The base class of all concrete expressions. More...
#include <Concrete_Expression_types.hh>
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| static bool | add_linearize (const Binary_Operator< Target > &bop_expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| static bool | sub_linearize (const Binary_Operator< Target > &bop_expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| static bool | mul_linearize (const Binary_Operator< Target > &bop_expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| static bool | div_linearize (const Binary_Operator< Target > &bop_expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| static bool | cast_linearize (const Cast_Operator< Target > &cast_expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| template<typename Target , typename FP_Interval_Type > | |
| bool | linearize (const Concrete_Expression< Target > &expr, const FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type > &oracle, const std::map< dimension_type, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > > &lf_store, Linear_Form< FP_Interval_Type > &result) |
| Linearizes a floating point expression. More... | |
Detailed Description
template<typename Target>
class Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Concrete_Expression< Target >
The base class of all concrete expressions.
Definition at line 28 of file Concrete_Expression_types.hh.
Friends And Related Function Documentation
|
related |
Helper function used by linearize to linearize a sum of floating point expressions.
Makes result become the linearization of *this in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
bop_expr The binary operator concrete expression to linearize. Its binary operator type must be ADD.oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result The modified linear form.
- Linearization of sum floating-point expressions
Let 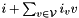 and
and 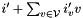 be two linear forms and
be two linear forms and  a sound abstract operator on linear forms such that:
a sound abstract operator on linear forms such that:
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v \right) \aslf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v \right) = \left(i \asifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \asifp i'_{v} \right)v. \]](form_811.png)
Given an expression  and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 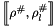 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form 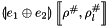 as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \oplus e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \aslf \linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \aslf \varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left(\linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right) \aslf \varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left(\linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right) \aslf mf_{\mathbf{f}}[-1, 1] \]](form_982.png)
where 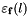 is the relative error associated to
is the relative error associated to 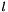 (see method
(see method relative_error of class Linear_Form) and 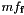 is a rounding error computed by function
is a rounding error computed by function compute_absolute_error.
Definition at line 110 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::relative_error().
|
related |
Helper function used by linearize to linearize a cast floating point expression.
Makes result become the linearization of *this in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
cast_expr The cast operator concrete expression to linearize. oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result The modified linear form.
Definition at line 635 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type >::get_integer_expr_value(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::is_less_precise_than(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::relative_error().
|
related |
Helper function used by linearize to linearize a division of floating point expressions.
Makes result become the linearization of *this in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
bop_expr The binary operator concrete expression to linearize. Its binary operator type must be DIV.oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result The modified linear form.
- Linearization of division floating-point expressions
Let 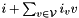 and
and 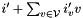 be two linear forms,
be two linear forms,  and
and  two sound abstract operator on linear forms such that:
two sound abstract operator on linear forms such that:
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v\right) \aslf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v\right) = \left(i \asifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \asifp i'_{v}\right)v, \]](form_919.png)
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v\right) \adivlf i' = \left(i \adivifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \adivifp i'\right)v. \]](form_926.png)
Given an expression ![$e_{1} \oslash [a, b]$](form_927.png) and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 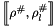 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form ![$ \linexprenv{e_{1} \oslash [a, b]}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} $](form_928.png) as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \oslash [a, b]}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \left(\linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \adivlf [a, b]\right) \aslf \left(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left( \linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right) \adivlf [a, b]\right) \aslf mf_{\mathbf{f}}[-1, 1], \]](form_929.png)
given an expression  and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 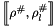 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form 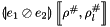 as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \oslash e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \linexprenv{e_{1} \oslash \iota\left( \linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right)\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}, \]](form_932.png)
where 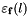 is the relative error associated to
is the relative error associated to 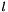 (see method
(see method relative_error of class Linear_Form), 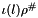 is the intervalization of
is the intervalization of 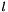 (see method
(see method intervalize of class Linear_Form), and 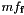 is a rounding error computed by function
is a rounding error computed by function compute_absolute_error.
Definition at line 560 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::relative_error().
|
related |
Linearizes a floating point expression.
Makes result become a linear form that correctly approximates the value of expr in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
expr The concrete expression to linearize. oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result Becomes the linearized expression.
Formally, if expr represents the expression 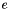 and
and lf_store represents the linear form abstract store 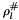 , then
, then result will become 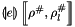 if the linearization succeeds.
if the linearization succeeds.
Definition at line 729 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::EMPTY, Parma_Polyhedra_Library::FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type >::get_associated_dimensions(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type >::get_fp_constant_value(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::FP_Oracle< Target, FP_Interval_Type >::get_interval(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::negate(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::not_a_dimension(), Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and PPL_COMPILE_TIME_CHECK.
|
related |
Helper function used by linearize to linearize a product of floating point expressions.
Makes result become the linearization of *this in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
bop_expr The binary operator concrete expression to linearize. Its binary operator type must be MUL.oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result The modified linear form.
- Linearization of multiplication floating-point expressions
Let 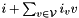 and
and 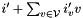 be two linear forms,
be two linear forms,  and
and  two sound abstract operators on linear forms such that:
two sound abstract operators on linear forms such that:
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v\right) \aslf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v\right) = \left(i \asifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \asifp i'_{v}\right)v, \]](form_919.png)
![\[ i \amlf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v\right) = \left(i \amifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i \amifp i'_{v}\right)v. \]](form_984.png)
Given an expression ![$[a, b] \otimes e_{2}$](form_985.png) and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 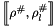 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form ![$\linexprenv{[a, b] \otimes e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}$](form_986.png) as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{[a, b] \otimes e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \left([a, b] \amlf \linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}\right) \aslf \left([a, b] \amlf \varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left(\linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right)\right) \aslf mf_{\mathbf{f}}[-1, 1]. \]](form_987.png)
.
Given an expression ![$e_{1} \otimes [a, b]$](form_988.png) and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 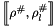 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form ![$\linexprenv{e_{1} \otimes [a, b]}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}$](form_989.png) as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \otimes [a, b]}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \linexprenv{[a, b] \otimes e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}. \]](form_990.png)
Given an expression  and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 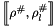 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form 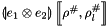 as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \otimes e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \linexprenv{\iota\left(\linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right)\rho^{\#} \otimes e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l}, \]](form_993.png)
where 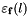 is the relative error associated to
is the relative error associated to 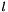 (see method
(see method relative_error of class Linear_Form), 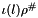 is the intervalization of
is the intervalization of 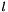 (see method
(see method intervalize of class Linear_Form), and 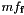 is a rounding error computed by function
is a rounding error computed by function compute_absolute_error.
Even though we intervalize the first operand in the above example, the actual implementation utilizes an heuristics for choosing which of the two operands must be intervalized in order to obtain the most precise result.
Definition at line 366 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::relative_error().
|
related |
Helper function used by linearize to linearize a difference of floating point expressions.
Makes result become the linearization of *this in the given composite abstract store.
- Template Parameters
-
Target A type template parameter specifying the instantiation of Concrete_Expression to be used. FP_Interval_Type A type template parameter for the intervals used in the abstract domain. The interval bounds should have a floating point type.
- Returns
trueif the linearization succeeded,falseotherwise.
- Parameters
-
bop_expr The binary operator concrete expression to linearize. Its binary operator type must be SUB.oracle The FP_Oracle to be queried. lf_store The linear form abstract store. result The modified linear form.
- Linearization of difference floating-point expressions
Let 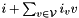 and
and 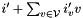 be two linear forms,
be two linear forms,  and
and  two sound abstract operators on linear form such that:
two sound abstract operators on linear form such that:
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v\right) \aslf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v\right) = \left(i \asifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \asifp i'_{v}\right)v, \]](form_919.png)
![\[ \left(i + \sum_{v \in \cV}i_{v}v\right) \adlf \left(i' + \sum_{v \in \cV}i'_{v}v\right) = \left(i \adifp i'\right) + \sum_{v \in \cV}\left(i_{v} \adifp i'_{v}\right)v. \]](form_920.png)
Given an expression  and a composite abstract store
and a composite abstract store 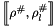 , we construct the interval linear form
, we construct the interval linear form 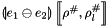 on
on 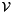 as follows:
as follows:
![\[ \linexprenv{e_{1} \ominus e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} = \linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \adlf \linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \aslf \varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left(\linexprenv{e_{1}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right) \aslf \varepsilon_{\mathbf{f}}\left(\linexprenv{e_{2}}{\rho^{\#}}{\rho^{\#}_l} \right) \aslf mf_{\mathbf{f}}[-1, 1] \]](form_923.png)
where 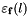 is the relative error associated to
is the relative error associated to 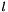 (see method
(see method relative_error of class Linear_Form) and 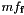 is a rounding error computed by function
is a rounding error computed by function compute_absolute_error.
Definition at line 224 of file linearize.hh.
References Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::overflows(), and Parma_Polyhedra_Library::Linear_Form< C >::relative_error().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
