A Parametric Integer (linear) Programming problem. More...
#include <PIP_Problem_defs.hh>
Public Types | |
| enum | Control_Parameter_Name { CUTTING_STRATEGY, PIVOT_ROW_STRATEGY, CONTROL_PARAMETER_NAME_SIZE } |
| Possible names for PIP_Problem control parameters. More... | |
| enum | Control_Parameter_Value { CUTTING_STRATEGY_FIRST, CUTTING_STRATEGY_DEEPEST, CUTTING_STRATEGY_ALL, PIVOT_ROW_STRATEGY_FIRST, PIVOT_ROW_STRATEGY_MAX_COLUMN, CONTROL_PARAMETER_VALUE_SIZE } |
| Possible values for PIP_Problem control parameters. More... | |
| typedef Constraint_Sequence::const_iterator | const_iterator |
| A type alias for the read-only iterator on the constraints defining the feasible region. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| PIP_Problem (dimension_type dim=0) | |
| Builds a trivial PIP problem. More... | |
| template<typename In > | |
| PIP_Problem (dimension_type dim, In first, In last, const Variables_Set &p_vars) | |
Builds a PIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range 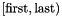 ; those dimensions whose indices occur in ; those dimensions whose indices occur in p_vars are interpreted as parameters. More... | |
| PIP_Problem (const PIP_Problem &y) | |
| Ordinary copy-constructor. More... | |
| ~PIP_Problem () | |
| Destructor. More... | |
| PIP_Problem & | operator= (const PIP_Problem &y) |
| Assignment operator. More... | |
| dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
| Returns the space dimension of the PIP problem. More... | |
| const Variables_Set & | parameter_space_dimensions () const |
| Returns a set containing all the variables' indexes representing the parameters of the PIP problem. More... | |
| const_iterator | constraints_begin () const |
| Returns a read-only iterator to the first constraint defining the feasible region. More... | |
| const_iterator | constraints_end () const |
| Returns a past-the-end read-only iterator to the sequence of constraints defining the feasible region. More... | |
| void | clear () |
Resets *this to be equal to the trivial PIP problem. More... | |
| void | add_space_dimensions_and_embed (dimension_type m_vars, dimension_type m_params) |
Adds m_vars + m_params new space dimensions and embeds the old PIP problem in the new vector space. More... | |
| void | add_to_parameter_space_dimensions (const Variables_Set &p_vars) |
Sets the space dimensions whose indexes which are in set p_vars to be parameter space dimensions. More... | |
| void | add_constraint (const Constraint &c) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the PIP problem. More... | |
| void | add_constraints (const Constraint_System &cs) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the PIP problem. More... | |
| bool | is_satisfiable () const |
Checks satisfiability of *this. More... | |
| PIP_Problem_Status | solve () const |
| Optimizes the PIP problem. More... | |
| PIP_Tree | solution () const |
Returns a feasible solution for *this, if it exists. More... | |
| PIP_Tree | optimizing_solution () const |
Returns an optimizing solution for *this, if it exists. More... | |
| bool | OK () const |
| Checks if all the invariants are satisfied. More... | |
| void | print_solution (std::ostream &s, int indent=0) const |
Prints on s the solution computed for *this. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump () const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | ascii_dump (std::ostream &s) const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this. More... | |
| void | print () const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<. More... | |
| bool | ascii_load (std::istream &s) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise. More... | |
| memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this. More... | |
| memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this. More... | |
| void | m_swap (PIP_Problem &y) |
Swaps *this with y. More... | |
| Control_Parameter_Value | get_control_parameter (Control_Parameter_Name name) const |
Returns the value of control parameter name. More... | |
| void | set_control_parameter (Control_Parameter_Value value) |
Sets control parameter value. More... | |
| void | set_big_parameter_dimension (dimension_type big_dim) |
Sets the dimension for the big parameter to big_dim. More... | |
| dimension_type | get_big_parameter_dimension () const |
| Returns the space dimension for the big parameter. More... | |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static dimension_type | max_space_dimension () |
| Returns the maximum space dimension a PIP_Problem can handle. More... | |
Private Types | |
| enum | Status { UNSATISFIABLE, OPTIMIZED, PARTIALLY_SATISFIABLE } |
| An enumerated type describing the internal status of the PIP problem. More... | |
| typedef std::vector< Constraint > | Constraint_Sequence |
| A type alias for a sequence of constraints. More... | |
| typedef Sparse_Row | Row |
Private Member Functions | |
| void | control_parameters_init () |
| Initializes the control parameters with default values. More... | |
| void | control_parameters_copy (const PIP_Problem &y) |
Copies the control parameters from problem object y. More... | |
Private Attributes | |
| dimension_type | external_space_dim |
| The dimension of the vector space. More... | |
| dimension_type | internal_space_dim |
The space dimension of the current (partial) solution of the PIP problem; it may be smaller than external_space_dim. More... | |
| Status | status |
| The internal state of the MIP problem. More... | |
| PIP_Tree_Node * | current_solution |
| The current solution decision tree. More... | |
| Constraint_Sequence | input_cs |
| The sequence of constraints describing the feasible region. More... | |
| dimension_type | first_pending_constraint |
| The first index of `input_cs' containing a pending constraint. More... | |
| Variables_Set | parameters |
| A set containing all the indices of space dimensions that are interpreted as problem parameters. More... | |
| Matrix< Row > | initial_context |
| The initial context. More... | |
| Control_Parameter_Value | control_parameters [CONTROL_PARAMETER_NAME_SIZE] |
| The control parameters for the problem object. More... | |
| dimension_type | big_parameter_dimension |
The dimension for the big parameter, or not_a_dimension() if not set. More... | |
Friends | |
| class | PIP_Solution_Node |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const PIP_Problem &pip) |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const PIP_Problem &pip) |
| Output operator. More... | |
| void | swap (PIP_Problem &x, PIP_Problem &y) |
Swaps x with y. More... | |
| void | swap (PIP_Problem &x, PIP_Problem &y) |
Detailed Description
A Parametric Integer (linear) Programming problem.
An object of this class encodes a parametric integer (linear) programming problem. The PIP problem is specified by providing:
- the dimension of the vector space;
- the subset of those dimensions of the vector space that are interpreted as integer parameters (the other space dimensions are interpreted as non-parameter integer variables);
- a finite set of linear equality and (strict or non-strict) inequality constraints involving variables and/or parameters; these constraints are used to define:
- the feasible region, if they involve one or more problem variable (and maybe some parameters);
- the initial context, if they only involve the parameters;
- optionally, the so-called big parameter, i.e., a problem parameter to be considered arbitrarily big.
Note that all problem variables and problem parameters are assumed to take non-negative integer values, so that there is no need to specify non-negativity constraints.
The class provides support for the (incremental) solution of the PIP problem based on variations of the revised simplex method and on Gomory cut generation techniques.
The solution for a PIP problem is the lexicographic minimum of the integer points of the feasible region, expressed in terms of the parameters. As the problem to be solved only involves non-negative variables and parameters, the problem will always be either unfeasible or optimizable.
As the feasibility and the solution value of a PIP problem depend on the values of the parameters, the solution is a binary decision tree, dividing the context parameter set into subsets. The tree nodes are of two kinds:
- Decision nodes. These are internal tree nodes encoding one or more linear tests on the parameters; if all the tests are satisfied, then the solution is the node's true child; otherwise, the solution is the node's false child;
- Solution nodes. These are leaf nodes in the tree, encoding the solution of the problem in the current context subset, where each variable is defined in terms of a linear expression of the parameters. Solution nodes also optionally embed a set of parameter constraints: if all these constraints are satisfied, the solution is described by the node, otherwise the problem has no solution.
It may happen that a decision node has no false child. This means that there is no solution if at least one of the corresponding constraints is not satisfied. Decision nodes having two or more linear tests on the parameters cannot have a false child. Decision nodes always have a true child.
Both kinds of tree nodes may also contain the definition of extra parameters which are artificially introduced by the solver to enforce an integral solution. Such artificial parameters are defined by the integer division of a linear expression on the parameters by an integer coefficient.
By exploiting the incremental nature of the solver, it is possible to reuse part of the computational work already done when solving variants of a given PIP_Problem: currently, incremental resolution supports the addition of space dimensions, the addition of parameters and the addition of constraints.
- Example problem
- An example PIP problem can be defined the following: where3*j >= -2*i+8j <= 4*i - 4i <= nj <= m
iandjare the problem variables andnandmare the problem parameters. This problem can be optimized; the resulting solution tree may be represented as follows:if 7*n >= 10 then if 7*m >= 12 then {i = 2 ; j = 2} else Parameter P = (m) div 2 if 2*n + 3*m >= 8 then {i = -m - P + 4 ; j = m} else _|_ else _|_The solution tree starts with a decision node depending on the context constraint7*n >= 10. If this constraint is satisfied by the values assigned to the problem parameters, then the (textually first)thenbranch is taken, reaching the true child of the root node (which in this case is another decision node); otherwise, the (textually last)elsebranch is taken, for which there is no corresponding false child.
- The
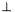 notation, also called bottom, denotes the lexicographic minimum of an empty set of solutions, here meaning the corresponding subproblem is unfeasible.
notation, also called bottom, denotes the lexicographic minimum of an empty set of solutions, here meaning the corresponding subproblem is unfeasible.
- Notice that a tree node may introduce new (non-problem) parameters, as is the case for parameter
Pin the (textually first)elsebranch above. These artificial parameters are only meaningful inside the subtree where they are defined and are used to define the parametric values of the problem variables in solution nodes (e.g., the{i,j}vector in the textually thirdthenbranch).
- Context restriction
- The above solution is correct in an unrestricted initial context, meaning all possible values are allowed for the parameters. If we restrict the context with the following parameter inequalities: then the resulting optimizing tree will be a simple solution node:m >= nn >= 5
{i = 2 ; j = 2}
- Creating the PIP_Problem object
- The PIP_Problem object corresponding to the above example can be created as follows: If you want to restrict the initial context, simply add the parameter constraints the same way as for normal constraints.Variable i(0);Variable j(1);Variable n(2);Variable m(3);Variables_Set params(n, m);Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(3*j >= -2*i+8);cs.insert(j <= 4*i - 4);cs.insert(j <= m);cs.insert(i <= n);PIP_Problem pip(cs.space_dimension(), cs.begin(), cs.end(), params);cs.insert(m >= n);cs.insert(n >= 5);
- Solving the problem
- Once the PIP_Problem object has been created, you can start the resolution of the problem by calling the solve() method: where the returnedPIP_Problem_Status status = pip.solve();
statusindicates if the problem has been optimized or if it is unfeasible for any possible configuration of the parameter values. The resolution process is also started if an attempt is made to get its solution, as follows:In this case, an unfeasible problem will result in an empty solution tree, i.e., assigning a null pointer toconst PIP_Tree_Node* node = pip.solution();node.
- Printing the solution tree
- A previously computed solution tree may be printed as follows: This will produce the following output (note: variables and parameters are printed according to the default output function; seepip.print_solution(std::cout);
Variable::set_output_function):if 7*C >= 10 then if 7*D >= 12 then {2 ; 2} else Parameter E = (D) div 2 if 2*C + 3*D >= 8 then {-D - E + 4 ; D} else _|_ else _|_
- Spanning the solution tree
- A parameter assignment for a PIP problem binds each of the problem parameters to a non-negative integer value. After fixing a parameter assignment, the ``spanning'' of the PIP problem solution tree refers to the process whereby the solution tree is navigated, starting from the root node: the value of artificial parameters is computed according to the parameter assignment and the node's constraints are evaluated, thereby descending in either the true or the false subtree of decision nodes and eventually reaching a solution node or a bottom node. If a solution node is found, each of the problem variables is provided with a parametric expression, which can be evaluated to a fixed value using the given parameter assignment and the computed values for artificial parameters.
- The coding of the spanning process can be done as follows. First, the root of the PIP solution tree is retrieved: Ifconst PIP_Tree_Node* node = pip.solution();
noderepresents an unfeasible solution (i.e.,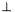 ), its value will be
), its value will be 0. For a non-null tree node, the virtual methodsPIP_Tree_Node::as_decision()andPIP_Tree_Node::as_solution()can be used to check whether the node is a decision or a solution node:const PIP_Solution_Node* sol = node->as_solution();if (sol != 0) {// The node is a solution node...}else {// The node is a decision nodeconst PIP_Decision_Node* dec = node->as_decision();...}
- The true (resp., false) child node of a Decision Node may be accessed by using method
PIP_Decision_Node::child_node(bool), passingtrue(resp.,false) as the input argument.
- Artificial parameters
- A PIP_Tree_Node::Artificial_Parameter object represents the result of the integer division of a Linear_Expression (on the other parameters, including the previously-defined artificials) by an integer denominator (a Coefficient object). The dimensions of the artificial parameters (if any) in a tree node have consecutive indices starting from
dim+1, where the value ofdimis computed as follows:- for the tree root node,
dimis the space dimension of the PIP_Problem; - for any other node of the tree, it is recursively obtained by adding the value of
dimcomputed for the parent node to the number of artificial parameters defined in the parent node.
- for the tree root node,
- Since the numbering of dimensions for artificial parameters follows the rule above, the addition of new problem variables and/or new problem parameters to an already solved PIP_Problem object (as done when incrementally solving a problem) will result in the systematic renumbering of all the existing artificial parameters.
- Node constraints
- All kind of tree nodes can contain context constraints. Decision nodes always contain at least one of them. The node's local constraint system can be obtained using method PIP_Tree_Node::constraints. These constraints only involve parameters, including both the problem parameters and the artificial parameters that have been defined in nodes occurring on the path from the root node to the current node. The meaning of these constraints is as follows:
- On a decision node, if all tests in the constraints are true, then the solution is the true child; otherwise it is the false child.
- On a solution node, if the (possibly empty) system of constraints evaluates to true for a given parameter assignment, then the solution is described by the node; otherwise the solution is
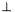 (i.e., the problem is unfeasible for that parameter assignment).
(i.e., the problem is unfeasible for that parameter assignment).
- Getting the optimal values for the variables
- After spanning the solution tree using the given parameter assignment, if a solution node has been reached, then it is possible to retrieve the parametric expression for each of the problem variables using method PIP_Solution_Node::parametric_values. The retrieved expression will be defined in terms of all the parameters (problem parameters and artificial parameters defined along the path).
- Solving maximization problems
- You can solve a lexicographic maximization problem by reformulating its constraints using variable substitution. Proceed the following steps:
- Create a big parameter (see PIP_Problem::set_big_parameter_dimension), which we will call
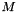 .
. - Reformulate each of the maximization problem constraints by substituting each
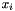 variable with an expression of the form
variable with an expression of the form 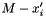 , where the
, where the 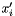 variables are positive variables to be minimized.
variables are positive variables to be minimized. - Solve the lexicographic minimum for the
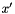 variable vector.
variable vector. - In the solution expressions, the values of the
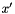 variables will be expressed in the form:
variables will be expressed in the form: 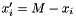 . To get back the value of the expression of each
. To get back the value of the expression of each 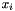 variable, just apply the formula:
variable, just apply the formula: 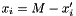 .
.
- Create a big parameter (see PIP_Problem::set_big_parameter_dimension), which we will call
- Note that if the resulting expression of one of the
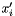 variables is not in the
variables is not in the 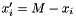 form, this means that the sign-unrestricted problem is unbounded.
form, this means that the sign-unrestricted problem is unbounded.
- You can choose to maximize only a subset of the variables while minimizing the other variables. In that case, just apply the variable substitution method on the variables you want to be maximized. The variable optimization priority will still be in lexicographic order.
- Example: consider you want to find the lexicographic maximum of the
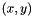 vector, under the constraints:
vector, under the constraints: ![\[\left\{\begin{array}{l} y \geq 2x - 4\\ y \leq -x + p \end{array}\right.\]](form_1059.png)
- where
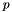 is a parameter.
is a parameter.
- After variable substitution, the constraints become:
![\[\left\{\begin{array}{l} M - y \geq 2M - 2x - 4\\ M - y \leq -M + x + p \end{array}\right.\]](form_1060.png)
- The code for creating the corresponding problem object is the following: Solving the problem provides the following solution:Variable x(0);Variable y(1);Variable p(2);Variable M(3);Variables_Set params(p, M);Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(M - y >= 2*M - 2*x - 4);cs.insert(M - y <= -M + x + p);PIP_Problem pip(cs.space_dimension(), cs.begin(), cs.end(), params);pip.set_big_parameter_dimension(3); // M is the big parameter
Parameter E = (C + 1) div 3 {D - E - 1 ; -C + D + E + 1}Under the notations above, the solution is:![\[ \left\{\begin{array}{l} x' = M - \left\lfloor\frac{p+1}{3}\right\rfloor - 1 \\ y' = M - p + \left\lfloor\frac{p+1}{3}\right\rfloor + 1 \end{array}\right. \]](form_1061.png)
- Performing substitution again provides us with the values of the original variables:
![\[ \left\{\begin{array}{l} x = \left\lfloor\frac{p+1}{3}\right\rfloor + 1 \\ y = p - \left\lfloor\frac{p+1}{3}\right\rfloor - 1 \end{array}\right. \]](form_1062.png)
- Allowing variables to be arbitrarily signed
- You can deal with arbitrarily signed variables by reformulating the constraints using variable substitution. Proceed the following steps:
- Create a big parameter (see PIP_Problem::set_big_parameter_dimension), which we will call
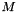 .
. - Reformulate each of the maximization problem constraints by substituting each
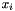 variable with an expression of the form
variable with an expression of the form 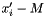 , where the
, where the 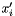 variables are positive.
variables are positive. - Solve the lexicographic minimum for the
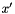 variable vector.
variable vector. - The solution expression can be read in the form:
- In the solution expressions, the values of the
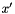 variables will be expressed in the form:
variables will be expressed in the form: 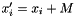 . To get back the value of the expression of each signed
. To get back the value of the expression of each signed 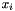 variable, just apply the formula:
variable, just apply the formula: 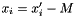 .
.
- Create a big parameter (see PIP_Problem::set_big_parameter_dimension), which we will call
- Note that if the resulting expression of one of the
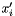 variables is not in the
variables is not in the 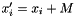 form, this means that the sign-unrestricted problem is unbounded.
form, this means that the sign-unrestricted problem is unbounded.
- You can choose to define only a subset of the variables to be sign-unrestricted. In that case, just apply the variable substitution method on the variables you want to be sign-unrestricted.
- Example: consider you want to find the lexicographic minimum of the
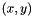 vector, where the
vector, where the 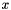 and
and 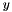 variables are sign-unrestricted, under the constraints:
variables are sign-unrestricted, under the constraints: ![\[\left\{\begin{array}{l} y \geq -2x - 4\\ 2y \leq x + 2p \end{array}\right.\]](form_1066.png)
- where
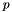 is a parameter.
is a parameter.
- After variable substitution, the constraints become:
![\[\left\{\begin{array}{l} y' - M \geq -2x' + 2M - 4\\ 2y' - 2M \leq x' - M + 2p \end{array}\right.\]](form_1067.png)
- The code for creating the corresponding problem object is the following: Variable x(0);Variable y(1);Variable p(2);Variable M(3);Variables_Set params(p, M);Constraint_System cs;cs.insert(y - M >= -2*x + 2*M - 4);cs.insert(2*y - 2*M <= x - M + 2*p);PIP_Problem pip(cs.space_dimension(), cs.begin(), cs.end(), params);pip.set_big_parameter_dimension(3); // M is the big parameter
- Solving the problem provides the following solution:
Parameter E = (2*C + 3) div 5 {D - E - 1 ; D + 2*E - 2}Under the notations above, the solution is:![\[ \left\{\begin{array}{l} x' = M - \left\lfloor\frac{2p+3}{5}\right\rfloor - 1 \\ y' = M + 2\left\lfloor\frac{2p+3}{5}\right\rfloor - 2 \end{array}\right. \]](form_1068.png)
- Performing substitution again provides us with the values of the original variables:
![\[ \left\{\begin{array}{l} x = -\left\lfloor\frac{2p+3}{5}\right\rfloor - 1 \\ y = 2\left\lfloor\frac{2p+3}{5}\right\rfloor - 2 \end{array}\right. \]](form_1069.png)
- Allowing parameters to be arbitrarily signed
- You can consider a parameter
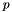 arbitrarily signed by replacing
arbitrarily signed by replacing 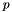 with
with 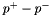 , where both
, where both 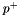 and
and 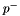 are positive parameters. To represent a set of arbitrarily signed parameters, replace each parameter
are positive parameters. To represent a set of arbitrarily signed parameters, replace each parameter 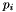 with
with 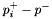 , where
, where 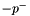 is the minimum negative value of all parameters.
is the minimum negative value of all parameters.
- Minimizing a linear cost function
- Lexicographic solving can be used to find the parametric minimum of a linear cost function.
- Suppose the variables are named
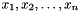 , and the parameters
, and the parameters 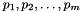 . You can minimize a linear cost function
. You can minimize a linear cost function 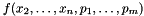 by simply adding the constraint
by simply adding the constraint 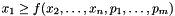 to the constraint system. As lexicographic minimization ensures
to the constraint system. As lexicographic minimization ensures 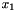 is minimized in priority, and because
is minimized in priority, and because 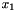 is forced by a constraint to be superior or equal to the cost function, optimal solutions of the problem necessarily ensure that the solution value of
is forced by a constraint to be superior or equal to the cost function, optimal solutions of the problem necessarily ensure that the solution value of 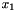 is the optimal value of the cost function.
is the optimal value of the cost function.
Definition at line 493 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Member Typedef Documentation
| typedef Constraint_Sequence::const_iterator Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::const_iterator |
A type alias for the read-only iterator on the constraints defining the feasible region.
Definition at line 572 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
A type alias for a sequence of constraints.
Definition at line 565 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
Definition at line 805 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
|
explicit |
Builds a trivial PIP problem.
A trivial PIP problem requires to compute the lexicographic minimum on a vector space under no constraints and with no parameters: due to the implicit non-negativity constraints, the origin of the vector space is an optimal solution.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space enclosing *this(optional argument with default value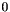 ).
).
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().
Definition at line 50 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References control_parameters_init(), max_space_dimension(), and OK().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::PIP_Problem | ( | dimension_type | dim, |
| In | first, | ||
| In | last, | ||
| const Variables_Set & | p_vars | ||
| ) |
Builds a PIP problem having space dimension dim from the sequence of constraints in the range 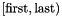 ; those dimensions whose indices occur in
; those dimensions whose indices occur in p_vars are interpreted as parameters.
- Parameters
-
dim The dimension of the vector space (variables and parameters) enclosing *this.first An input iterator to the start of the sequence of constraints. last A past-the-end input iterator to the sequence of constraints. p_vars The set of variables' indexes that are interpreted as parameters.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if dimexceedsmax_space_dimension().std::invalid_argument Thrown if the space dimension of a constraint in the sequence (resp., the parameter variables) is strictly greater than dim.
Definition at line 32 of file PIP_Problem_templates.hh.
References control_parameters_init(), external_space_dim, input_cs, max_space_dimension(), OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::PIP_Problem | ( | const PIP_Problem & | y | ) |
Ordinary copy-constructor.
Definition at line 70 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::clone(), control_parameters_copy(), current_solution, OK(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::set_owner().
| Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::~PIP_Problem | ( | ) |
Destructor.
Definition at line 88 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
Member Function Documentation
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::add_constraint | ( | const Constraint & | c | ) |
Adds a copy of constraint c to the PIP problem.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the space dimension of cis strictly greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 697 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::add_constraints | ( | const Constraint_System & | cs | ) |
Adds a copy of the constraints in cs to the PIP problem.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if the space dimension of constraint system csis strictly greater than the space dimension of*this.
Definition at line 713 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::begin(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint_System::end().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::add_space_dimensions_and_embed | ( | dimension_type | m_vars, |
| dimension_type | m_params | ||
| ) |
Adds m_vars + m_params new space dimensions and embeds the old PIP problem in the new vector space.
- Parameters
-
m_vars The number of space dimensions to add that are interpreted as PIP problem variables (i.e., non parameters). These are added before adding the m_paramsparameters.m_params The number of space dimensions to add that are interpreted as PIP problem parameters. These are added after having added the m_varsproblem variables.
- Exceptions
-
std::length_error Thrown if adding m_vars + m_paramsnew space dimensions would cause the vector space to exceed dimensionmax_space_dimension().
The new space dimensions will be those having the highest indexes in the new PIP problem; they are initially unconstrained.
Definition at line 632 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::max_space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::add_to_parameter_space_dimensions | ( | const Variables_Set & | p_vars | ) |
Sets the space dimensions whose indexes which are in set p_vars to be parameter space dimensions.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument Thrown if some index in p_varsdoes not correspond to a space dimension in*this.
Definition at line 670 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Variables_Set::space_dimension().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::ascii_dump | ( | ) | const |
Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::ascii_dump | ( | std::ostream & | s | ) | const |
Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this.
Definition at line 372 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Decision_Node::as_decision(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::as_solution(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::ascii_dump(), and value.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::ascii_load | ( | std::istream & | s | ) |
Loads from s an ASCII representation (as produced by ascii_dump(std::ostream&) const) and sets *this accordingly. Returns true if successful, false otherwise.
Definition at line 453 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::ascii_load(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Decision_Node::ascii_load(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::set_owner(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Decision_Node::set_owner(), value, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::zero_dim_positivity().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::clear | ( | ) |
Resets *this to be equal to the trivial PIP problem.
The space dimension is reset to 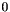 .
.
Definition at line 614 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension().
|
inline |
Returns a read-only iterator to the first constraint defining the feasible region.
Definition at line 40 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References input_cs.
Referenced by operator<<().
|
inline |
Returns a past-the-end read-only iterator to the sequence of constraints defining the feasible region.
Definition at line 45 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References input_cs.
Referenced by operator<<().
|
private |
Copies the control parameters from problem object y.
Definition at line 99 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References control_parameters.
Referenced by PIP_Problem().
|
private |
Initializes the control parameters with default values.
Definition at line 93 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
Referenced by PIP_Problem().
| PPL::memory_size_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::external_memory_in_bytes | ( | ) | const |
Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this.
Definition at line 766 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
|
inline |
Returns the space dimension for the big parameter.
If a big parameter was not set, returns not_a_dimension().
Definition at line 85 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References big_parameter_dimension.
Referenced by operator<<().
|
inline |
Returns the value of control parameter name.
Definition at line 79 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References CONTROL_PARAMETER_NAME_SIZE, and control_parameters.
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::is_satisfiable | ( | ) | const |
Checks satisfiability of *this.
- Returns
trueif and only if the PIP problem is satisfiable.
Definition at line 721 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
|
inline |
Swaps *this with y.
Definition at line 55 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References big_parameter_dimension, CONTROL_PARAMETER_NAME_SIZE, control_parameters, current_solution, external_space_dim, first_pending_constraint, initial_context, input_cs, internal_space_dim, parameters, status, swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::swap().
Referenced by operator=(), and swap().
|
inlinestatic |
Returns the maximum space dimension a PIP_Problem can handle.
Definition at line 35 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::max_space_dimension().
Referenced by PIP_Problem().
| bool Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::OK | ( | ) | const |
Checks if all the invariants are satisfied.
Definition at line 277 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::ascii_dump(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension().
Referenced by PIP_Problem().
|
inline |
Assignment operator.
Definition at line 72 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
| PPL::PIP_Tree Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::optimizing_solution | ( | ) | const |
Returns an optimizing solution for *this, if it exists.
A null pointer is returned for an unfeasible PIP problem.
Definition at line 269 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
|
inline |
Returns a set containing all the variables' indexes representing the parameters of the PIP problem.
Definition at line 50 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References parameters.
Referenced by operator<<(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::parametric_values(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::print(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::update_solution().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::print | ( | ) | const |
Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::print_solution | ( | std::ostream & | s, |
| int | indent = 0 |
||
| ) | const |
Prints on s the solution computed for *this.
- Parameters
-
s The output stream. indent An indentation parameter (default value 0).
- Exceptions
-
std::logic_error Thrown if trying to print the solution when the PIP problem still has to be solved.
Definition at line 790 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::indent_and_print().
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::set_big_parameter_dimension | ( | dimension_type | big_dim | ) |
Sets the dimension for the big parameter to big_dim.
Definition at line 750 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
| void Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::set_control_parameter | ( | Control_Parameter_Value | value | ) |
Sets control parameter value.
Definition at line 729 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References value.
| PPL::PIP_Tree Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::solution | ( | ) | const |
Returns a feasible solution for *this, if it exists.
A null pointer is returned for an unfeasible PIP problem.
Definition at line 261 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
| PPL::PIP_Problem_Status Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::solve | ( | ) | const |
Optimizes the PIP problem.
- Returns
- A PIP_Problem_Status flag indicating the outcome of the optimization attempt (unfeasible or optimized problem).
Definition at line 106 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Expression_Hide_Last< T >::all_zeroes_except(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::begin(), c, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::coefficient(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::compatibility_check(), current_solution, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::end(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::expression(), first_pending_constraint, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::inhomogeneous_term(), initial_context, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Sparse_Row::insert(), internal_space_dim, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_equality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::is_strict_inequality(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::neg_assign(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::nth_iter(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::OPTIMIZED_PIP_PROBLEM, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::solve(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Constraint::space_dimension(), status, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::UNFEASIBLE_PIP_PROBLEM, and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::update_tableau().
|
inline |
Returns the space dimension of the PIP problem.
Definition at line 30 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References external_space_dim.
Referenced by operator<<(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::parametric_values(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Tree_Node::print(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::update_solution().
| PPL::memory_size_type Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Problem::total_memory_in_bytes | ( | ) | const |
Returns the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this.
Definition at line 785 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::external_memory_in_bytes().
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Definition at line 32 of file PIP_Problem.cc.
References constraints_begin(), constraints_end(), get_big_parameter_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension(), parameter_space_dimensions(), and space_dimension().
|
related |
Output operator.
|
friend |
Definition at line 827 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
related |
Swaps x with y.
Referenced by m_swap().
|
related |
Definition at line 91 of file PIP_Problem_inlines.hh.
References m_swap().
Member Data Documentation
|
private |
The dimension for the big parameter, or not_a_dimension() if not set.
Definition at line 825 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by get_big_parameter_dimension(), m_swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::update_tableau().
|
private |
The control parameters for the problem object.
Definition at line 819 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by control_parameters_copy(), get_control_parameter(), m_swap(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::solve().
|
private |
The current solution decision tree.
Definition at line 790 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by m_swap(), PIP_Problem(), and solve().
|
private |
The dimension of the vector space.
Definition at line 764 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by m_swap(), PIP_Problem(), space_dimension(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::update_tableau().
|
private |
The first index of `input_cs' containing a pending constraint.
Definition at line 796 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
The initial context.
Contains problem constraints on parameters only
Definition at line 815 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
|
private |
The sequence of constraints describing the feasible region.
Definition at line 793 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by constraints_begin(), constraints_end(), m_swap(), and PIP_Problem().
|
private |
The space dimension of the current (partial) solution of the PIP problem; it may be smaller than external_space_dim.
Definition at line 770 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by m_swap(), solve(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::PIP_Solution_Node::update_tableau().
|
private |
A set containing all the indices of space dimensions that are interpreted as problem parameters.
Definition at line 802 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
Referenced by m_swap(), and parameter_space_dimensions().
|
private |
The internal state of the MIP problem.
Definition at line 787 of file PIP_Problem_defs.hh.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
