modify the Polyhedron | |
| dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this. More... | |
| dimension_type | affine_dimension () const |
Returns 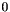 , if , if *this is empty; otherwise, returns the affine dimension of *this. More... | |
| const Constraint_System & | constraints () const |
| Returns the system of constraints. More... | |
| const Constraint_System & | minimized_constraints () const |
| Returns the system of constraints, with no redundant constraint. More... | |
| const Generator_System & | generators () const |
| Returns the system of generators. More... | |
| const Generator_System & | minimized_generators () const |
| Returns the system of generators, with no redundant generator. More... | |
| Congruence_System | congruences () const |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this. More... | |
| Congruence_System | minimized_congruences () const |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this, with no redundant congruences and having the same affine dimension as *this. More... | |
| Poly_Con_Relation | relation_with (const Constraint &c) const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the constraint c. More... | |
| Poly_Gen_Relation | relation_with (const Generator &g) const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the generator g. More... | |
| Poly_Con_Relation | relation_with (const Congruence &cg) const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the congruence c. More... | |
| bool | is_empty () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is an empty polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | is_universe () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a universe polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | is_topologically_closed () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a topologically closed subset of the vector space. More... | |
| bool | is_disjoint_from (const Polyhedron &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this and y are disjoint. More... | |
| bool | is_discrete () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is discrete. More... | |
| bool | is_bounded () const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a bounded polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | contains_integer_point () const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains at least one integer point. More... | |
| bool | constrains (Variable var) const |
Returns true if and only if var is constrained in *this. More... | |
| bool | bounds_from_above (const Linear_Expression &expr) const |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from above in *this. More... | |
| bool | bounds_from_below (const Linear_Expression &expr) const |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from below in *this. More... | |
| bool | maximize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &sup_n, Coefficient &sup_d, bool &maximum) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value is computed. More... | |
| bool | maximize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &sup_n, Coefficient &sup_d, bool &maximum, Generator &g) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed. More... | |
| bool | minimize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &inf_n, Coefficient &inf_d, bool &minimum) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value is computed. More... | |
| bool | minimize (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &inf_n, Coefficient &inf_d, bool &minimum, Generator &g) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed. More... | |
| bool | frequency (const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient &freq_n, Coefficient &freq_d, Coefficient &val_n, Coefficient &val_d) const |
Returns true if and only if there exist a unique value val such that *this saturates the equality expr = val. More... | |
| bool | contains (const Polyhedron &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains y. More... | |
| bool | strictly_contains (const Polyhedron &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this strictly contains y. More... | |
| bool | OK (bool check_not_empty=false) const |
| Checks if all the invariants are satisfied. More... | |
Space Dimension Preserving Member Functions that May Modify the Polyhedron | |
| void | add_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_generator (const Generator &g) |
Adds a copy of generator g to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_congruence (const Congruence &cg) |
Adds a copy of congruence cg to *this, if cg can be exactly represented by a polyhedron. More... | |
| void | add_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_recycled_constraints (Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_generators (const Generator_System &gs) |
Adds a copy of the generators in gs to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_recycled_generators (Generator_System &gs) |
Adds the generators in gs to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result). More... | |
| void | add_congruences (const Congruence_System &cgs) |
Adds a copy of the congruences in cgs to *this, if all the congruences can be exactly represented by a polyhedron. More... | |
| void | add_recycled_congruences (Congruence_System &cgs) |
Adds the congruences in cgs to *this, if all the congruences can be exactly represented by a polyhedron. More... | |
| void | refine_with_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_congruence (const Congruence &cg) |
Uses a copy of congruence cg to refine *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Uses a copy of the constraints in cs to refine *this. More... | |
| void | refine_with_congruences (const Congruence_System &cgs) |
Uses a copy of the congruences in cgs to refine *this. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | refine_with_linear_form_inequality (const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &right, bool is_strict=false) |
Refines *this with the constraint expressed by left  right if is_strict is set, with the constraint left 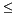 right otherwise. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | generalized_refine_with_linear_form_inequality (const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &left, const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &right, Relation_Symbol relsym) |
Refines *this with the constraint expressed by left 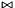 right, where 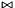 is the relation symbol specified by is the relation symbol specified by relsym.. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | refine_fp_interval_abstract_store (Box< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &store) const |
Refines store with the constraints defining *this. More... | |
| void | unconstrain (Variable var) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to space dimension var, assigning the result to *this. More... | |
| void | unconstrain (const Variables_Set &vars) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to the set of space dimensions vars, assigning the result to *this. More... | |
| void | intersection_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this the intersection of *this and y. More... | |
| void | poly_hull_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this the poly-hull of *this and y. More... | |
| void | upper_bound_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
| Same as poly_hull_assign(y). More... | |
| void | poly_difference_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this the poly-difference of *this and y. More... | |
| void | difference_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
| Same as poly_difference_assign(y). More... | |
| bool | simplify_using_context_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this a meet-preserving simplification of *this with respect to y. If false is returned, then the intersection is empty. More... | |
| void | affine_image (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the affine image of *this under the function mapping variable var to the affine expression specified by expr and denominator. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | affine_form_image (Variable var, const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &lf) |
| void | affine_preimage (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the affine preimage of *this under the function mapping variable var to the affine expression specified by expr and denominator. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_image (Variable var, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 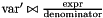 , where , where 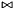 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_preimage (Variable var, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 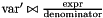 , where , where 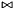 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_image (const Linear_Expression &lhs, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &rhs) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 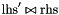 , where , where 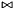 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | generalized_affine_preimage (const Linear_Expression &lhs, Relation_Symbol relsym, const Linear_Expression &rhs) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 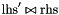 , where , where 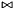 is the relation symbol encoded by is the relation symbol encoded by relsym. More... | |
| void | bounded_affine_image (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &lb_expr, const Linear_Expression &ub_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 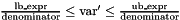 . More... . More... | |
| void | bounded_affine_preimage (Variable var, const Linear_Expression &lb_expr, const Linear_Expression &ub_expr, Coefficient_traits::const_reference denominator=Coefficient_one()) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 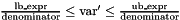 . More... . More... | |
| void | time_elapse_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the time-elapse between *this and y. More... | |
| void | positive_time_elapse_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this (the best approximation of) the result of computing the positive time-elapse between *this and y. More... | |
| void | wrap_assign (const Variables_Set &vars, Bounded_Integer_Type_Width w, Bounded_Integer_Type_Representation r, Bounded_Integer_Type_Overflow o, const Constraint_System *cs_p=0, unsigned complexity_threshold=16, bool wrap_individually=true) |
| Wraps the specified dimensions of the vector space. More... | |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points (Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates. More... | |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points (const Variables_Set &vars, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to vars. More... | |
| void | topological_closure_assign () |
Assigns to *this its topological closure. More... | |
| void | BHRZ03_widening_assign (const Polyhedron &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the BHRZ03-widening between *this and y. More... | |
| void | limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign (const Polyhedron &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the limited extrapolation between *this and y using the BHRZ03-widening operator. More... | |
| void | bounded_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign (const Polyhedron &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the bounded extrapolation between *this and y using the BHRZ03-widening operator. More... | |
| void | H79_widening_assign (const Polyhedron &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the H79_widening between *this and y. More... | |
| void | widening_assign (const Polyhedron &y, unsigned *tp=0) |
| Same as H79_widening_assign(y, tp). More... | |
| void | limited_H79_extrapolation_assign (const Polyhedron &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the limited extrapolation between *this and y using the H79-widening operator. More... | |
| void | bounded_H79_extrapolation_assign (const Polyhedron &y, const Constraint_System &cs, unsigned *tp=0) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the bounded extrapolation between *this and y using the H79-widening operator. More... | |
Member Functions that May Modify the Dimension of the Vector Space | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_embed (dimension_type m) |
Adds m new space dimensions and embeds the old polyhedron in the new vector space. More... | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_project (dimension_type m) |
Adds m new space dimensions to the polyhedron and does not embed it in the new vector space. More... | |
| void | concatenate_assign (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assigns to *this the concatenation of *this and y, taken in this order. More... | |
| void | remove_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &vars) |
| Removes all the specified dimensions from the vector space. More... | |
| void | remove_higher_space_dimensions (dimension_type new_dimension) |
Removes the higher dimensions of the vector space so that the resulting space will have dimension new_dimension. More... | |
| template<typename Partial_Function > | |
| void | map_space_dimensions (const Partial_Function &pfunc) |
| Remaps the dimensions of the vector space according to a partial function. More... | |
| void | expand_space_dimension (Variable var, dimension_type m) |
Creates m copies of the space dimension corresponding to var. More... | |
| void | fold_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &vars, Variable dest) |
Folds the space dimensions in vars into dest. More... | |
Miscellaneous Member Functions | |
| ~Polyhedron () | |
| Destructor. More... | |
| void | m_swap (Polyhedron &y) |
Swaps *this with polyhedron y. (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible.) More... | |
| void | ascii_dump () const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump (std::ostream &s) const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | print () const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<. More... | |
| bool | ascii_load (std::istream &s) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise. More... | |
| memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this. More... | |
| memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this. More... | |
| int32_t | hash_code () const |
Returns a 32-bit hash code for *this. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static dimension_type | max_space_dimension () |
| Returns the maximum space dimension all kinds of Polyhedron can handle. More... | |
| static bool | can_recycle_constraint_systems () |
Returns true indicating that this domain has methods that can recycle constraints. More... | |
| static void | initialize () |
| Initializes the class. More... | |
| static void | finalize () |
| Finalizes the class. More... | |
| static bool | can_recycle_congruence_systems () |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle congruences. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, dimension_type num_dimensions, Degenerate_Element kind) | |
| Builds a polyhedron having the specified properties. More... | |
| Polyhedron (const Polyhedron &y, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Ordinary copy constructor. More... | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, const Constraint_System &cs) | |
| Builds a polyhedron from a system of constraints. More... | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, Constraint_System &cs, Recycle_Input dummy) | |
| Builds a polyhedron recycling a system of constraints. More... | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, const Generator_System &gs) | |
| Builds a polyhedron from a system of generators. More... | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, Generator_System &gs, Recycle_Input dummy) | |
| Builds a polyhedron recycling a system of generators. More... | |
| template<typename Interval > | |
| Polyhedron (Topology topol, const Box< Interval > &box, Complexity_Class complexity=ANY_COMPLEXITY) | |
| Builds a polyhedron from a box. More... | |
| Polyhedron & | operator= (const Polyhedron &y) |
The assignment operator. (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible.) More... | |
| bool | BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact (const Polyhedron &y) |
If the poly-hull of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| bool | BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact (const Polyhedron &y) |
| bool | BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact (const Polyhedron &y) |
| bool | BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact (const Polyhedron &y) |
| void | drop_some_non_integer_points (const Variables_Set *vars_p, Complexity_Class complexity) |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to *vars_p. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| void | overapproximate_linear_form (const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &lf, const dimension_type lf_dimension, Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &result) |
| Helper function that overapproximates an interval linear form. More... | |
| void | positive_time_elapse_assign_impl (const Polyhedron &y) |
Assuming *this is NNC, assigns to *this the result of the "positive time-elapse" between *this and y. More... | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| static void | convert_to_integer_expression (const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &lf, const dimension_type lf_dimension, Linear_Expression &result) |
Helper function that makes result become a Linear_Expression obtained by normalizing the denominators in lf. More... | |
| template<typename FP_Format , typename Interval_Info > | |
| static void | convert_to_integer_expressions (const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > &lf, const dimension_type lf_dimension, Linear_Expression &res, Coefficient &res_low_coeff, Coefficient &res_hi_coeff, Coefficient &denominator) |
| Normalization helper function. More... | |
| template<typename Linear_System1 , typename Row2 > | |
| static bool | add_to_system_and_check_independence (Linear_System1 &eq_sys, const Row2 &eq) |
Private Types | |
| enum | Three_Valued_Boolean { TVB_TRUE, TVB_FALSE, TVB_DONT_KNOW } |
Private Member Functions | |
| Topology | topology () const |
| Returns the topological kind of the polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | is_necessarily_closed () const |
Returns true if and only if the polyhedron is necessarily closed. More... | |
| void | refine_no_check (const Constraint &c) |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine the system of constraints of *this. More... | |
| Three_Valued_Boolean | quick_equivalence_test (const Polyhedron &y) const |
| Polynomial but incomplete equivalence test between polyhedra. More... | |
| bool | is_included_in (const Polyhedron &y) const |
Returns true if and only if *this is included in y. More... | |
| bool | bounds (const Linear_Expression &expr, bool from_above) const |
Checks if and how expr is bounded in *this. More... | |
| bool | max_min (const Linear_Expression &expr, bool maximize, Coefficient &ext_n, Coefficient &ext_d, bool &included, Generator &g) const |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this. More... | |
Private Verifiers: Verify if Individual Flags are Set | |
| bool | marked_empty () const |
Returns true if the polyhedron is known to be empty. More... | |
| bool | constraints_are_up_to_date () const |
Returns true if the system of constraints is up-to-date. More... | |
| bool | generators_are_up_to_date () const |
Returns true if the system of generators is up-to-date. More... | |
| bool | constraints_are_minimized () const |
Returns true if the system of constraints is minimized. More... | |
| bool | generators_are_minimized () const |
Returns true if the system of generators is minimized. More... | |
| bool | has_pending_constraints () const |
Returns true if there are pending constraints. More... | |
| bool | has_pending_generators () const |
Returns true if there are pending generators. More... | |
| bool | has_something_pending () const |
Returns true if there are either pending constraints or pending generators. More... | |
| bool | can_have_something_pending () const |
Returns true if the polyhedron can have something pending. More... | |
| bool | sat_c_is_up_to_date () const |
Returns true if the saturation matrix sat_c is up-to-date. More... | |
| bool | sat_g_is_up_to_date () const |
Returns true if the saturation matrix sat_g is up-to-date. More... | |
State Flag Setters: Set Only the Specified Flags | |
| void | set_zero_dim_univ () |
Sets status to express that the polyhedron is the universe 0-dimension vector space, clearing all corresponding matrices. More... | |
| void | set_empty () |
Sets status to express that the polyhedron is empty, clearing all corresponding matrices. More... | |
| void | set_constraints_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that constraints are up-to-date. More... | |
| void | set_generators_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that generators are up-to-date. More... | |
| void | set_constraints_minimized () |
Sets status to express that constraints are minimized. More... | |
| void | set_generators_minimized () |
Sets status to express that generators are minimized. More... | |
| void | set_constraints_pending () |
Sets status to express that constraints are pending. More... | |
| void | set_generators_pending () |
Sets status to express that generators are pending. More... | |
| void | set_sat_c_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that sat_c is up-to-date. More... | |
| void | set_sat_g_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that sat_g is up-to-date. More... | |
State Flag Cleaners: Clear Only the Specified Flag | |
| void | clear_empty () |
Clears the status flag indicating that the polyhedron is empty. More... | |
| void | clear_constraints_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that constraints are no longer up-to-date. More... | |
| void | clear_generators_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that generators are no longer up-to-date. More... | |
| void | clear_constraints_minimized () |
Sets status to express that constraints are no longer minimized. More... | |
| void | clear_generators_minimized () |
Sets status to express that generators are no longer minimized. More... | |
| void | clear_pending_constraints () |
Sets status to express that there are no longer pending constraints. More... | |
| void | clear_pending_generators () |
Sets status to express that there are no longer pending generators. More... | |
| void | clear_sat_c_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that sat_c is no longer up-to-date. More... | |
| void | clear_sat_g_up_to_date () |
Sets status to express that sat_g is no longer up-to-date. More... | |
The Handling of Pending Rows | |
| bool | process_pending () const |
| Processes the pending rows of either description of the polyhedron and obtains a minimized polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | process_pending_constraints () const |
| Processes the pending constraints and obtains a minimized polyhedron. More... | |
| void | process_pending_generators () const |
| Processes the pending generators and obtains a minimized polyhedron. More... | |
| void | remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints () const |
| Lazily integrates the pending descriptions of the polyhedron to obtain a constraint system without pending rows. More... | |
| bool | remove_pending_to_obtain_generators () const |
| Lazily integrates the pending descriptions of the polyhedron to obtain a generator system without pending rows. More... | |
Updating and Sorting Matrices | |
| void | update_constraints () const |
| Updates constraints starting from generators and minimizes them. More... | |
| bool | update_generators () const |
| Updates generators starting from constraints and minimizes them. More... | |
| void | update_sat_c () const |
Updates sat_c using the updated constraints and generators. More... | |
| void | update_sat_g () const |
Updates sat_g using the updated constraints and generators. More... | |
| void | obtain_sorted_constraints () const |
| Sorts the matrix of constraints keeping status consistency. More... | |
| void | obtain_sorted_generators () const |
| Sorts the matrix of generators keeping status consistency. More... | |
| void | obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c () const |
Sorts the matrix of constraints and updates sat_c. More... | |
| void | obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g () const |
Sorts the matrix of generators and updates sat_g. More... | |
Weak and Strong Minimization of Descriptions | |
| bool | minimize () const |
| Applies (weak) minimization to both the constraints and generators. More... | |
| bool | strongly_minimize_constraints () const |
| Applies strong minimization to the constraints of an NNC polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | strongly_minimize_generators () const |
| Applies strong minimization to the generators of an NNC polyhedron. More... | |
| Constraint_System | simplified_constraints () const |
| If constraints are up-to-date, obtain a simplified copy of them. More... | |
Static Private Member Functions | |
| template<typename Linear_System1 , typename Linear_System2 > | |
| static void | add_space_dimensions (Linear_System1 &sys1, Linear_System2 &sys2, Bit_Matrix &sat1, Bit_Matrix &sat2, dimension_type add_dim) |
| Adds new space dimensions to the given linear systems. More... | |
Minimization-Related Static Member Functions | |
| template<typename Source_Linear_System , typename Dest_Linear_System > | |
| static bool | minimize (bool con_to_gen, Source_Linear_System &source, Dest_Linear_System &dest, Bit_Matrix &sat) |
| Builds and simplifies constraints from generators (or vice versa). More... | |
| template<typename Source_Linear_System1 , typename Source_Linear_System2 , typename Dest_Linear_System > | |
| static bool | add_and_minimize (bool con_to_gen, Source_Linear_System1 &source1, Dest_Linear_System &dest, Bit_Matrix &sat, const Source_Linear_System2 &source2) |
| Adds given constraints and builds minimized corresponding generators or vice versa. More... | |
| template<typename Source_Linear_System , typename Dest_Linear_System > | |
| static bool | add_and_minimize (bool con_to_gen, Source_Linear_System &source, Dest_Linear_System &dest, Bit_Matrix &sat) |
Adds given constraints and builds minimized corresponding generators or vice versa. The given constraints are in source. More... | |
| template<typename Source_Linear_System , typename Dest_Linear_System > | |
| static dimension_type | conversion (Source_Linear_System &source, dimension_type start, Dest_Linear_System &dest, Bit_Matrix &sat, dimension_type num_lines_or_equalities) |
| Performs the conversion from constraints to generators and vice versa. More... | |
| template<typename Linear_System1 > | |
| static dimension_type | simplify (Linear_System1 &sys, Bit_Matrix &sat) |
Uses Gauss' elimination method to simplify the result of conversion(). More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| Constraint_System | con_sys |
| The system of constraints. More... | |
| Generator_System | gen_sys |
| The system of generators. More... | |
| Bit_Matrix | sat_c |
| The saturation matrix having constraints on its columns. More... | |
| Bit_Matrix | sat_g |
| The saturation matrix having generators on its columns. More... | |
| Status | status |
| The status flags to keep track of the polyhedron's internal state. More... | |
| dimension_type | space_dim |
| The number of dimensions of the enclosing vector space. More... | |
Static Private Attributes | |
| static const Representation | default_con_sys_repr = DENSE |
| static const Representation | default_gen_sys_repr = DENSE |
| static dimension_type * | simplify_num_saturators_p = 0 |
| Pointer to an array used by simplify(). More... | |
| static size_t | simplify_num_saturators_size = 0 |
| Dimension of an array used by simplify(). More... | |
Friends | |
| template<typename Interval > | |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box |
| template<typename T > | |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape |
| template<typename T > | |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate |
| class | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate |
| bool | operator== (const Polyhedron &x, const Polyhedron &y) |
| bool | Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interfaces::is_necessarily_closed_for_interfaces (const Polyhedron &) |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| template<typename PH > | |
| bool | poly_hull_assign_if_exact (PH &p, const PH &q) |
If the poly-hull of p and q is exact it is assigned to p and true is returned, otherwise false is returned. More... | |
| template<typename PH > | |
| bool | poly_hull_assign_if_exact (PH &p, const PH &q) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const Polyhedron &ph) |
| Output operator. More... | |
| void | swap (Polyhedron &x, Polyhedron &y) |
Swaps x with y. More... | |
| bool | operator== (const Polyhedron &x, const Polyhedron &y) |
Returns true if and only if x and y are the same polyhedron. More... | |
| bool | operator!= (const Polyhedron &x, const Polyhedron &y) |
Returns true if and only if x and y are different polyhedra. More... | |
| void | swap (Polyhedron &x, Polyhedron &y) |
| bool | operator!= (const Polyhedron &x, const Polyhedron &y) |
| bool | operator== (const Polyhedron &x, const Polyhedron &y) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const Polyhedron &ph) |
Widening- and Extrapolation-Related Functions | |
| void | select_CH78_constraints (const Polyhedron &y, Constraint_System &cs_selection) const |
Copies to cs_selection the constraints of y corresponding to the definition of the CH78-widening of *this and y. More... | |
| void | select_H79_constraints (const Polyhedron &y, Constraint_System &cs_selected, Constraint_System &cs_not_selected) const |
Splits the constraints of `x' into two subsets, depending on whether or not they are selected to compute the H79-widening of *this and y. More... | |
| bool | BHRZ03_combining_constraints (const Polyhedron &y, const BHRZ03_Certificate &y_cert, const Polyhedron &H79, const Constraint_System &x_minus_H79_cs) |
| bool | BHRZ03_evolving_points (const Polyhedron &y, const BHRZ03_Certificate &y_cert, const Polyhedron &H79) |
| bool | BHRZ03_evolving_rays (const Polyhedron &y, const BHRZ03_Certificate &y_cert, const Polyhedron &H79) |
| static void | modify_according_to_evolution (Linear_Expression &ray, const Linear_Expression &x, const Linear_Expression &y) |
Exception Throwers | |
| void | throw_invalid_argument (const char *method, const char *reason) const |
| void | throw_topology_incompatible (const char *method, const char *ph_name, const Polyhedron &ph) const |
| void | throw_topology_incompatible (const char *method, const char *c_name, const Constraint &c) const |
| void | throw_topology_incompatible (const char *method, const char *g_name, const Generator &g) const |
| void | throw_topology_incompatible (const char *method, const char *cs_name, const Constraint_System &cs) const |
| void | throw_topology_incompatible (const char *method, const char *gs_name, const Generator_System &gs) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *other_name, dimension_type other_dim) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *ph_name, const Polyhedron &ph) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *le_name, const Linear_Expression &le) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *c_name, const Constraint &c) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *g_name, const Generator &g) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *cg_name, const Congruence &cg) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *cs_name, const Constraint_System &cs) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *gs_name, const Generator_System &gs) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *cgs_name, const Congruence_System &cgs) const |
| template<typename C > | |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *lf_name, const Linear_Form< C > &lf) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, const char *var_name, Variable var) const |
| void | throw_dimension_incompatible (const char *method, dimension_type required_space_dim) const |
| void | throw_invalid_generator (const char *method, const char *g_name) const |
| void | throw_invalid_generators (const char *method, const char *gs_name) const |
| static dimension_type | check_space_dimension_overflow (dimension_type dim, dimension_type max, const Topology topol, const char *method, const char *reason) |
| static dimension_type | check_space_dimension_overflow (dimension_type dim, const Topology topol, const char *method, const char *reason) |
| template<typename Object > | |
| static Object & | check_obj_space_dimension_overflow (Object &input, Topology topol, const char *method, const char *reason) |
Detailed Description
The base class for convex polyhedra.
An object of the class Polyhedron represents a convex polyhedron in the vector space 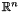 .
.
A polyhedron can be specified as either a finite system of constraints or a finite system of generators (see Section Representations of Convex Polyhedra) and it is always possible to obtain either representation. That is, if we know the system of constraints, we can obtain from this the system of generators that define the same polyhedron and vice versa. These systems can contain redundant members: in this case we say that they are not in the minimal form.
Two key attributes of any polyhedron are its topological kind (recording whether it is a C_Polyhedron or an NNC_Polyhedron object) and its space dimension (the dimension 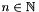 of the enclosing vector space):
of the enclosing vector space):
- all polyhedra, the empty ones included, are endowed with a specific topology and space dimension;
- most operations working on a polyhedron and another object (i.e., another polyhedron, a constraint or generator, a set of variables, etc.) will throw an exception if the polyhedron and the object are not both topology-compatible and dimension-compatible (see Section Representations of Convex Polyhedra);
- the topology of a polyhedron cannot be changed; rather, there are constructors for each of the two derived classes that will build a new polyhedron with the topology of that class from another polyhedron from either class and any topology;
- the only ways in which the space dimension of a polyhedron can be changed are:
- explicit calls to operators provided for that purpose;
- standard copy, assignment and swap operators.
Note that four different polyhedra can be defined on the zero-dimension space: the empty polyhedron, either closed or NNC, and the universe polyhedron 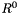 , again either closed or NNC.
, again either closed or NNC.
- In all the examples it is assumed that variables
xandyare defined (where they are used) as follows:Variable x(0);Variable y(1);
- Example 1
- The following code builds a polyhedron corresponding to a square in
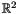 , given as a system of constraints: The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from a system of generators specifying the four vertices of the square:Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 3);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 3);C_Polyhedron ph(cs);Generator_System gs;gs.insert(point(0*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(0*x + 3*y));gs.insert(point(3*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(3*x + 3*y));C_Polyhedron ph(gs);
, given as a system of constraints: The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from a system of generators specifying the four vertices of the square:Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x <= 3);cs.insert(y >= 0);cs.insert(y <= 3);C_Polyhedron ph(cs);Generator_System gs;gs.insert(point(0*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(0*x + 3*y));gs.insert(point(3*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(3*x + 3*y));C_Polyhedron ph(gs);
- Example 2
- The following code builds an unbounded polyhedron corresponding to a half-strip in
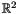 , given as a system of constraints: The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from the system of generators specifying the two vertices of the polyhedron and one ray:Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x - y <= 0);cs.insert(x - y + 1 >= 0);C_Polyhedron ph(cs);Generator_System gs;gs.insert(point(0*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(0*x + y));gs.insert(ray(x - y));C_Polyhedron ph(gs);
, given as a system of constraints: The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from the system of generators specifying the two vertices of the polyhedron and one ray:Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(x >= 0);cs.insert(x - y <= 0);cs.insert(x - y + 1 >= 0);C_Polyhedron ph(cs);Generator_System gs;gs.insert(point(0*x + 0*y));gs.insert(point(0*x + y));gs.insert(ray(x - y));C_Polyhedron ph(gs);
- Example 3
- The following code builds the polyhedron corresponding to a half-plane by adding a single constraint to the universe polyhedron in
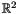 : The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from the empty polyhedron in the spaceC_Polyhedron ph(2);ph.add_constraint(y >= 0);
: The following code builds the same polyhedron as above, but starting from the empty polyhedron in the spaceC_Polyhedron ph(2);ph.add_constraint(y >= 0);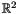 and inserting the appropriate generators (a point, a ray and a line). Note that, although the above polyhedron has no vertices, we must add one point, because otherwise the result of the Minkowski's sum would be an empty polyhedron. To avoid subtle errors related to the minimization process, it is required that the first generator inserted in an empty polyhedron is a point (otherwise, an exception is thrown).C_Polyhedron ph(2, EMPTY);ph.add_generator(point(0*x + 0*y));ph.add_generator(ray(y));ph.add_generator(line(x));
and inserting the appropriate generators (a point, a ray and a line). Note that, although the above polyhedron has no vertices, we must add one point, because otherwise the result of the Minkowski's sum would be an empty polyhedron. To avoid subtle errors related to the minimization process, it is required that the first generator inserted in an empty polyhedron is a point (otherwise, an exception is thrown).C_Polyhedron ph(2, EMPTY);ph.add_generator(point(0*x + 0*y));ph.add_generator(ray(y));ph.add_generator(line(x));
- Example 4
- The following code shows the use of the function
add_space_dimensions_and_embed:We build the universe polyhedron in the 1-dimension spaceC_Polyhedron ph(1);ph.add_constraint(x == 2);ph.add_space_dimensions_and_embed(1);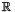 . Then we add a single equality constraint, thus obtaining the polyhedron corresponding to the singleton set
. Then we add a single equality constraint, thus obtaining the polyhedron corresponding to the singleton set 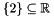 . After the last line of code, the resulting polyhedron is
. After the last line of code, the resulting polyhedron is ![\[ \bigl\{\, (2, y)^\transpose \in \Rset^2 \bigm| y \in \Rset \,\bigr\}. \]](form_695.png)
- Example 5
- The following code shows the use of the function
add_space_dimensions_and_project:The first two lines of code are the same as in Example 4 forC_Polyhedron ph(1);ph.add_constraint(x == 2);ph.add_space_dimensions_and_project(1);add_space_dimensions_and_embed. After the last line of code, the resulting polyhedron is the singleton set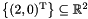 .
.
- Example 6
- The following code shows the use of the function
affine_image:In this example the starting polyhedron is a square inC_Polyhedron ph(2, EMPTY);ph.add_generator(point(0*x + 0*y));ph.add_generator(point(0*x + 3*y));ph.add_generator(point(3*x + 0*y));ph.add_generator(point(3*x + 3*y));Linear_Expression expr = x + 4;ph.affine_image(x, expr);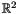 , the considered variable is
, the considered variable is 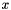 and the affine expression is
and the affine expression is 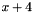 . The resulting polyhedron is the same square translated to the right. Moreover, if the affine transformation for the same variable
. The resulting polyhedron is the same square translated to the right. Moreover, if the affine transformation for the same variable xis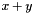 : the resulting polyhedron is a parallelogram with the height equal to the side of the square and the oblique sides parallel to the lineLinear_Expression expr = x + y;
: the resulting polyhedron is a parallelogram with the height equal to the side of the square and the oblique sides parallel to the lineLinear_Expression expr = x + y; . Instead, if we do not use an invertible transformation for the same variable; for example, the affine expression
. Instead, if we do not use an invertible transformation for the same variable; for example, the affine expression 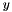 : the resulting polyhedron is a diagonal of the square.Linear_Expression expr = y;
: the resulting polyhedron is a diagonal of the square.Linear_Expression expr = y;
- Example 7
- The following code shows the use of the function
affine_preimage:In this example the starting polyhedron,C_Polyhedron ph(2);ph.add_constraint(x >= 0);ph.add_constraint(x <= 3);ph.add_constraint(y >= 0);ph.add_constraint(y <= 3);Linear_Expression expr = x + 4;ph.affine_preimage(x, expr);varand the affine expression and the denominator are the same as in Example 6, while the resulting polyhedron is again the same square, but translated to the left. Moreover, if the affine transformation forxis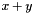 the resulting polyhedron is a parallelogram with the height equal to the side of the square and the oblique sides parallel to the lineLinear_Expression expr = x + y;
the resulting polyhedron is a parallelogram with the height equal to the side of the square and the oblique sides parallel to the lineLinear_Expression expr = x + y;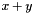 . Instead, if we do not use an invertible transformation for the same variable
. Instead, if we do not use an invertible transformation for the same variable x, for example, the affine expression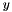 : the resulting polyhedron is a line that corresponds to theLinear_Expression expr = y;
: the resulting polyhedron is a line that corresponds to theLinear_Expression expr = y;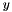 axis.
axis.
- Example 8
- For this example we use also the variables: The following code shows the use of the functionVariable z(2);Variable w(3);
remove_space_dimensions:The starting polyhedron is the singleton setGenerator_System gs;gs.insert(point(3*x + y + 0*z + 2*w));C_Polyhedron ph(gs);Variables_Set vars;vars.insert(y);vars.insert(z);ph.remove_space_dimensions(vars);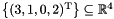 , while the resulting polyhedron is
, while the resulting polyhedron is 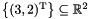 . Be careful when removing space dimensions incrementally: since dimensions are automatically renamed after each application of the
. Be careful when removing space dimensions incrementally: since dimensions are automatically renamed after each application of the remove_space_dimensionsoperator, unexpected results can be obtained. For instance, by using the following code we would obtain a different result:In this case, the result is the polyhedronset<Variable> vars1;vars1.insert(y);ph.remove_space_dimensions(vars1);set<Variable> vars2;vars2.insert(z);ph.remove_space_dimensions(vars2);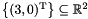 : when removing the set of dimensions
: when removing the set of dimensions vars2we are actually removing variable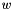 of the original polyhedron. For the same reason, the operator
of the original polyhedron. For the same reason, the operator remove_space_dimensionsis not idempotent: removing twice the same non-empty set of dimensions is never the same as removing them just once.
Definition at line 369 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Member Typedef Documentation
The numeric type of coefficients.
Definition at line 372 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron having the specified properties.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; num_dimensions The number of dimensions of the vector space enclosing the polyhedron; kind Specifies whether the universe or the empty polyhedron has to be built.
Definition at line 52 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::add_low_level_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, max_space_dimension(), OK(), set_constraints_minimized(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_empty(), space_dim, and status.
Referenced by affine_form_image().
|
protected |
Ordinary copy constructor.
The complexity argument is ignored.
Definition at line 74 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::assign_with_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::assign_with_pending(), con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), and topology().
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron from a system of constraints.
The polyhedron inherits the space dimension of the constraint system.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; cs The system of constraints defining the polyhedron.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the topology of csis incompatible withtopol.
Definition at line 95 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::add_low_level_constraints(), con_sys, max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_pending_rows(), OK(), set_constraints_up_to_date(), set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_sorted(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::unset_pending_rows().
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron recycling a system of constraints.
The polyhedron inherits the space dimension of the constraint system.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; cs The system of constraints defining the polyhedron. It is not declared constbecause its data-structures may be recycled to build the polyhedron.dummy A dummy tag to syntactically differentiate this one from the other constructors.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the topology of csis incompatible withtopol.
Definition at line 145 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::add_low_level_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), con_sys, max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_pending_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), OK(), set_constraints_up_to_date(), set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_sorted(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), swap(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::unset_pending_rows().
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron from a system of generators.
The polyhedron inherits the space dimension of the generator system.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; gs The system of generators defining the polyhedron.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the topology of gsis incompatible withtopol, or if the system of generators is not empty but has no points.
Definition at line 195 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::add_corresponding_closure_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_points(), max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_pending_rows(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_empty(), set_generators_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::set_sorted(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::space_dimension(), status, swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), throw_invalid_generators(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows().
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron recycling a system of generators.
The polyhedron inherits the space dimension of the generator system.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; gs The system of generators defining the polyhedron. It is not declared constbecause its data-structures may be recycled to build the polyhedron.dummy A dummy tag to syntactically differentiate this one from the other constructors.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the topology of gsis incompatible withtopol, or if the system of generators is not empty but has no points.
Definition at line 261 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::add_corresponding_closure_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_points(), max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_pending_rows(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_empty(), set_generators_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::set_sorted(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::space_dimension(), status, swap(), throw_invalid_generators(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows().
|
protected |
Builds a polyhedron from a box.
This will use an algorithm whose complexity is polynomial and build the smallest polyhedron with topology topol containing box.
- Parameters
-
topol The topology of the polyhedron; box The box representing the polyhedron to be built; complexity This argument is ignored.
Definition at line 39 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::add_low_level_constraints(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::has_lower_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::has_upper_bound(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, OK(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, set_constraints_up_to_date(), set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_space_dimension(), set_zero_dim_univ(), space_dim, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Member Function Documentation
|
staticprivate |
Adds given constraints and builds minimized corresponding generators or vice versa.
- Returns
trueif the obtained polyhedron is empty,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
con_to_gen trueifsource1andsource2are system of constraints,falseotherwise;source1 The first element of the given DD pair; dest The second element of the given DD pair; sat The saturation matrix that bind source1todest;source2 The new system of generators or constraints.
It is assumed that source1 and source2 are sorted and have no pending rows. It is also assumed that dest has no pending rows. On entry, the rows of sat are indexed by the rows of dest and its columns are indexed by the rows of source1. On exit, the rows of sat are indexed by the rows of dest and its columns are indexed by the rows of the system obtained by merging source1 and source2.
Let us suppose we want to add some constraints to a given system of constraints source1. This method, given a minimized double description pair (source1, dest) and a system of new constraints source2, modifies source1 by adding to it the constraints of source2 that are not in source1. Then, by invoking add_and_minimize(bool, Linear_System_Class&, Linear_System_Class&, Bit_Matrix&), processes the added constraints obtaining a new DD pair.
This method treats also the dual case, i.e., adding new generators to a previous system of generators. In this case source1 contains the old generators, source2 the new ones and dest is the system of constraints in the given minimized DD pair.
Since source2 contains the constraints (or the generators) that will be added to source1, it is constant: it will not be modified.
Definition at line 267 of file Polyhedron_minimize_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::cmp(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::compare().
|
staticprivate |
Adds given constraints and builds minimized corresponding generators or vice versa. The given constraints are in source.
- Returns
trueif the obtained polyhedron is empty,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
con_to_gen trueifsourceis a system of constraints,falseotherwise;source The first element of the given DD pair. It also contains the pending rows to be processed; dest The second element of the given DD pair. It cannot have pending rows; sat The saturation matrix that bind the upper part of sourcetodest.
On entry, the rows of sat are indexed by the rows of dest and its columns are indexed by the non-pending rows of source. On exit, the rows of sat are indexed by the rows of dest and its columns are indexed by the rows of source.
Let us suppose that source is a system of constraints. This method assumes that the non-pending part of source and system dest form a double description pair in minimal form and will build a new DD pair in minimal form by processing the pending constraints in source. To this end, it will call conversion()) and simplify.
This method treats also the dual case, i.e., processing pending generators. In this case source contains generators and dest is the system of constraints corresponding to the non-pending part of source.
Definition at line 372 of file Polyhedron_minimize_templates.hh.
References conversion(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::resize(), and simplify().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_congruence | ( | const Congruence & | cg | ) |
Adds a copy of congruence cg to *this, if cg can be exactly represented by a polyhedron.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecgare dimension-incompatible, of ifcgis a proper congruence which is neither a tautology, nor a contradiction.
Definition at line 1329 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_proper_congruence(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_congruences | ( | const Congruence_System & | cgs | ) |
Adds a copy of the congruences in cgs to *this, if all the congruences can be exactly represented by a polyhedron.
- Parameters
-
cgs The congruences to be added.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible, of if there exists incgsa proper congruence which is neither a tautology, nor a contradiction.
Definition at line 1707 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_proper_congruence(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by add_recycled_congruences(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::NNC_Polyhedron().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_constraint | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Parameters
-
c The constraint that will be added to the system of constraints of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1301 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::affine_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::linear_partition_aux().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_constraints | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Parameters
-
cs Contains the constraints that will be added to the system of constraints of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1602 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::NNC_Polyhedron(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_generator | ( | const Generator & | g | ) |
Adds a copy of generator g to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand generatorgare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible, or if*thisis an empty polyhedron andgis not a point.
Definition at line 1369 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type().
Referenced by BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_generators | ( | const Generator_System & | gs | ) |
Adds a copy of the generators in gs to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Parameters
-
gs Contains the generators that will be added to the system of generators of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandgsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible, or if*thisis empty and the system of generatorsgsis not empty, but has no points.
Definition at line 1700 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
|
inline |
Adds the congruences in cgs to *this, if all the congruences can be exactly represented by a polyhedron.
- Parameters
-
cgs The congruences to be added. Its elements may be recycled.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible, of if there exists incgsa proper congruence which is neither a tautology, nor a contradiction
- Warning
- The only assumption that can be made on
cgsupon successful or exceptional return is that it can be safely destroyed.
Definition at line 377 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References add_congruences().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_recycled_constraints | ( | Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Adds the constraints in cs to the system of constraints of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Parameters
-
cs The constraint system to be added to *this. The constraints incsmay be recycled.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
- Warning
- The only assumption that can be made on
csupon successful or exceptional return is that it can be safely destroyed.
Definition at line 1522 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
Referenced by BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), H79_widening_assign(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_recycled_generators | ( | Generator_System & | gs | ) |
Adds the generators in gs to the system of generators of *this (without minimizing the result).
- Parameters
-
gs The generator system to be added to *this. The generators ingsmay be recycled.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandgsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible, or if*thisis empty and the system of generatorsgsis not empty, but has no points.
- Warning
- The only assumption that can be made on
gsupon successful or exceptional return is that it can be safely destroyed.
Definition at line 1609 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::add_corresponding_closure_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::clear(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_closure_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sys.
Referenced by BHRZ03_evolving_points(), and BHRZ03_evolving_rays().
|
staticprivate |
Adds new space dimensions to the given linear systems.
- Parameters
-
sys1 The linear system to which columns are added; sys2 The linear system to which rows and columns are added; sat1 The saturation matrix whose columns are indexed by the rows of sys1. On entry it is up-to-date;sat2 The saturation matrix whose columns are indexed by the rows of sys2;add_dim The number of space dimensions to add.
Adds new space dimensions to the vector space modifying the linear systems and saturation matrices. This function is invoked only by add_space_dimensions_and_embed() and add_space_dimensions_and_project(), passing the linear system of constraints and that of generators (and the corresponding saturation matrices) in different order (see those methods for details).
Definition at line 32 of file Polyhedron_chdims_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::num_columns(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::resize(), swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_space_dimensions_and_embed | ( | dimension_type | m | ) |
Adds m new space dimensions and embeds the old polyhedron in the new vector space.
- Parameters
-
m The number of dimensions to add.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if adding mnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
The new space dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new polyhedron, which is characterized by a system of constraints in which the variables running through the new dimensions are not constrained. For instance, when starting from the polyhedron 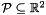 and adding a third space dimension, the result will be the polyhedron
and adding a third space dimension, the result will be the polyhedron
![\[ \bigl\{\, (x, y, z)^\transpose \in \Rset^3 \bigm| (x, y)^\transpose \in \cP \,\bigr\}. \]](form_729.png)
Definition at line 35 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References add_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::add_universe_rows_and_space_dimensions(), check_space_dimension_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::clear(), con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), max_space_dimension(), OK(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_space_dimension(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), space_dimension(), status, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_zero_dim_univ(), topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE, and update_sat_c().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::add_space_dimensions_and_project | ( | dimension_type | m | ) |
Adds m new space dimensions to the polyhedron and does not embed it in the new vector space.
- Parameters
-
m The number of space dimensions to add.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if adding mnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
The new space dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new polyhedron, which is characterized by a system of constraints in which the variables running through the new dimensions are all constrained to be equal to 0. For instance, when starting from the polyhedron 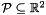 and adding a third space dimension, the result will be the polyhedron
and adding a third space dimension, the result will be the polyhedron
![\[ \bigl\{\, (x, y, 0)^\transpose \in \Rset^3 \bigm| (x, y)^\transpose \in \cP \,\bigr\}. \]](form_730.png)
Definition at line 107 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_space_dimension_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::zero_dim_closure_point(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::zero_dim_point().
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 2135 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
| PPL::dimension_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_dimension | ( | ) | const |
Returns 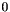 , if
, if *this is empty; otherwise, returns the affine dimension of *this.
Definition at line 61 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::affine_dimension(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), and is_discrete().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_form_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > & | lf | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine form image of *this under the function mapping variable var into the affine expression(s) specified by lf.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is assigned. lf The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that defines the affine expression(s). ALL of its coefficients MUST be bounded.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if lfand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
This function is used in abstract interpretation to model an assignment of a value that is correctly overapproximated by lf to the floating point variable represented by var.
Definition at line 372 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References bounded_affine_image(), convert_to_integer_expressions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), marked_empty(), overapproximate_linear_form(), Polyhedron(), PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, space_dim, throw_dimension_incompatible(), topology(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine image of *this under the function mapping variable var to the affine expression specified by expr and denominator.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is assigned; expr The numerator of the affine expression; denominator The denominator of the affine expression (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
When considering the generators of a polyhedron, the affine transformation
![\[ \frac{\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} a_i x_i + b}{\mathrm{denominator}} \]](form_704.png)
is assigned to var where expr is 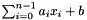 (
( 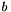 is the inhomogeneous term).
is the inhomogeneous term).
If constraints are up-to-date, it uses the specialized function affine_preimage() (for the system of constraints) and inverse transformation to reach the same result. To obtain the inverse transformation we use the following observation.
Observation:
- The affine transformation is invertible if the coefficient of
varin this transformation (i.e.,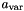 ) is different from zero.
) is different from zero. - If the transformation is invertible, then we can write
so that the inverse transformation is![\[ \mathrm{denominator} * {x'}_\mathrm{var} = \sum_{i = 0}^{n - 1} a_i x_i + b = a_\mathrm{var} x_\mathrm{var} + \sum_{i \neq var} a_i x_i + b, \]](form_707.png)
![\[ a_\mathrm{var} x_\mathrm{var} = \mathrm{denominator} * {x'}_\mathrm{var} - \sum_{i \neq j} a_i x_i - b. \]](form_708.png)
Then, if the transformation is invertible, all the entities that were up-to-date remain up-to-date. Otherwise only generators remain up-to-date.
In other words, if  is a
is a  matrix representing the rays of the polyhedron,
matrix representing the rays of the polyhedron, 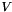 is a
is a 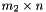 matrix representing the points of the polyhedron and
matrix representing the points of the polyhedron and
![\[ P = \bigl\{\, \vect{x} = (x_0, \ldots, x_{n-1})^\mathrm{T} \bigm| \vect{x} = \vect{\lambda} R + \vect{\mu} V, \vect{\lambda} \in \Rset^{m_1}_+, \vect{\mu} \in \Rset^{m_2}_+, \sum_{i = 0}^{m_2 - 1} \mu_i = 1 \,\bigr\} \]](form_719.png)
and 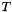 is the affine transformation to apply to
is the affine transformation to apply to 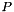 , then the resulting polyhedron is
, then the resulting polyhedron is
![\[ P' = \bigl\{\, (x_0, \ldots, T(x_0, \ldots, x_{n-1}), \ldots, x_{n-1})^\mathrm{T} \bigm| (x_0, \ldots, x_{n-1})^\mathrm{T} \in P \,\bigr\}. \]](form_721.png)
Affine transformations are, for example:
- translations
- rotations
- symmetries.
Definition at line 2745 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
Referenced by fold_space_dimensions().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the affine preimage of *this under the function mapping variable var to the affine expression specified by expr and denominator.
- Parameters
-
var The variable to which the affine expression is substituted; expr The numerator of the affine expression; denominator The denominator of the affine expression (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
When considering constraints of a polyhedron, the affine transformation
![\[ \frac{\sum_{i=0}^{n-1} a_i x_i + b}{denominator}, \]](form_722.png)
is assigned to var where expr is 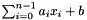 (
(  is the inhomogeneous term).
is the inhomogeneous term).
If generators are up-to-date, then the specialized function affine_image() is used (for the system of generators) and inverse transformation to reach the same result. To obtain the inverse transformation, we use the following observation.
Observation:
- The affine transformation is invertible if the coefficient of
varin this transformation (i.e. ) is different from zero.
) is different from zero. - If the transformation is invertible, then we can write
, the inverse transformation is![\[ \mathrm{denominator} * {x'}_\mathrm{var} = \sum_{i = 0}^{n - 1} a_i x_i + b = a_\mathrm{var} x_\mathrm{var} + \sum_{i \neq \mathrm{var}} a_i x_i + b, \]](form_723.png)
.![\[ a_\mathrm{var} x_\mathrm{var} = \mathrm{denominator} * {x'}_\mathrm{var} - \sum_{i \neq j} a_i x_i - b. \]](form_708.png)
Then, if the transformation is invertible, all the entities that were up-to-date remain up-to-date. Otherwise only constraints remain up-to-date.
In other words, if  is a
is a 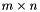 matrix representing the constraints of the polyhedron,
matrix representing the constraints of the polyhedron, 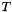 is the affine transformation to apply to
is the affine transformation to apply to 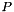 and
and
![\[ P = \bigl\{\, \vect{x} = (x_0, \ldots, x_{n-1})^\mathrm{T} \bigm| A\vect{x} \geq \vect{0} \,\bigr\}. \]](form_724.png)
The resulting polyhedron is
![\[ P' = \bigl\{\, \vect{x} = (x_0, \ldots, x_{n-1}))^\mathrm{T} \bigm| A'\vect{x} \geq \vect{0} \,\bigr\}, \]](form_725.png)
where 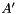 is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:
![\[ {a'}_{ij} = \begin{cases} a_{ij} * \mathrm{denominator} + a_{i\mathrm{var}}*\mathrm{expr}[j] \quad \mathrm{for } j \neq \mathrm{var}; \\ \mathrm{expr}[\mathrm{var}] * a_{i\mathrm{var}}, \quad \text{for } j = \mathrm{var}. \end{cases} \]](form_726.png)
Definition at line 2833 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::inverse(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::ascii_dump | ( | ) | const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::ascii_dump | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this.
Definition at line 3965 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::ascii_load | ( | std::istream & | s | ) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise.
Definition at line 3988 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
|
protected |
If the poly-hull of *this and y is exact it is assigned to *this and true is returned, otherwise false is returned.
Current implementation is based on (a variant of) Algorithm 8.1 in A. Bemporad, K. Fukuda, and F. D. Torrisi Convexity Recognition of the Union of Polyhedra Technical Report AUT00-13, ETH Zurich, 2000
- Note
- It is assumed that
*thisandyare topologically closed and dimension-compatible; if the assumption does not hold, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 2024 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_equality(), is_necessarily_closed(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::nothing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), relation_with(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::set_is_ray_or_point_or_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::sign_normalize(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::subsumes(), topology(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::upper_bound_assign().
|
private |
Definition at line 399 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::clear(), con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), contains(), gen_sys, generators_are_minimized(), has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::is_stabilizing(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), OK(), relation_with(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::strictly_intersects(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::topology(), and topology().
Referenced by BHRZ03_widening_assign().
|
private |
Definition at line 531 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::compare(), constraints_are_minimized(), contains(), gen_sys, generators_are_minimized(), has_something_pending(), intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::is_stabilizing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::linear_combine(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::nothing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), OK(), relation_with(), space_dim, and topology().
Referenced by BHRZ03_widening_assign().
|
private |
Definition at line 679 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_generators(), constraints_are_minimized(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, gen_sys, generators_are_minimized(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_no_rows(), has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::is_stabilizing(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::nothing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), OK(), relation_with(), space_dim, and topology().
Referenced by BHRZ03_widening_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::BHRZ03_widening_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the BHRZ03-widening between *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 744 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::is_stabilizing(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), minimize(), OK(), select_H79_constraints(), space_dim, topology(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
Referenced by limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign().
|
protected |
Definition at line 1540 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References affine_dimension(), con_sys, gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), is_included_in(), is_necessarily_closed(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), relation_with(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set_until(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::subsumes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::union_assign(), and update_sat_g().
Referenced by BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact().
|
protected |
Definition at line 1654 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References add_constraint(), add_generator(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::clear(), con_sys, constraints(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::difference_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::first(), gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::intersection_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_disjoint(), is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::next(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::reduced_sign(), relation_with(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set_until(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::subsumes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::union_assign(), and update_sat_g().
Referenced by BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact().
|
protected |
Definition at line 1505 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), is_empty(), is_necessarily_closed(), marked_empty(), space_dim, topology(), and upper_bound_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::bounded_affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | lb_expr, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | ub_expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 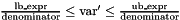 .
.
- Parameters
-
var The variable updated by the affine relation; lb_expr The numerator of the lower bounding affine expression; ub_expr The numerator of the upper bounding affine expression; denominator The (common) denominator for the lower and upper bounding affine expressions (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or iflb_expr(resp.,ub_expr) and*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 2919 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
Referenced by affine_form_image().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::bounded_affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| const Linear_Expression & | lb_expr, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | ub_expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the bounded affine relation 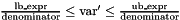 .
.
- Parameters
-
var The variable updated by the affine relation; lb_expr The numerator of the lower bounding affine expression; ub_expr The numerator of the upper bounding affine expression; denominator The (common) denominator for the lower and upper bounding affine expressions (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or iflb_expr(resp.,ub_expr) and*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 3004 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::bounded_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the bounded extrapolation between *this and y using the BHRZ03-widening operator.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened polyhedron; tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 928 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ANY_COMPLEXITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::CC76_widening_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::constraints().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::bounded_H79_extrapolation_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the bounded extrapolation between *this and y using the H79-widening operator.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened polyhedron; tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 386 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ANY_COMPLEXITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::CC76_widening_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::constraints().
|
private |
Checks if and how expr is bounded in *this.
Returns true if and only if from_above is true and expr is bounded from above in *this, or from_above is false and expr is bounded from below in *this.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to test; from_above trueif and only if the boundedness of interest is "from above".
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 569 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::homogeneous_sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_ray(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
Referenced by bounds_from_above(), and bounds_from_below().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from above in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 314 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References bounds().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if expr is bounded from below in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 319 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References bounds().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the polyhedron can have something pending.
Definition at line 180 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References constraints_are_minimized(), generators_are_minimized(), sat_c_is_up_to_date(), and sat_g_is_up_to_date().
Referenced by intersection_assign(), poly_hull_assign(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inlinestatic |
Returns false indicating that this domain cannot recycle congruences.
Definition at line 125 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
|
inlinestatic |
Returns true indicating that this domain has methods that can recycle constraints.
Definition at line 120 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
| Input& Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::check_obj_space_dimension_overflow | ( | Input & | input, |
| const Topology | topol, | ||
| const char * | method, | ||
| const char * | reason | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 599 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References check_space_dimension_overflow(), and max_space_dimension().
|
staticprotected |
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 2717 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_space_dimension_overflow(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), and check_obj_space_dimension_overflow().
|
staticprotected |
Definition at line 2728 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_space_dimension_overflow(), and max_space_dimension().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that constraints are no longer minimized.
Definition at line 248 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_c_minimized(), and status.
Referenced by clear_constraints_up_to_date(), intersection_assign(), and remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that constraints are no longer up-to-date.
This also implies that they are neither minimized and both saturation matrices are no longer meaningful.
Definition at line 280 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References clear_constraints_minimized(), clear_pending_constraints(), clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_c_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by poly_hull_assign(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), strongly_minimize_generators(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Clears the status flag indicating that the polyhedron is empty.
Definition at line 243 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_empty(), and status.
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that generators are no longer minimized.
Definition at line 253 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_g_minimized(), and status.
Referenced by clear_generators_up_to_date(), poly_hull_assign(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that generators are no longer up-to-date.
This also implies that they are neither minimized and both saturation matrices are no longer meaningful.
Definition at line 290 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References clear_generators_minimized(), clear_pending_generators(), clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_g_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by intersection_assign(), remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints(), and strongly_minimize_constraints().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that there are no longer pending constraints.
Definition at line 258 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_c_pending(), and status.
Referenced by clear_constraints_up_to_date(), process_pending_constraints(), and remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that there are no longer pending generators.
Definition at line 263 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_g_pending(), and status.
Referenced by clear_generators_up_to_date(), process_pending_generators(), and remove_pending_to_obtain_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that sat_c is no longer up-to-date.
Definition at line 268 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_sat_c_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_generators_up_to_date(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), and update_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that sat_g is no longer up-to-date.
Definition at line 274 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::reset_sat_g_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_generators_up_to_date(), obtain_sorted_generators(), process_pending_constraints(), and update_constraints().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::concatenate_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the concatenation of *this and y, taken in this order.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible.std::length_error Thrown if the concatenation would cause the vector space to exceed dimension max_space_dimension().
Definition at line 184 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_space_dimension_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::clear(), constraints(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sys, and topology().
|
inline |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this.
Definition at line 367 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References minimized_constraints().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::constrains | ( | Variable | var | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if var is constrained in *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if varis not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 729 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| const PPL::Constraint_System & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::constraints | ( | ) | const |
Returns the system of constraints.
Definition at line 78 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::zero_dim_empty().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), concatenate_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::NNC_Polyhedron(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), and poly_difference_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of constraints is minimized.
Note that only weak minimization is entailed, so that an NNC polyhedron may still have  -redundant constraints.
-redundant constraints.
Definition at line 145 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_c_minimized().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), can_have_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), is_included_in(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), quick_equivalence_test(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), simplified_constraints(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of constraints is up-to-date.
Definition at line 135 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_c_up_to_date().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), simplified_constraints(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::contains | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3927 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References is_empty(), is_included_in(), marked_empty(), quick_equivalence_test(), space_dim, topology(), and TVB_TRUE.
Referenced by BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::check_containment(), H79_widening_assign(), poly_difference_assign(), poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), and strictly_contains().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::contains_integer_point | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this contains at least one integer point.
Definition at line 598 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::gcd(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::gcd_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_canonical(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_DOWN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::STRICT_INEQUALITY, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::type().
|
staticprivate |
Performs the conversion from constraints to generators and vice versa.
- Returns
- The number of lines of the polyhedron or the number of equality constraints in the result of conversion.
- Parameters
-
source The system to use to convert dest:it may be modified;start The index of sourcerow from which conversion begin;dest The result of the conversion; sat The saturation matrix telling us, for each row in source, which are the rows ofdestthat satisfy but do not saturate it;num_lines_or_equalities The number of rows in the system destthat are either lines of the polyhedron (whendestis a system of generators) or equality constraints (whendestis a system of constraints).
For simplicity, all the following comments assume we are converting a constraint system source to a generator system dest; the comments for the symmetric case can be obtained by duality.
If some of the constraints in source are redundant, they will be removed. This is why the source is not declared to be a constant parameter.
If start is 0, then source is a sorted system; also, dest is a generator system corresponding to an empty constraint system. If otherwise start is greater than 0, then the two sub-systems of source made by the non-pending rows and the pending rows, respectively, are both sorted; also, dest is the generator system corresponding to the non-pending constraints of source.
Independently from the value of start, dest has lines from index 0 to index num_lines_or_equalities - 1 and rays/points from index num_lines_or_equalities to the last of its rows.
Note that here the rows of sat are indexed by rows of dest and its columns are indexed by rows of source.
We know that polyhedra can be represented by both a system of constraints or a system of generators (points, rays and lines) (see Section Representations of Convex Polyhedra). When we have both descriptions for a polyhedron  we have what is called a double description (or DD pair) for
we have what is called a double description (or DD pair) for  .
.
Here, the representation system refers to the system  whose rows represent the constraints that characterize
whose rows represent the constraints that characterize  and the generating system, the system
and the generating system, the system  whose rows represent the generators of
whose rows represent the generators of  . We say that a pair
. We say that a pair  of (real) systems is a double description pair if
of (real) systems is a double description pair if
![\[ C\vect{x} \geq \vect{0} \quad\iff\quad \exists \vect{\lambda} \geq \vect{0} \mathrel{.} \vect{x} = G\vect{\lambda}. \]](form_1098.png)
The term "double description" is quite natural in the sense that such a pair contains two different description of the same object. In fact, if we refer to the cone representation of a polyhedron  and we call
and we call  and
and 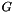 the systems of constraints and rays respectively, we have
the systems of constraints and rays respectively, we have
![\[ P = \{\, \vect{x} \in \Rset^n \mid C\vect{x} \geq \vect{0}\, \} = \{\, \vect{x} \in \Rset^n \mid \vect{x} = G\vect{\lambda} \text{ for some } \vect{\lambda} \geq \vect{0}\, \}. \]](form_1099.png)
Because of the theorem of Minkowski (see Section Further Notation and Terminology), we can say that, given a 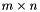 representation system
representation system 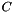 such that
such that 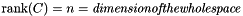 for a non-empty polyhedron
for a non-empty polyhedron  , it is always possible to find a generating system
, it is always possible to find a generating system  for
for  such that
such that  is a DD pair. Conversely, Weyl's theorem ensures that, for each generating system
is a DD pair. Conversely, Weyl's theorem ensures that, for each generating system  , it is possible to find a representation system
, it is possible to find a representation system  such that
such that  is a DD pair.
is a DD pair.
For efficiency reasons, our representation of polyhedra makes use of a double description. We are thus left with two problems:
- given
 find
find  such that
such that  is a DD pair;
is a DD pair; - given
 find
find  such that
such that 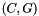 is a DD pair.
is a DD pair.
Using Farkas' Lemma we can prove that these two problems are computationally equivalent (i.e., linear-time reducible to each other). Farkas' Lemma establishes a fundamental property of vectors in 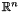 that, in a sense, captures the essence of duality. Consider a matrix
that, in a sense, captures the essence of duality. Consider a matrix 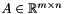 and let
and let 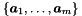 be its set of row vectors. Consider also another vector
be its set of row vectors. Consider also another vector 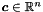 such that, whenever a vector
such that, whenever a vector 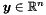 has a non-negative projection on the
has a non-negative projection on the 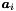 's, it also has a non-negative projection on
's, it also has a non-negative projection on 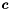 . The lemma states that
. The lemma states that 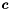 has this property if and only if it is in the cone generated by the
has this property if and only if it is in the cone generated by the 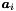 's. Formally, the lemma states the equivalence of the two following assertions:
's. Formally, the lemma states the equivalence of the two following assertions:
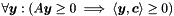 ;
;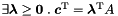 .
.
With this result we can prove that 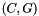 is a DD pair if and only if
is a DD pair if and only if 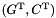 is a DD pair.
is a DD pair.
Suppose 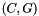 is a DD pair. Thus, for each
is a DD pair. Thus, for each 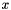 of the appropriate dimension,
of the appropriate dimension, 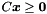 if and only if
if and only if 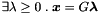 , which is of course equivalent to
, which is of course equivalent to 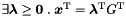 .
.
First, we assume that 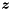 is such that
is such that 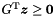 and we will show that
and we will show that 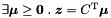 . Let
. Let  be such that
be such that 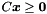 . Since
. Since 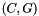 is a DD pair, this is equivalent to
is a DD pair, this is equivalent to 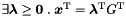 , which, by Farkas' Lemma is equivalent to
, which, by Farkas' Lemma is equivalent to 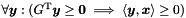 . Taking
. Taking  and recalling our assumption that
and recalling our assumption that 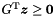 we can conclude that
we can conclude that 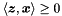 , that is equivalent to
, that is equivalent to 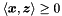 . We have thus established that
. We have thus established that 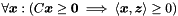 . By Farkas' Lemma, this is equivalent to
. By Farkas' Lemma, this is equivalent to 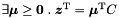 , which is equivalent to what we wanted to prove, that is,
, which is equivalent to what we wanted to prove, that is, 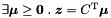 .
.
In order to prove the reverse implication, the following observation turns out to be useful: when  is a DD pair,
is a DD pair,  . In fact, let
. In fact, let 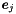 be the vector whose components are all
be the vector whose components are all  apart from the
apart from the  -th one, which is
-th one, which is  . Clearly
. Clearly 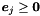 and, taking
and, taking 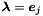 and
and 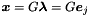 , we have
, we have 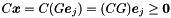 , since
, since  is a DD pair. Thus, as
is a DD pair. Thus, as  is the
is the  -th column of
-th column of  and since the choice of
and since the choice of 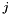 was arbitrary,
was arbitrary, 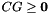 .
.
We now assume that 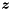 is such that
is such that 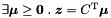 and we will prove that
and we will prove that 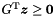 . By Farkas' Lemma, the assumption
. By Farkas' Lemma, the assumption 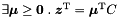 , is equivalent to
, is equivalent to 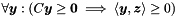 . If we take
. If we take 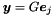 then
then 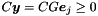 , since
, since 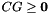 . So
. So  , that is, the
, that is, the 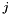 -th component of
-th component of 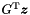 is non-negative. The arbitrary choice of
is non-negative. The arbitrary choice of  allows us to conclude that
allows us to conclude that 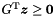 , as required.
, as required.
In view of this result, the following exposition assumes, for clarity, that the conversion being performed is from constraints to generators. Thus, even if the roles of source and dest can be interchanged, in the sequel we assume the source system will contain the constraints that represent the polyhedron and the dest system will contain the generator that generates it.
There are some observations that are useful to understand this function:
Observation 1: Let  be a system of constraints that generate the polyhedron
be a system of constraints that generate the polyhedron 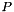 and
and 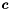 a new constraint that must be added. Suppose that there is a line
a new constraint that must be added. Suppose that there is a line 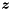 that does not saturate the constraint
that does not saturate the constraint 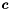 . If we combine the old lines and rays that do not saturate
. If we combine the old lines and rays that do not saturate 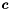 (except
(except 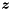 ) with
) with 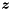 such that the new ones saturate
such that the new ones saturate 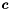 , the new lines and rays also saturate the constraints saturated by the old lines and rays.
, the new lines and rays also saturate the constraints saturated by the old lines and rays.
In fact, if 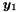 is the old generator that does not saturate
is the old generator that does not saturate 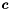 ,
, 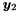 is the new one such that
is the new one such that
![\[ \vect{y}_2 = \lambda \vect{y}_1 + \mu \vect{z} \]](form_1136.png)
and 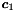 is a previous constraint that
is a previous constraint that 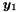 and
and 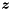 saturates, we can see
saturates, we can see
![\[ \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{y}_2 \rangle = \langle \vect{c}_1, (\lambda \vect{y}_1 + \mu \vect{z}) \rangle = \lambda \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{y}_1 \rangle + \mu \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{z} \rangle = 0 + \mu \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{z} \rangle = \mu \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{z} \rangle \]](form_1138.png)
and
![\[ \mu \langle \vect{c}_1, \vect{z} \rangle = 0. \]](form_1139.png)
Proposition 1: Let 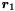 and
and 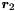 be distinct rays of
be distinct rays of 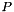 . Then the following statements are equivalent: a)
. Then the following statements are equivalent: a) 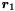 and
and 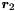 are adjacent extreme rays (see Section Further Notation and Terminology); b)
are adjacent extreme rays (see Section Further Notation and Terminology); b) 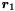 and
and 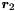 are extreme rays and the rank of the system composed by the constraints saturated by both
are extreme rays and the rank of the system composed by the constraints saturated by both 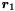 and
and 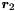 is equal to
is equal to 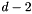 , where
, where 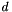 is the rank of the system of constraints.
is the rank of the system of constraints.
In fact, let 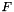 be the system of generators that saturate the constraints saturated by both
be the system of generators that saturate the constraints saturated by both 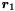 and
and 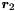 . If b) holds, the set
. If b) holds, the set 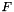 is 2-dimensional and
is 2-dimensional and 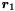 and
and 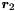 generate this set. So, every generator
generate this set. So, every generator 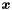 of
of 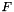 can be built as a combination of
can be built as a combination of 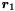 and
and 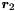 , i.e.
, i.e.
![\[ \vect{x} = \lambda \vect{r}_1 + \mu \vect{r}_2. \]](form_1141.png)
This combination is non-negative because there exists at least a constraint 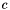 saturated by
saturated by  and not
and not  (or vice versa) (because they are distinct) for which
(or vice versa) (because they are distinct) for which
![\[ \langle \vect{c}, \vect{x} \rangle \geq 0 \]](form_1142.png)
and
![\[ \langle \vect{c}, \vect{x} \rangle = \lambda \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_1 \rangle (or = \mu \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_2 \rangle). \]](form_1143.png)
So, there is no other extreme ray in  and a) holds. Otherwise, if b) does not hold, the rank of the system generated by the constraints saturated by both
and a) holds. Otherwise, if b) does not hold, the rank of the system generated by the constraints saturated by both  and
and 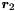 is equal to
is equal to  , with
, with k >= 3, the set 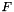 is
is k -dimensional and at least k extreme rays are necessary to generate 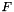 . So,
. So, 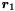 and
and 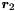 are not adjacent and a) does not hold.
are not adjacent and a) does not hold.
Proposition 2: When we build the new system of generators starting from a system  of constraints of
of constraints of  , if
, if  is the constraint to add to
is the constraint to add to 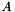 and all lines of
and all lines of 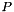 saturate
saturate 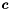 , the new set of rays is the union of those rays that saturate, of those that satisfy and of a set
, the new set of rays is the union of those rays that saturate, of those that satisfy and of a set 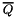 of rays such that each of them
of rays such that each of them
- lies on the hyper-plane represented by the k-th constraint,
- is a positive combination of two adjacent rays
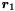 and
and 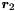 such that the first one satisfies the constraint and the other does not satisfy it. If the adjacency property is not taken in account, the new set of rays is not irredundant, in general.
such that the first one satisfies the constraint and the other does not satisfy it. If the adjacency property is not taken in account, the new set of rays is not irredundant, in general.
In fact, if 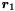 and
and 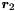 are not adjacent, the rank of the system composed by the constraints saturated by both
are not adjacent, the rank of the system composed by the constraints saturated by both 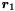 and
and 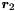 is different from
is different from 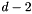 (see the previous proposition) or neither
(see the previous proposition) or neither 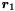 nor
nor 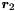 are extreme rays. Since the new ray
are extreme rays. Since the new ray 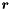 is a combination of
is a combination of 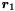 and
and 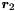 , it saturates the same constraints saturated by both
, it saturates the same constraints saturated by both  and
and  . If the rank is less than
. If the rank is less than  , the rank of the system composed by
, the rank of the system composed by  (that is saturated by
(that is saturated by 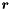 ) and by the constraints of
) and by the constraints of 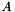 saturated by
saturated by 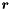 is less than
is less than 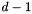 . It means that
. It means that 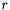 is redundant (see Section Further Notation and Terminology). If neither
is redundant (see Section Further Notation and Terminology). If neither  nor
nor  are extreme rays, they belong to a 2-dimensional face containing exactly two extreme rays of
are extreme rays, they belong to a 2-dimensional face containing exactly two extreme rays of  . These two adjacent rays build a ray equal to
. These two adjacent rays build a ray equal to 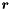 and so
and so 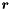 is redundant.
is redundant.
Definition at line 369 of file Polyhedron_conversion_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::add_recycled_row(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::count_ones(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::maybe_abandon(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::normalize2(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::num_columns(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::num_rows(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::remove_trailing_columns(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::remove_trailing_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), WEIGHT_ADD_MUL, and WEIGHT_BEGIN.
Referenced by add_and_minimize(), and minimize().
|
staticprotected |
Helper function that makes result become a Linear_Expression obtained by normalizing the denominators in lf.
- Parameters
-
lf The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries to normalize. It should be the result of an application of static method overapproximate_linear_form.lf_dimension Must be the space dimension of lf.result Used to store the result.
This function ignores the upper bound of intervals in lf, so that in fact result can be seen as lf multiplied by a proper normalization constant.
Definition at line 476 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::lcm_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom(), and PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT.
Referenced by refine_with_linear_form_inequality().
|
staticprotected |
Normalization helper function.
- Parameters
-
lf The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries to normalize. It should be the result of an application of static method overapproximate_linear_form.lf_dimension Must be the space dimension of lf.res Stores the normalized linear form, except its inhomogeneous term. res_low_coeff Stores the lower boundary of the inhomogeneous term of the result. res_hi_coeff Stores the higher boundary of the inhomogeneous term of the result. denominator Becomes the common denominator of res_low_coeff,res_hi_coeffand all coefficients inres.
Results are obtained by normalizing denominators in lf, ignoring the upper bounds of variable coefficients in lf.
Definition at line 524 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::lcm_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::numer_denom().
Referenced by affine_form_image().
|
inline |
Same as poly_difference_assign(y).
Definition at line 86 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References poly_difference_assign().
|
inline |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates.
- Parameters
-
complexity The maximal complexity of any algorithms used.
- Note
- Currently there is no optimality guarantee, not even if
complexityisANY_COMPLEXITY.
Definition at line 442 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
Referenced by drop_some_non_integer_points().
|
inline |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to vars.
- Parameters
-
vars Points with non-integer coordinates for these variables/space-dimensions can be discarded. complexity The maximal complexity of any algorithms used.
- Note
- Currently there is no optimality guarantee, not even if
complexityisANY_COMPLEXITY.
Definition at line 448 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References drop_some_non_integer_points().
|
protected |
Possibly tightens *this by dropping some points with non-integer coordinates for the space dimensions corresponding to *vars_p.
- Parameters
-
vars_p When nonzero, points with non-integer coordinates for the variables/space-dimensions contained in *vars_pcan be discarded.complexity The maximal complexity of any algorithms used.
- Note
- Currently there is no optimality guarantee, not even if
complexityisANY_COMPLEXITY.
Definition at line 2232 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_zeroes(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ANY_COMPLEXITY, c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_leq_one(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::exact_div_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::gcd(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::OK(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::set_epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::zero_dim_positivity().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::expand_space_dimension | ( | Variable | var, |
| dimension_type | m | ||
| ) |
Creates m copies of the space dimension corresponding to var.
- Parameters
-
var The variable corresponding to the space dimension to be replicated; m The number of replicas to be created.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if vardoes not correspond to a dimension of the vector space.std::length_error Thrown if adding mnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
If *this has space dimension 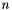 , with
, with  , and
, and var has space dimension 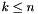 , then the
, then the  -th space dimension is expanded to
-th space dimension is expanded to m new space dimensions  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 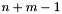 .
.
Definition at line 401 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::check_space_dimension_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::topology().
| PPL::memory_size_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::external_memory_in_bytes | ( | ) | const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this.
Definition at line 4049 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
Referenced by total_memory_in_bytes().
|
static |
Finalizes the class.
Definition at line 54 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Init::~Init().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::fold_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars, |
| Variable | dest | ||
| ) |
Folds the space dimensions in vars into dest.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the space dimensions to be folded; dest The variable corresponding to the space dimension that is the destination of the folding operation.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withdestor with one of the Variable objects contained invars. Also thrown ifdestis contained invars.
If *this has space dimension 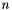 , with
, with 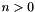 ,
, dest has space dimension 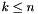 ,
, vars is a set of variables whose maximum space dimension is also less than or equal to 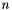 , and
, and dest is not a member of vars, then the space dimensions corresponding to variables in vars are folded into the 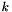 -th space dimension.
-th space dimension.
Definition at line 455 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References affine_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::frequency | ( | const Linear_Expression & | expr, |
| Coefficient & | freq_n, | ||
| Coefficient & | freq_d, | ||
| Coefficient & | val_n, | ||
| Coefficient & | val_d | ||
| ) | const |
Returns true if and only if there exist a unique value val such that *this saturates the equality expr = val.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression for which the frequency is needed; freq_n If trueis returned, the value is set to ; Present for interface compatibility with class Grid, where the frequency can have a non-zero value;
; Present for interface compatibility with class Grid, where the frequency can have a non-zero value;freq_d If trueis returned, the value is set to ;
;val_n The numerator of val;val_d The denominator of val;
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If false is returned, then freq_n, freq_d, val_n and val_d are left untouched.
Definition at line 3732 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::homogeneous_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension(), and value.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generalized_affine_image | ( | Variable | var, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 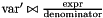 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
var The left hand side variable of the generalized affine relation; relsym The relation symbol; expr The numerator of the right hand side affine expression; denominator The denominator of the right hand side affine expression (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*thisor if*thisis a C_Polyhedron andrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 3082 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::set_epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generalized_affine_image | ( | const Linear_Expression & | lhs, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | rhs | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the image of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 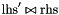 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
lhs The left hand side affine expression; relsym The relation symbol; rhs The right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withlhsorrhsor if*thisis a C_Polyhedron andrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 3306 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::have_a_common_variable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generalized_affine_preimage | ( | Variable | var, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | expr, | ||
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | denominator = Coefficient_one() |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 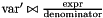 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
var The left hand side variable of the generalized affine relation; relsym The relation symbol; expr The numerator of the right hand side affine expression; denominator The denominator of the right hand side affine expression (optional argument with default value 1).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if denominatoris zero or ifexprand*thisare dimension-incompatible or ifvaris not a space dimension of*thisor if*thisis a C_Polyhedron andrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 3198 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generalized_affine_preimage | ( | const Linear_Expression & | lhs, |
| Relation_Symbol | relsym, | ||
| const Linear_Expression & | rhs | ||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the preimage of *this with respect to the generalized affine relation 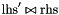 , where
, where  is the relation symbol encoded by
is the relation symbol encoded by relsym.
- Parameters
-
lhs The left hand side affine expression; relsym The relation symbol; rhs The right hand side affine expression.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible withlhsorrhsor if*thisis a C_Polyhedron andrelsymis a strict relation symbol.
Definition at line 3466 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::have_a_common_variable(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::last_nonzero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
inline |
Refines *this with the constraint expressed by left 
right, where  is the relation symbol specified by
is the relation symbol specified by relsym..
- Parameters
-
left The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is on the left of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. right The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is on the right of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. relsym The relation symbol.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if left(orright) is dimension-incompatible with*this.std::runtime_error Thrown if relsymis not a valid relation symbol.
This function is used in abstract interpretation to model a filter that is generated by a comparison of two expressions that are correctly approximated by left and right respectively.
Definition at line 383 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::GREATER_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_OR_EQUAL, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::LESS_THAN, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_EQUAL, and refine_with_linear_form_inequality().
| const PPL::Generator_System & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::generators | ( | ) | const |
Returns the system of generators.
Definition at line 138 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::adjust_topology_and_space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::zero_dim_univ().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), map_space_dimensions(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of generators is minimized.
Note that only weak minimization is entailed, so that an NNC polyhedron may still have 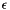 -redundant generators.
-redundant generators.
Definition at line 150 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_g_minimized().
Referenced by BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), can_have_something_pending(), quick_equivalence_test(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the system of generators is up-to-date.
Definition at line 140 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_g_up_to_date().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), is_empty(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), operator=(), poly_hull_assign(), Polyhedron(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), select_H79_constraints(), and time_elapse_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::H79_widening_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the H79_widening between *this and y.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 165 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_constraints(), con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_no_rows(), has_pending_generators(), intersection_assign(), is_empty(), is_necessarily_closed(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_equalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), OK(), process_pending_generators(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), space_dim, throw_dimension_incompatible(), throw_topology_incompatible(), topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE, and update_constraints().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::H79_widening_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), and widening_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if there are pending constraints.
Definition at line 165 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_c_pending().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), intersection_assign(), is_empty(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), poly_hull_assign(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending(), remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), simplified_constraints(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if there are pending generators.
Definition at line 170 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_g_pending().
Referenced by H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), poly_hull_assign(), process_pending(), remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if there are either pending constraints or pending generators.
Definition at line 175 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_c_pending(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_g_pending().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), process_pending(), quick_equivalence_test(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inline |
Returns a 32-bit hash code for *this.
If x and y are such that x == y, then x.hash_code() == y.hash_code().
Definition at line 45 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::hash_code_from_dimension(), and space_dimension().
|
static |
Initializes the class.
Definition at line 47 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References simplify_num_saturators_p, and simplify_num_saturators_size.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Init::Init().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::intersection_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the intersection of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1986 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References can_have_something_pending(), clear_constraints_minimized(), clear_generators_up_to_date(), con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::is_sorted(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::merge_rows_assign(), OK(), process_pending_generators(), set_constraints_pending(), set_empty(), space_dim, topology(), and update_constraints().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), H79_widening_assign(), and is_disjoint_from().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::is_bounded | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a bounded polyhedron.
Definition at line 526 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is discrete.
Definition at line 69 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References affine_dimension().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::is_disjoint_from | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this and y are disjoint.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if xandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3958 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References intersection_assign(), and is_empty().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::check_containment().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is an empty polyhedron.
Definition at line 187 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), marked_empty(), and minimize().
Referenced by BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::check_containment(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), H79_widening_assign(), is_disjoint_from(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::linear_partition_aux(), operator<<(), operator==(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::Pointset_Powerset(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
private |
Returns true if and only if *this is included in y.
Definition at line 425 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), constraints_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, has_pending_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::NONSTRICT_INEQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, process_pending_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::reduced_sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::STRICT_INEQUALITY, topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::type(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type(), and update_constraints().
Referenced by BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), contains(), and operator==().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if and only if the polyhedron is necessarily closed.
Definition at line 74 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References con_sys, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::is_necessarily_closed().
Referenced by BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::H79_Certificate(), H79_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Interfaces::is_necessarily_closed_for_interfaces(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), select_H79_constraints(), simplify_using_context_assign(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and time_elapse_assign().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::is_topologically_closed | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a topologically closed subset of the vector space.
Definition at line 549 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_matching_closure_point(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::is_universe | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if and only if *this is a universe polyhedron.
Definition at line 388 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the limited extrapolation between *this and y using the BHRZ03-widening operator.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened polyhedron; tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 840 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_constraints(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), c, gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), is_necessarily_closed(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), process_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::satisfied_by_all_generators(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and update_generators().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::limited_H79_extrapolation_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y, |
| const Constraint_System & | cs, | ||
| unsigned * | tp = 0 |
||
| ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the limited extrapolation between *this and y using the H79-widening operator.
- Parameters
-
y A polyhedron that must be contained in *this;cs The system of constraints used to improve the widened polyhedron; tp An optional pointer to an unsigned variable storing the number of available tokens (to be used when applying the widening with tokens delay technique).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *this,yandcsare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 300 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References add_recycled_constraints(), c, gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), H79_widening_assign(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_strict_inequalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), is_necessarily_closed(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), process_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::satisfied_by_all_generators(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), and update_generators().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::limited_H79_extrapolation_assign().
|
inline |
Swaps *this with polyhedron y. (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible.)
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if xandyare topology-incompatible.
Definition at line 100 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References con_sys, gen_sys, sat_c, sat_g, space_dim, status, swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), throw_topology_incompatible(), and topology().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), H79_widening_assign(), map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::operator=(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::operator=(), and swap().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::map_space_dimensions | ( | const Partial_Function & | pfunc | ) |
Remaps the dimensions of the vector space according to a partial function.
- Parameters
-
pfunc The partial function specifying the destiny of each space dimension.
The template type parameter Partial_Function must provide the following methods.
returns true if and only if the represented partial function has an empty codomain (i.e., it is always undefined). The has_empty_codomain() method will always be called before the methods below. However, if has_empty_codomain() returns true, none of the functions below will be called.
returns the maximum value that belongs to the codomain of the partial function. The max_in_codomain() method is called at most once.
Let 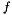 be the represented function and
be the represented function and 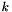 be the value of
be the value of i. If 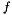 is defined in
is defined in 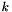 , then
, then 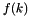 is assigned to
is assigned to j and true is returned. If 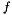 is undefined in
is undefined in  , then
, then false is returned. This method is called at most  times, where
times, where  is the dimension of the vector space enclosing the polyhedron.
is the dimension of the vector space enclosing the polyhedron.
The result is undefined if pfunc does not encode a partial function with the properties described in the specification of the mapping operator.
Definition at line 153 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::add_mul_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::clear(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::divisor(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), gen_sys, generators(), generators_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::has_empty_codomain(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::has_no_rows(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, m_swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::maps(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partial_Function::max_in_codomain(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::permute_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::permute_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), set_zero_dim_univ(), space_dim, throw_invalid_argument(), topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type(), and update_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the polyhedron is known to be empty.
The return value false does not necessarily implies that *this is non-empty.
Definition at line 130 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_empty().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), affine_form_image(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::compare(), concatenate_assign(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::H79_Certificate(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_empty(), is_included_in(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), map_space_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), operator=(), operator==(), poly_difference_assign(), poly_hull_assign(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending(), quick_equivalence_test(), refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
private |
Maximizes or minimizes expr subject to *this.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized or minimized subject to this;maximize trueif maximization is what is wanted;ext_n The numerator of the extremum value; ext_d The denominator of the extremum value; included trueif and only if the extremum ofexprcan actually be reached in*this;g When maximization or minimization succeeds, will be assigned a point or closure point where exprreaches the corresponding extremum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded in the appropriate direction, false is returned and ext_n, ext_d, included and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 608 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::assign_r(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::homogeneous_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_closure_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line_or_ray(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP, PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, PPL_UNINITIALIZED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ROUND_NOT_NEEDED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
Referenced by maximize(), and minimize().
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the maximum space dimension all kinds of Polyhedron can handle.
Definition at line 50 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::max_space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::max_space_dimension().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), check_obj_space_dimension_overflow(), check_space_dimension_overflow(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension(), and Polyhedron().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value is computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized subject to *this;sup_n The numerator of the supremum value; sup_d The denominator of the supremum value; maximum trueif and only if the supremum is also the maximum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from above, false is returned and sup_n, sup_d and maximum are left untouched.
Definition at line 324 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References max_min().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from above in *this, in which case the supremum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be maximized subject to *this;sup_n The numerator of the supremum value; sup_d The denominator of the supremum value; maximum trueif and only if the supremum is also the maximum value;g When maximization succeeds, will be assigned the point or closure point where exprreaches its supremum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from above, false is returned and sup_n, sup_d, maximum and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 332 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References max_min().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value is computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be minimized subject to *this;inf_n The numerator of the infimum value; inf_d The denominator of the infimum value; minimum trueif and only if the infimum is also the minimum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from below, false is returned and inf_n, inf_d and minimum are left untouched.
Definition at line 339 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References max_min().
Referenced by BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::H79_Certificate(), H79_widening_assign(), is_included_in(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), poly_difference_assign(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this is not empty and expr is bounded from below in *this, in which case the infimum value and a point where expr reaches it are computed.
- Parameters
-
expr The linear expression to be minimized subject to *this;inf_n The numerator of the infimum value; inf_d The denominator of the infimum value; minimum trueif and only if the infimum is also the minimum value;g When minimization succeeds, will be assigned a point or closure point where exprreaches its infimum value.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if exprand*thisare dimension-incompatible.
If *this is empty or expr is not bounded from below, false is returned and inf_n, inf_d, minimum and g are left untouched.
Definition at line 347 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References max_min().
|
private |
Applies (weak) minimization to both the constraints and generators.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
Minimization is not attempted if the Status field already declares both systems to be minimized.
Definition at line 1105 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by is_empty().
|
staticprivate |
Builds and simplifies constraints from generators (or vice versa).
- Returns
trueif the polyhedron is empty,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
con_to_gen trueifsourcerepresents the constraints,falseotherwise;source The given system, which is not empty; dest The system to build and minimize; sat The saturation matrix.
dest is not const because it will be built (and then modified) during minimize(). Also, sat and source are not const because the former will be built during dest creation and the latter will maybe be sorted and modified by conversion() and simplify().
sat has the generators on its columns and the constraints on its rows if con_to_gen is true, otherwise it has the generators on its rows and the constraints on its columns.
Given source, this function builds (by means of conversion()) dest and then simplifies (invoking simplify()) source, erasing redundant rows. For the sequel we assume that source is the system of constraints and dest is the system of generators. This will simplify the description of the function; the dual case is similar.
Definition at line 71 of file Polyhedron_minimize_templates.hh.
References conversion(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NOT_NECESSARILY_CLOSED, OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_space_dimension(), simplify(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
|
inline |
Returns a system of (equality) congruences satisfied by *this, with no redundant congruences and having the same affine dimension as *this.
Definition at line 372 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References minimized_constraints().
| const PPL::Constraint_System & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::minimized_constraints | ( | ) | const |
Returns the system of constraints, with no redundant constraint.
Definition at line 125 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::assign_all_inequalities_approximation(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::compare(), congruences(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::H79_Certificate(), minimized_congruences(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Partially_Reduced_Product< D1, D2, R >::minimized_constraints(), and operator<<().
| const PPL::Generator_System & Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::minimized_generators | ( | ) | const |
Returns the system of generators, with no redundant generator.
Definition at line 193 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare().
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 602 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::begin(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Coefficient_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::id(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::sgn(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::sub_mul_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::const_iterator::variable().
|
private |
Sorts the matrix of constraints keeping status consistency.
It is assumed that constraints are up-to-date. If at least one of the saturation matrices is up-to-date, then sat_g is kept consistent with the sorted matrix of constraints. The method is declared const because reordering the constraints does not modify the polyhedron from a logical point of view.
Definition at line 975 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::is_sorted(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sort_and_remove_with_sat(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sort_rows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
Referenced by quick_equivalence_test().
|
private |
Sorts the matrix of constraints and updates sat_c.
It is assumed that both constraints and generators are up-to-date and minimized. The method is declared const because reordering the constraints does not modify the polyhedron from a logical point of view.
Definition at line 1033 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::is_sorted(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_sat_c_up_to_date(), set_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sort_and_remove_with_sat(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign(), and update_sat_c().
Referenced by process_pending_constraints().
|
private |
Sorts the matrix of generators keeping status consistency.
It is assumed that generators are up-to-date. If at least one of the saturation matrices is up-to-date, then sat_c is kept consistent with the sorted matrix of generators. The method is declared const because reordering the generators does not modify the polyhedron from a logical point of view.
Definition at line 1004 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_sat_c_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_and_remove_with_sat(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_rows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
Referenced by quick_equivalence_test().
|
private |
Sorts the matrix of generators and updates sat_g.
It is assumed that both constraints and generators are up-to-date and minimized. The method is declared const because reordering the generators does not modify the polyhedron from a logical point of view.
Definition at line 1069 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_sat_c_up_to_date(), set_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::set_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_and_remove_with_sat(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign(), and update_sat_g().
Referenced by process_pending_generators().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::OK | ( | bool | check_not_empty = false | ) | const |
Checks if all the invariants are satisfied.
- Returns
trueif and only if*thissatisfies all the invariants and eithercheck_not_emptyisfalseor*thisis not empty.
- Parameters
-
check_not_empty trueif and only if, in addition to checking the invariants,*thismust be checked to be not empty.
The check is performed so as to intrude as little as possible. If the library has been compiled with run-time assertions enabled, error messages are written on std::cerr in case invariants are violated. This is useful for the purpose of debugging the library.
Definition at line 832 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ascii_dump(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::ascii_dump(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::ascii_dump(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::BD_Shapes::empty, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_equalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_lines(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rays(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::remove_trailing_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::remove_trailing_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::simplify(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sort_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::strong_normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::strong_normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::unset_pending_rows().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::C_Polyhedron(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), map_space_dimensions(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::NNC_Polyhedron(), poly_hull_assign(), Polyhedron(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), simplify_using_context_assign(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
protected |
The assignment operator. (*this and y can be dimension-incompatible.)
Definition at line 327 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References con_sys, constraints_are_up_to_date(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), marked_empty(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), space_dim, status, and topology().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::operator=(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::operator=().
|
protected |
Helper function that overapproximates an interval linear form.
- Parameters
-
lf The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries to approximate. ALL of its coefficients MUST be bounded. lf_dimension Must be the space dimension of lf.result Used to store the result.
This function makes result become a linear form that is a correct approximation of lf under the constraints specified by *this. The resulting linear form has the property that all of its variable coefficients have a non-significant upper bound and can thus be considered as singletons.
Definition at line 431 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::get_interval(), and PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
Referenced by affine_form_image(), and refine_with_linear_form_inequality().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::poly_difference_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the poly-difference of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2648 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, constraints(), contains(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), marked_empty(), minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::NONSTRICT_INEQUALITY, poly_hull_assign(), refine_no_check(), relation_with(), set_empty(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::STRICT_INEQUALITY, topology(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::type().
Referenced by difference_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::poly_hull_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the poly-hull of *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2576 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References can_have_something_pending(), clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_generators_minimized(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::merge_rows_assign(), OK(), process_pending_constraints(), set_generators_pending(), space_dim, topology(), and update_generators().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::affine_dimension(), poly_difference_assign(), and upper_bound_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::positive_time_elapse_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this (the best approximation of) the result of computing the positive time-elapse between *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
|
protected |
Assuming *this is NNC, assigns to *this the result of the "positive time-elapse" between *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2375 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::add_corresponding_closure_points(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::convert_into_non_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, process_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, set_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_inhomogeneous_term(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows(), and update_generators().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::positive_time_elapse_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::print | ( | ) | const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<.
|
inlineprivate |
Processes the pending rows of either description of the polyhedron and obtains a minimized polyhedron.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
It is assumed that the polyhedron does have some constraints or generators pending.
Definition at line 300 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), has_something_pending(), marked_empty(), process_pending_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), and space_dim.
|
private |
Processes the pending constraints and obtains a minimized polyhedron.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
It is assumed that the polyhedron does have some pending constraints.
Definition at line 737 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_pending_constraints(), clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::BD_Shapes::empty, gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::is_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_pending_rows(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), sat_c, sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g, set_empty(), set_sat_c_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::sort_pending_and_remove_duplicates(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
Referenced by limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), poly_hull_assign(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
private |
Processes the pending generators and obtains a minimized polyhedron.
It is assumed that the polyhedron does have some pending generators.
Definition at line 777 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_pending_generators(), clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), con_sys, gen_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_pending_rows(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), sat_c, sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_sat_g_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_pending_and_remove_duplicates(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
Referenced by H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), process_pending(), and remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints().
|
private |
Polynomial but incomplete equivalence test between polyhedra.
Definition at line 356 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), gen_sys, generators_are_minimized(), has_something_pending(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_equalities(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_lines(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_generators(), space_dim, topology(), TVB_DONT_KNOW, TVB_FALSE, and TVB_TRUE.
Referenced by contains(), and operator==().
|
inline |
Refines store with the constraints defining *this.
- Parameters
-
store The interval floating point abstract store to refine.
Definition at line 416 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
|
private |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine the system of constraints of *this.
- Parameters
-
c The constraint to be added. If it is dimension-incompatible with *this, the behavior is undefined.
Definition at line 1434 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_necessarily_closed(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by poly_difference_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_congruence | ( | const Congruence & | cg | ) |
Uses a copy of congruence cg to refine *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecgare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1757 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_congruences | ( | const Congruence_System & | cgs | ) |
Uses a copy of the congruences in cgs to refine *this.
- Parameters
-
cgs Contains the congruences used to refine the system of constraints of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcgsare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1879 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_constraint | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) |
Uses a copy of constraint c to refine *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1745 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by refine_with_linear_form_inequality().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_constraints | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Uses a copy of the constraints in cs to refine *this.
- Parameters
-
cs Contains the constraints used to refine the system of constraints of *this.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandcsare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 1784 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::has_no_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::refine_with_linear_form_inequality | ( | const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > & | left, |
| const Linear_Form< Interval< FP_Format, Interval_Info > > & | right, | ||
| bool | is_strict = false |
||
| ) |
Refines *this with the constraint expressed by left 
right if is_strict is set, with the constraint left 
right otherwise.
- Parameters
-
left The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is on the left of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. right The linear form on intervals with floating point boundaries that is on the right of the comparison operator. All of its coefficients MUST be bounded. is_strict True if the comparison is strict.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if left(orright) is dimension-incompatible with*this.
This function is used in abstract interpretation to model a filter that is generated by a comparison of two expressions that are correctly approximated by left and right respectively.
Definition at line 300 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References convert_to_integer_expression(), is_necessarily_closed(), marked_empty(), overapproximate_linear_form(), PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK, refine_with_constraint(), space_dim, and throw_dimension_incompatible().
Referenced by generalized_refine_with_linear_form_inequality().
| PPL::Poly_Con_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::relation_with | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the constraint c.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand constraintcare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 209 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_disjoint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::saturates(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
Referenced by BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), and poly_difference_assign().
| PPL::Poly_Gen_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::relation_with | ( | const Generator & | g | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the generator g.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand generatorgare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 255 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::nothing(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Gen_Relation::subsumes().
| PPL::Poly_Con_Relation Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::relation_with | ( | const Congruence & | cg | ) | const |
Returns the relations holding between the polyhedron *this and the congruence c.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisand congruencecare dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 285 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::assign(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::implies(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_disjoint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::is_included(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::is_inconsistent(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::modulus(), PPL_DIRTY_TEMP_COEFFICIENT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::saturates(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Poly_Con_Relation::strictly_intersects().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::remove_higher_space_dimensions | ( | dimension_type | new_dimension | ) |
Removes the higher dimensions of the vector space so that the resulting space will have dimension new_dimension.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if new_dimensionsis greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 353 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_quasi_ranking_functions_MS(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::Termination::all_affine_ranking_functions_MS(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR().
|
private |
Lazily integrates the pending descriptions of the polyhedron to obtain a constraint system without pending rows.
It is assumed that the polyhedron does have some constraints or generators pending.
Definition at line 810 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_constraints_minimized(), clear_generators_up_to_date(), clear_pending_constraints(), con_sys, has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), process_pending_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::set_sorted(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::unset_pending_rows().
|
private |
Lazily integrates the pending descriptions of the polyhedron to obtain a generator system without pending rows.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
It is assumed that the polyhedron does have some constraints or generators pending.
Definition at line 834 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_generators_minimized(), clear_pending_generators(), gen_sys, has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), process_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::set_sorted(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows().
Referenced by map_space_dimensions().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::remove_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars | ) |
Removes all the specified dimensions from the vector space.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the space dimensions to be removed.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible with one of the Variable objects contained invars.
Definition at line 301 of file Polyhedron_chdims.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Termination_Helpers::all_affine_ranking_functions_PR_original().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the saturation matrix sat_c is up-to-date.
Definition at line 155 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_sat_c_up_to_date().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), can_have_something_pending(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), and process_pending_constraints().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns true if the saturation matrix sat_g is up-to-date.
Definition at line 160 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References status, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::test_sat_g_up_to_date().
Referenced by BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), can_have_something_pending(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), process_pending_generators(), and select_H79_constraints().
|
private |
Copies to cs_selection the constraints of y corresponding to the definition of the CH78-widening of *this and y.
Definition at line 40 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References c, con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::topology(), and topology().
Referenced by H79_widening_assign().
|
private |
Splits the constraints of `x' into two subsets, depending on whether or not they are selected to compute the H79-widening of *this and y.
Definition at line 68 of file Polyhedron_widenings.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::clear(), con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::remove_trailing_rows(), sat_g, sat_g_is_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::sort_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::sorted_contains(), space_dim, strongly_minimize_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Affine_Space::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::topology(), topology(), update_generators(), and update_sat_g().
Referenced by BHRZ03_widening_assign(), and H79_widening_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that constraints are minimized.
Definition at line 211 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_c_minimized(), set_constraints_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by Polyhedron(), update_constraints(), and update_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that constraints are pending.
Definition at line 223 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_c_pending(), and status.
Referenced by intersection_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that constraints are up-to-date.
Definition at line 201 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_c_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by Polyhedron(), and set_constraints_minimized().
|
private |
Sets status to express that the polyhedron is empty, clearing all corresponding matrices.
Definition at line 727 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by intersection_assign(), poly_difference_assign(), Polyhedron(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending_constraints(), time_elapse_assign(), and update_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that generators are minimized.
Definition at line 217 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_g_minimized(), set_generators_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by update_constraints(), and update_generators().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that generators are pending.
Definition at line 228 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_g_pending(), and status.
Referenced by poly_hull_assign(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that generators are up-to-date.
Definition at line 206 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_g_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by Polyhedron(), and set_generators_minimized().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that sat_c is up-to-date.
Definition at line 233 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_sat_c_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), process_pending_constraints(), update_constraints(), and update_sat_c().
|
inlineprivate |
Sets status to express that sat_g is up-to-date.
Definition at line 238 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::Status::set_sat_g_up_to_date(), and status.
Referenced by obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), process_pending_generators(), update_generators(), and update_sat_g().
|
private |
Sets status to express that the polyhedron is the universe 0-dimension vector space, clearing all corresponding matrices.
Definition at line 719 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by map_space_dimensions(), Polyhedron(), and simplify_using_context_assign().
|
inlineprivate |
If constraints are up-to-date, obtain a simplified copy of them.
Definition at line 354 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), constraints_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_pending_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::simplify(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::unset_pending_rows().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box().
|
staticprivate |
Uses Gauss' elimination method to simplify the result of conversion().
- Returns
- The rank of
sys.
- Parameters
-
sys The system to simplify: it will be modified; sat The saturation matrix corresponding to sys.
sys may be modified by swapping some of its rows and by possibly removing some of them, if they turn out to be redundant.
If sys is a system of constraints, then the rows of sat are indexed by constraints and its columns are indexed by generators; otherwise, if sys is a system of generators, then the rows of sat are indexed by generators and its columns by constraints.
Given a system of constraints or a system of generators, this function simplifies it using Gauss' elimination method (to remove redundant equalities/lines), deleting redundant inequalities/rays/points and making back-substitution. The explanation that follows assumes that sys is a system of constraints. For the case when sys is a system of generators, a similar explanation can be obtain by applying duality.
The explanation relies on the notion of redundancy. (See the Introduction.)
First we make some observations that can help the reader in understanding the function:
Proposition: An inequality that is saturated by all the generators can be transformed to an equality.
In fact, by combining any number of generators that saturate the constraints, we obtain a generator that saturates the constraints too:
![\[ \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_1 \rangle = 0 \land \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_2 \rangle = 0 \Rightarrow \langle \vect{c}, (\lambda_1 \vect{r}_1 + \lambda_2 \vect{r}_2) \rangle = \lambda_1 \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_1 \rangle + \lambda_2 \langle \vect{c}, \vect{r}_2 \rangle = 0, \]](form_1151.png)
where  can be any real number.
can be any real number.
Definition at line 84 of file Polyhedron_simplify_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::compute_capacity(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::BD_Shapes::empty, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NECESSARILY_CLOSED, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::num_columns(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::remove_trailing_rows(), simplify_num_saturators_p, simplify_num_saturators_size, swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
Referenced by add_and_minimize(), and minimize().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::simplify_using_context_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this a meet-preserving simplification of *this with respect to y. If false is returned, then the intersection is empty.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 2155 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraint(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraints(), add_constraints(), add_recycled_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, con_sys, constraints_are_minimized(), constraints_are_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::EQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), gen_sys, generators_are_minimized(), has_pending_generators(), has_something_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), is_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_line(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Boundary_NS::le(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, minimize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::NONSTRICT_INEQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::optimal_value(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_MIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::satisfied_by_all_generators(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::set_is_line_or_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_objective_function(), set_zero_dim_univ(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::sign_normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::STRICT_INEQUALITY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::type(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNIVERSE.
|
inline |
Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.
Definition at line 40 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References space_dim.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::BHRZ03_Certificate(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Box< ITV >::Box(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Pointset_Powerset< PSET >::check_containment(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::compare(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Grid::Grid(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::H79_Certificate::H79_Certificate(), hash_code(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::NNC_Polyhedron::poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::C_Polyhedron::poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), and throw_dimension_incompatible().
|
inline |
Returns true if and only if *this strictly contains y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 436 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References contains().
|
private |
Applies strong minimization to the constraints of an NNC polyhedron.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
Definition at line 1148 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), c, clear_generators_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_leq_one(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Adapter< T >::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::insert(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::mark_as_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::mark_as_not_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MAXIMIZATION, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_pending_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::remove_row(), sat_g, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_objective_function(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::set_optimization_mode(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::MIP_Problem::solve(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNBOUNDED_MIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_MIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::union_assign().
Referenced by select_H79_constraints().
|
private |
Applies strong minimization to the generators of an NNC polyhedron.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
Definition at line 1323 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_constraints_up_to_date(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::is_point(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_lines(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), sat_c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Row::set(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::set_epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::set_sorted(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sys, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::transpose_assign().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2609 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by affine_form_image(), H79_widening_assign(), refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), and throw_dimension_incompatible().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2622 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2630 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2637 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2644 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2651 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2658 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2666 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2674 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Congruence_System::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 591 of file Polyhedron_templates.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::space_dimension(), and throw_dimension_incompatible().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2681 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2700 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
|
protected |
Definition at line 2526 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by map_space_dimensions().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2737 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
|
protected |
Definition at line 2754 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
Referenced by Polyhedron().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2542 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References is_necessarily_closed().
Referenced by H79_widening_assign(), m_swap(), and Polyhedron().
|
protected |
Definition at line 2566 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
|
protected |
Definition at line 2577 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
|
protected |
Definition at line 2588 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
|
protected |
Definition at line 2599 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::time_elapse_assign | ( | const Polyhedron & | y | ) |
Assigns to *this the result of computing the time-elapse between *this and y.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisandyare topology-incompatible or dimension-incompatible.
Definition at line 3603 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::all_homogeneous_terms_are_zero(), can_have_something_pending(), clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_generators_minimized(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::CLOSURE_POINT, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::expression(), gen_sys, generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::insert_pending(), is_necessarily_closed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::is_sorted(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::LINE, marked_empty(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::merge_rows_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::num_rows(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::OK(), OK(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::POINT, process_pending_constraints(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::RAY, set_empty(), set_generators_pending(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::set_inhomogeneous_term(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sort_rows(), space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::sys, topology(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::type(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator_System::unset_pending_rows(), and update_generators().
Referenced by Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::time_elapse_assign(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::time_elapse_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::topological_closure_assign | ( | ) |
Assigns to *this its topological closure.
Definition at line 3817 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::epsilon_leq_one(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expr, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_tautological(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Expression::normalize(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::set_epsilon_coefficient().
|
inlineprivate |
Returns the topological kind of the polyhedron.
Definition at line 62 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References con_sys, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::topology().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), affine_form_image(), BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), concatenate_assign(), contains(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), m_swap(), map_space_dimensions(), operator=(), operator==(), poly_difference_assign(), poly_hull_assign(), Polyhedron(), quick_equivalence_test(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), simplify_using_context_assign(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
inline |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this.
Definition at line 35 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References external_memory_in_bytes().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::unconstrain | ( | Variable | var | ) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to space dimension var, assigning the result to *this.
- Parameters
-
var The space dimension that will be unconstrained.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if varis not a space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 1910 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::line(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variable::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::unconstrain | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars | ) |
Computes the cylindrification of *this with respect to the set of space dimensions vars, assigning the result to *this.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of space dimension that will be unconstrained.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *thisis dimension-incompatible with one of the Variable objects contained invars.
Definition at line 1941 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Generator::line(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
|
private |
Updates constraints starting from generators and minimizes them.
The resulting system of constraints is only partially sorted: the equalities are in the upper part of the matrix, while the inequalities in the lower part.
Definition at line 859 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), con_sys, gen_sys, sat_c, set_constraints_minimized(), set_generators_minimized(), and set_sat_c_up_to_date().
Referenced by H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), and is_included_in().
|
private |
Updates generators starting from constraints and minimizes them.
- Returns
falseif and only if*thisturns out to be an empty polyhedron.
The resulting system of generators is only partially sorted: the lines are in the upper part of the matrix, while rays and points are in the lower part. It is illegal to call this method when the Status field already declares the polyhedron to be empty.
Definition at line 878 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), con_sys, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::BD_Shapes::empty, gen_sys, sat_g, set_constraints_minimized(), set_empty(), set_generators_minimized(), and set_sat_g_up_to_date().
Referenced by limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), map_space_dimensions(), poly_hull_assign(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), select_H79_constraints(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
private |
Updates sat_c using the updated constraints and generators.
It is assumed that constraints and generators are up-to-date and minimized and that the Status field does not already flag sat_c to be up-to-date. The values of the saturation matrix are computed as follows:
![\[ \begin{cases} sat\_c[i][j] = 0, \quad \text{if } G[i] \cdot C^\mathrm{T}[j] = 0; \\ sat\_c[i][j] = 1, \quad \text{if } G[i] \cdot C^\mathrm{T}[j] > 0. \end{cases} \]](form_1149.png)
Definition at line 905 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::clear(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::resize(), sat_c, set_sat_c_up_to_date(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign().
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), and obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c().
|
private |
Updates sat_g using the updated constraints and generators.
It is assumed that constraints and generators are up-to-date and minimized and that the Status field does not already flag sat_g to be up-to-date. The values of the saturation matrix are computed as follows:
![\[ \begin{cases} sat\_g[i][j] = 0, \quad \text{if } C[i] \cdot G^\mathrm{T}[j] = 0; \\ sat\_g[i][j] = 1, \quad \text{if } C[i] \cdot G^\mathrm{T}[j] > 0. \end{cases} \]](form_1150.png)
Definition at line 940 of file Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::clear(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Bit_Matrix::resize(), sat_g, set_sat_g_up_to_date(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Scalar_Products::sign().
Referenced by BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), and select_H79_constraints().
|
inline |
Same as poly_hull_assign(y).
Definition at line 81 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References poly_hull_assign().
Referenced by BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact().
|
inline |
Same as H79_widening_assign(y, tp).
Definition at line 91 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References H79_widening_assign().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Polyhedron::wrap_assign | ( | const Variables_Set & | vars, |
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Width | w, | ||
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Representation | r, | ||
| Bounded_Integer_Type_Overflow | o, | ||
| const Constraint_System * | cs_p = 0, |
||
| unsigned | complexity_threshold = 16, |
||
| bool | wrap_individually = true |
||
| ) |
Wraps the specified dimensions of the vector space.
- Parameters
-
vars The set of Variable objects corresponding to the space dimensions to be wrapped. w The width of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. r The representation of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. o The overflow behavior of the bounded integer type corresponding to all the dimensions to be wrapped. cs_p Possibly null pointer to a constraint system whose variables are contained in vars. If*cs_pdepends on variables not invars, the behavior is undefined. When non-null, the pointed-to constraint system is assumed to represent the conditional or looping construct guard with respect to which wrapping is performed. Since wrapping requires the computation of upper bounds and due to non-distributivity of constraint refinement over upper bounds, passing a constraint system in this way can be more precise than refining the result of the wrapping operation with the constraints in*cs_p.complexity_threshold A precision parameter of the wrapping operator: higher values result in possibly improved precision. wrap_individually trueif the dimensions should be wrapped individually (something that results in much greater efficiency to the detriment of precision).
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if *cs_pis dimension-incompatible withvars, or if*thisis dimension-incompatiblevarsor with*cs_p.
Definition at line 4058 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Implementation::wrap_assign().
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Returns true if and only if x and y are different polyhedra.
Note that x and y may be topology- and/or dimension-incompatible polyhedra: in those cases, the value true is returned.
|
related |
Definition at line 431 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
|
related |
Output operator.
Writes a textual representation of ph on s: false is written if ph is an empty polyhedron; true is written if ph is a universe polyhedron; a minimized system of constraints defining ph is written otherwise, all constraints in one row separated by ", ".
|
related |
Definition at line 4081 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References is_empty(), and minimized_constraints().
|
related |
Returns true if and only if x and y are the same polyhedron.
Note that x and y may be topology- and/or dimension-incompatible polyhedra: in those cases, the value false is returned.
|
friend |
|
related |
Definition at line 3889 of file Polyhedron_public.cc.
References is_empty(), is_included_in(), marked_empty(), quick_equivalence_test(), space_dim, topology(), TVB_FALSE, and TVB_TRUE.
|
friend |
Definition at line 2621 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
friend |
Definition at line 2624 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
friend |
Definition at line 2620 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
friend |
Definition at line 2623 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
friend |
Definition at line 2625 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
friend |
|
friend |
Definition at line 2622 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
related |
If the poly-hull of p and q is exact it is assigned to p and true is returned, otherwise false is returned.
|
related |
|
related |
Swaps x with y.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions(), conversion(), m_swap(), Polyhedron(), and simplify().
|
related |
Definition at line 115 of file Polyhedron_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
The system of constraints.
Definition at line 2030 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BD_Shape< T >::BD_Shape(), BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), is_necessarily_closed(), m_swap(), map_space_dimensions(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Octagonal_Shape< T >::Octagonal_Shape(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), process_pending_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), quick_equivalence_test(), remove_pending_to_obtain_constraints(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), simplified_constraints(), simplify_using_context_assign(), strongly_minimize_constraints(), topology(), update_constraints(), and update_generators().
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 2026 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
staticprivate |
Definition at line 2027 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
|
private |
The system of generators.
Definition at line 2033 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), m_swap(), map_space_dimensions(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), operator=(), poly_hull_assign(), Polyhedron(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), quick_equivalence_test(), remove_pending_to_obtain_generators(), select_H79_constraints(), simplify_using_context_assign(), time_elapse_assign(), update_constraints(), and update_generators().
|
private |
The saturation matrix having constraints on its columns.
Definition at line 2036 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), m_swap(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), process_pending_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), strongly_minimize_generators(), update_constraints(), and update_sat_c().
|
private |
The saturation matrix having generators on its columns.
Definition at line 2039 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), m_swap(), obtain_sorted_constraints(), obtain_sorted_constraints_with_sat_c(), obtain_sorted_generators(), obtain_sorted_generators_with_sat_g(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), process_pending_constraints(), process_pending_generators(), select_H79_constraints(), strongly_minimize_constraints(), update_generators(), and update_sat_g().
|
staticprivate |
Pointer to an array used by simplify().
Holds (between class initialization and finalization) a pointer to an array, allocated with operator new[](), of simplify_num_saturators_size elements.
Definition at line 2610 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by initialize(), and simplify().
|
staticprivate |
Dimension of an array used by simplify().
Holds (between class initialization and finalization) the size of the array pointed to by simplify_num_saturators_p.
Definition at line 2618 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by initialize(), and simplify().
|
private |
The number of dimensions of the enclosing vector space.
Definition at line 2049 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), affine_form_image(), BFT00_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHRZ03_combining_constraints(), BHRZ03_evolving_points(), BHRZ03_evolving_rays(), BHRZ03_widening_assign(), BHZ09_C_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_NNC_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), BHZ09_poly_hull_assign_if_exact(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::BHRZ03_Certificate::compare(), concatenate_assign(), contains(), H79_widening_assign(), intersection_assign(), is_included_in(), limited_BHRZ03_extrapolation_assign(), limited_H79_extrapolation_assign(), m_swap(), map_space_dimensions(), operator=(), operator==(), poly_difference_assign(), poly_hull_assign(), Polyhedron(), positive_time_elapse_assign_impl(), process_pending(), quick_equivalence_test(), refine_with_linear_form_inequality(), select_CH78_constraints(), select_H79_constraints(), simplify_using_context_assign(), space_dimension(), strongly_minimize_constraints(), strongly_minimize_generators(), and time_elapse_assign().
|
private |
The status flags to keep track of the polyhedron's internal state.
Definition at line 2046 of file Polyhedron_defs.hh.
Referenced by add_space_dimensions_and_embed(), clear_constraints_minimized(), clear_constraints_up_to_date(), clear_empty(), clear_generators_minimized(), clear_generators_up_to_date(), clear_pending_constraints(), clear_pending_generators(), clear_sat_c_up_to_date(), clear_sat_g_up_to_date(), constraints_are_minimized(), constraints_are_up_to_date(), generators_are_minimized(), generators_are_up_to_date(), has_pending_constraints(), has_pending_generators(), has_something_pending(), m_swap(), marked_empty(), operator=(), Polyhedron(), sat_c_is_up_to_date(), sat_g_is_up_to_date(), set_constraints_minimized(), set_constraints_pending(), set_constraints_up_to_date(), set_generators_minimized(), set_generators_pending(), set_generators_up_to_date(), set_sat_c_up_to_date(), and set_sat_g_up_to_date().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- Polyhedron_defs.hh
- algorithms.hh
- Polyhedron_chdims.cc
- Polyhedron_chdims_templates.hh
- Polyhedron_conversion_templates.hh
- Polyhedron_inlines.hh
- Polyhedron_minimize_templates.hh
- Polyhedron_nonpublic.cc
- Polyhedron_public.cc
- Polyhedron_simplify_templates.hh
- Polyhedron_templates.hh
- Polyhedron_widenings.cc
