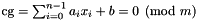|
|
| Congruence (Representation r=default_representation) |
| | Constructs the 0 = 0 congruence with space dimension 0 .
|
| |
| | Congruence (const Congruence &cg) |
| | Ordinary copy constructor. More...
|
| |
|
| Congruence (const Congruence &cg, Representation r) |
| | Copy constructor with specified representation.
|
| |
| | Congruence (const Constraint &c, Representation r=default_representation) |
| | Copy-constructs (modulo 0) from equality constraint c. More...
|
| |
|
| ~Congruence () |
| | Destructor.
|
| |
|
Congruence & | operator= (const Congruence &y) |
| | Assignment operator.
|
| |
|
Representation | representation () const |
| | Returns the current representation of *this.
|
| |
|
void | set_representation (Representation r) |
| | Converts *this to the specified representation.
|
| |
|
dimension_type | space_dimension () const |
| | Returns the dimension of the vector space enclosing *this.
|
| |
|
expr_type | expression () const |
| | Partial read access to the (adapted) internal expression.
|
| |
| Coefficient_traits::const_reference | coefficient (Variable v) const |
| | Returns the coefficient of v in *this. More...
|
| |
|
Coefficient_traits::const_reference | inhomogeneous_term () const |
| | Returns the inhomogeneous term of *this.
|
| |
|
Coefficient_traits::const_reference | modulus () const |
| | Returns a const reference to the modulus of *this.
|
| |
| void | set_modulus (Coefficient_traits::const_reference m) |
| |
|
void | scale (Coefficient_traits::const_reference factor) |
| | Multiplies all the coefficients, including the modulus, by factor .
|
| |
| Congruence & | operator/= (Coefficient_traits::const_reference k) |
| | Multiplies k into the modulus of *this. More...
|
| |
| bool | is_tautological () const |
| | Returns true if and only if *this is a tautology (i.e., an always true congruence). More...
|
| |
| bool | is_inconsistent () const |
| | Returns true if and only if *this is inconsistent (i.e., an always false congruence). More...
|
| |
| bool | is_proper_congruence () const |
| | Returns true if the modulus is greater than zero. More...
|
| |
| bool | is_equality () const |
| | Returns true if *this is an equality. More...
|
| |
|
memory_size_type | total_memory_in_bytes () const |
| | Returns a lower bound to the total size in bytes of the memory occupied by *this.
|
| |
|
memory_size_type | external_memory_in_bytes () const |
| | Returns the size in bytes of the memory managed by *this.
|
| |
|
bool | OK () const |
| | Checks if all the invariants are satisfied.
|
| |
|
void | ascii_dump () const |
| | Writes to std::cerr an ASCII representation of *this.
|
| |
|
void | ascii_dump (std::ostream &s) const |
| | Writes to s an ASCII representation of *this.
|
| |
|
void | print () const |
| | Prints *this to std::cerr using operator<<.
|
| |
|
bool | ascii_load (std::istream &s) |
| | Loads from s an ASCII representation of the internal representation of *this.
|
| |
|
void | m_swap (Congruence &y) |
| | Swaps *this with y.
|
| |
| | Congruence (const Congruence &cg, dimension_type new_space_dimension) |
| | Copy-constructs with the specified space dimension. More...
|
| |
|
| Congruence (const Congruence &cg, dimension_type new_space_dimension, Representation r) |
| | Copy-constructs with the specified space dimension and representation.
|
| |
| | Congruence (const Constraint &cg, dimension_type new_space_dimension, Representation r=default_representation) |
| |
| | Congruence (Linear_Expression &le, Coefficient_traits::const_reference m, Recycle_Input) |
| | Constructs from Linear_Expression le, using modulus m. More...
|
| |
|
void | swap_space_dimensions (Variable v1, Variable v2) |
| | Swaps the coefficients of the variables v1 and v2 .
|
| |
| void | set_space_dimension (dimension_type n) |
| |
| void | shift_space_dimensions (Variable v, dimension_type n) |
| |
| void | sign_normalize () |
| | Normalizes the signs. More...
|
| |
| void | normalize () |
| | Normalizes signs and the inhomogeneous term. More...
|
| |
| void | strong_normalize () |
| | Calls normalize, then divides out common factors. More...
|
| |
|
(Note that these are not member functions.)
|
| bool | operator== (const Congruence &x, const Congruence &y) |
| | Returns true if and only if x and y are equivalent. More...
|
| |
| bool | operator!= (const Congruence &x, const Congruence &y) |
| | Returns false if and only if x and y are equivalent. More...
|
| |
| std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &s, const Congruence &c) |
| | Output operators. More...
|
| |
| Congruence | operator%= (const Linear_Expression &e1, const Linear_Expression &e2) |
| | Returns the congruence 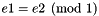 . More... . More...
|
| |
| Congruence | operator%= (const Linear_Expression &e, Coefficient_traits::const_reference n) |
| | Returns the congruence 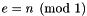 . More... . More...
|
| |
| Congruence | operator/ (const Congruence &cg, Coefficient_traits::const_reference k) |
| | Returns a copy of cg, multiplying k into the copy's modulus. More...
|
| |
| Congruence | operator/ (const Constraint &c, Coefficient_traits::const_reference m) |
| | Creates a congruence from c, with m as the modulus. More...
|
| |
| void | swap (Congruence &x, Congruence &y) |
| |
| Congruence | operator%= (const Linear_Expression &e1, const Linear_Expression &e2) |
| |
| Congruence | operator%= (const Linear_Expression &e, Coefficient_traits::const_reference n) |
| |
| Congruence | operator/ (const Congruence &cg, Coefficient_traits::const_reference k) |
| |
| Congruence | operator/ (const Constraint &c, Coefficient_traits::const_reference m) |
| |
| bool | operator== (const Congruence &x, const Congruence &y) |
| |
| bool | operator!= (const Congruence &x, const Congruence &y) |
| |
| void | swap (Congruence &x, Congruence &y) |
| |
A linear congruence.
An object of the class Congruence is a congruence:
where 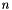 is the dimension of the space,
is the dimension of the space, 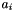 is the integer coefficient of variable
is the integer coefficient of variable 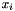 ,
, 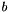 is the integer inhomogeneous term and
is the integer inhomogeneous term and 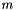 is the integer modulus; if
is the integer modulus; if 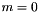 , then
, then 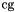 represents the equality congruence
represents the equality congruence 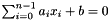 and, if
and, if 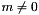 , then the congruence
, then the congruence 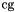 is said to be a proper congruence.
is said to be a proper congruence.
- How to build a congruence
- Congruences
 are typically built by applying the congruence symbol `
are typically built by applying the congruence symbol `%=' to a pair of linear expressions. Congruences with modulus m are typically constructed by building a congruence  using the given pair of linear expressions and then adding the modulus
using the given pair of linear expressions and then adding the modulus m using the modulus symbol is `/'.
The space dimension of a congruence is defined as the maximum space dimension of the arguments of its constructor.
- In the following examples it is assumed that variables
x, y and z are defined as follows: Variable x(0);
Variable y(1);
Variable z(2);
- Example 1
- The following code builds the equality congruence
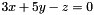 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 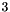 : The following code builds the congruence
: The following code builds the congruence 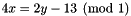 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 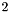 : The following code builds the congruence
: The following code builds the congruence 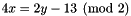 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 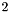 : An unsatisfiable congruence on the zero-dimension space
: An unsatisfiable congruence on the zero-dimension space 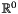 can be specified as follows: Equivalent, but more involved ways are the following: In contrast, the following code defines an unsatisfiable congruence having space dimension
can be specified as follows: Equivalent, but more involved ways are the following: In contrast, the following code defines an unsatisfiable congruence having space dimension 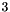 :
:
- How to inspect a congruence
- Several methods are provided to examine a congruence and extract all the encoded information: its space dimension, its modulus and the value of its integer coefficients.
- Example 2
- The following code shows how it is possible to access the modulus as well as each of the coefficients. Given a congruence with linear expression
e and modulus m (in this case 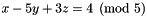 ), we construct a new congruence with the same modulus
), we construct a new congruence with the same modulus m but where the linear expression is 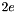 (
( 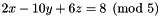 ).
).
cout << "Congruence cg1: " << cg1 << endl;
if (m == 0)
cout << "Congruence cg1 is an equality." << endl;
else {
Linear_Expression e;
e += 2 * cg1.coefficient(Variable(i)) * Variable(i);
e += 2 * cg1.inhomogeneous_term();
cout << "Congruence cg2: " << cg2 << endl;
}
The actual output could be the following: Note that, in general, the particular output obtained can be syntactically different from the (semantically equivalent) congruence considered.
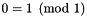 , also known as the integrality congruence.
, also known as the integrality congruence. 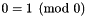 .
. 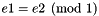 .
. 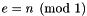 .
. 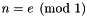 .
. 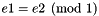 . More...
. More...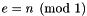 . More...
. More...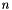 is the dimension of the space,
is the dimension of the space, 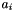 is the integer coefficient of variable
is the integer coefficient of variable 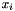 ,
, 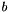 is the integer inhomogeneous term and
is the integer inhomogeneous term and 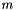 is the integer modulus; if
is the integer modulus; if 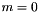 , then
, then 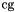 represents the equality congruence
represents the equality congruence 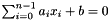 and, if
and, if 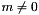 , then the congruence
, then the congruence 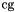 is said to be a proper congruence.
is said to be a proper congruence. are typically built by applying the congruence symbol `
are typically built by applying the congruence symbol `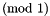 using the given pair of linear expressions and then adding the modulus
using the given pair of linear expressions and then adding the modulus 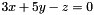 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 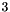 : The following code builds the congruenceCongruence eq_cg((3*x + 5*y - z %= 0) / 0);
: The following code builds the congruenceCongruence eq_cg((3*x + 5*y - z %= 0) / 0);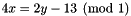 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 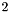 : The following code builds the congruenceCongruence mod1_cg(4*x %= 2*y - 13);
: The following code builds the congruenceCongruence mod1_cg(4*x %= 2*y - 13);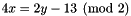 , having space dimension
, having space dimension 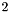 : An unsatisfiable congruence on the zero-dimension spaceCongruence mod2_cg((4*x %= 2*y - 13) / 2);
: An unsatisfiable congruence on the zero-dimension spaceCongruence mod2_cg((4*x %= 2*y - 13) / 2);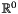 can be specified as follows: Equivalent, but more involved ways are the following:Congruence false_cg = Congruence::zero_dim_false();In contrast, the following code defines an unsatisfiable congruence having space dimensionCongruence false_cg1((Linear_Expression::zero() %= 1) / 0);Congruence false_cg2((Linear_Expression::zero() %= 1) / 2);
can be specified as follows: Equivalent, but more involved ways are the following:Congruence false_cg = Congruence::zero_dim_false();In contrast, the following code defines an unsatisfiable congruence having space dimensionCongruence false_cg1((Linear_Expression::zero() %= 1) / 0);Congruence false_cg2((Linear_Expression::zero() %= 1) / 2);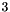 : Congruence false_cg3((0*z %= 1) / 0);
: Congruence false_cg3((0*z %= 1) / 0);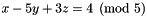 ), we construct a new congruence with the same modulus
), we construct a new congruence with the same modulus 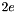 (
( 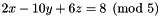 ). The actual output could be the following:Congruence cg1((x - 5*y + 3*z %= 4) / 5);cout << "Congruence cg1: " << cg1 << endl;const Coefficient& m = cg1.modulus();if (m == 0)cout << "Congruence cg1 is an equality." << endl;else {Linear_Expression e;for (dimension_type i = cg1.space_dimension(); i-- > 0; )e += 2 * cg1.coefficient(Variable(i)) * Variable(i);e += 2 * cg1.inhomogeneous_term();Congruence cg2((e %= 0) / m);cout << "Congruence cg2: " << cg2 << endl;}Note that, in general, the particular output obtained can be syntactically different from the (semantically equivalent) congruence considered.Congruence cg1: A - 5*B + 3*C %= 4 / 5Congruence cg2: 2*A - 10*B + 6*C %= 8 / 5
). The actual output could be the following:Congruence cg1((x - 5*y + 3*z %= 4) / 5);cout << "Congruence cg1: " << cg1 << endl;const Coefficient& m = cg1.modulus();if (m == 0)cout << "Congruence cg1 is an equality." << endl;else {Linear_Expression e;for (dimension_type i = cg1.space_dimension(); i-- > 0; )e += 2 * cg1.coefficient(Variable(i)) * Variable(i);e += 2 * cg1.inhomogeneous_term();Congruence cg2((e %= 0) / m);cout << "Congruence cg2: " << cg2 << endl;}Note that, in general, the particular output obtained can be syntactically different from the (semantically equivalent) congruence considered.Congruence cg1: A - 5*B + 3*C %= 4 / 5Congruence cg2: 2*A - 10*B + 6*C %= 8 / 5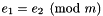 , then it returns with *this representing the congruence
, then it returns with *this representing the congruence 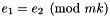 .
. 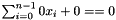 ; or
; or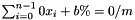 , where
, where 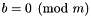 .
. 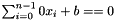 where
where 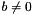 ; or
; or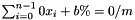 , where
, where 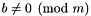 .
. 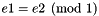 .
. 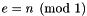 .
. 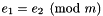 , then the result represents the congruence
, then the result represents the congruence 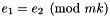 .
.